Breast augmentation, also known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a popular cosmetic surgical procedure designed to enhance the size, shape, and symmetry of the breasts. It involves the use of breast implants or fat transfer to increase breast volume or restore breast fullness lost due to weight reduction, pregnancy, aging, or congenital conditions.
Women pursue breast augmentation for a variety of reasons including improving body image, boosting self-confidence, correcting asymmetry, or reconstructing breasts after mastectomy. The procedure has evolved significantly over the decades, with advancements in implant technology, surgical techniques, and safety protocols making it one of the most commonly performed cosmetic surgeries worldwide.
This article offers an in-depth exploration of breast augmentation, including causes and risk factors leading to its consideration, symptoms or signs indicating its need, diagnostic evaluation, treatment options, prevention, potential complications, and guidance on living with breast implants.
Causes for Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation is one of the most commonly performed cosmetic surgical procedures worldwide. The motivations behind choosing breast augmentation are varied and often deeply personal. Understanding these causes helps both patients and surgeons set realistic goals and select the most appropriate surgical approach.
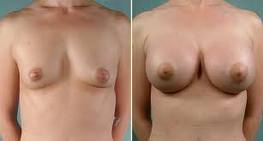
1. Cosmetic Enhancement and Self-Confidence
The primary cause for breast augmentation is cosmetic enhancement. Many individuals seek
breast augmentation to increase breast size, improve shape, and achieve better symmetry.
Cultural beauty standards, personal preferences, and a desire to feel more confident in
clothing or swimwear drive many to undergo this procedure. Enhanced breast appearance can
positively impact body image and self-esteem.
2. Correction of Breast Asymmetry
Breast asymmetry is common—most women have breasts that differ slightly in size or shape—but
in some cases, this discrepancy is pronounced enough to cause dissatisfaction or
self-consciousness. Breast augmentation can balance the size difference by increasing volume
in the smaller breast or adjusting shape to achieve symmetry, often combined with other
procedures such as lifts or reductions.
3. Post-Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Changes
Pregnancy and breastfeeding lead to hormonal and structural changes in the breasts,
including glandular tissue reduction, skin stretching, and loss of volume, commonly referred
to as "deflation." Women may experience ptosis (sagging) or flattening of the breasts.
Breast augmentation, often combined with mastopexy (breast lift), restores pre-pregnancy
breast fullness and contour.
4. Age-Related Breast Volume Loss
Natural aging causes the breasts to lose fat and glandular tissue, leading to volume loss,
sagging, and loss of firmness. This change can result in dissatisfaction with breast
appearance, motivating some to seek augmentation to rejuvenate their figure.
5. Weight Loss Effects
Significant weight loss can reduce overall body fat, including in the breasts, leading to
smaller, deflated breasts. For some individuals, breast augmentation helps restore lost
volume and improve breast shape after weight reduction.
6. Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy
Breast implants are integral in reconstructive surgery following mastectomy for breast
cancer or other medical conditions. Reconstruction helps restore the breast mound, offering
psychological benefits and aiding in body image restoration after cancer treatment.
Risk Factors Associated with Breast Augmentation
Although breast augmentation is widely considered safe, it is a surgical procedure that carries inherent risks. Certain patient-specific and procedural factors increase the likelihood of complications or influence surgical outcomes.
1. Age and Skin Quality
- Younger patients generally have more elastic skin that adapts well to implants.
- Older patients may have thinner skin, less elasticity, or significant sagging, which may increase the risk of visible implant edges, rippling, or implant malposition.
- Skin quality affects implant selection, size, and the potential need for adjunctive procedures like breast lifts.
2. Smoking and Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking significantly impairs wound healing and increases risks of infection, skin necrosis, and poor scarring.
- Nicotine reduces blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues, delaying recovery.
- Patients who smoke are more prone to complications such as capsular contracture (scar tissue tightening around the implant).
3. Pre-existing Medical Conditions
- Chronic illnesses such as diabetes mellitus, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease may impair healing and increase surgical risks.
- Patients with bleeding disorders may experience prolonged bleeding or hematoma formation.
- Allergies to anesthesia or implant materials, although rare, must be assessed.
4. Previous Breast Surgeries
- Scar tissue from prior breast procedures can complicate implant placement and increase the risk of implant malposition or capsular contracture.
- Revision surgeries often carry a higher complication rate than primary augmentations.
5. Implant Characteristics
- Size: Larger implants place more mechanical stress on breast tissue and skin, increasing the risk of thinning tissue, visible edges, and discomfort.
Recognizing symptoms that may indicate severe bone damage or loss is crucial for timely intervention. Symptoms vary based on the underlying condition, bone involved, and extent of damage.
General Symptoms
- Severe or persistent bone pain: Pain localized to the affected bone, often worsening with movement or weight-bearing.
- Swelling and tenderness: Inflammatory response due to injury, infection, or tumor.
- Visible deformity or abnormal angulation: Misalignment or shortening of the affected limb or bone.
- Instability or inability to bear weight: Feeling that the bone or limb cannot support normal load.
- Limited range of motion: Especially around joints adjacent to damaged bones.
- Delayed healing or nonunion of fractures: Persistent pain and movement at the fracture site months after injury.
Specific Symptoms Based on Underlying Conditions
- Osteomyelitis: Fever, redness, warmth, pus discharge from overlying skin.
- Bone tumors: Localized swelling, night pain, or systemic symptoms like weight loss.
- Dental bone loss: Loose teeth, difficulty chewing, jaw pain.
Determining the requirement for a bone implant involves a thorough assessment including clinical evaluation, imaging, and laboratory investigations.
Clinical Evaluation
- Detailed history focusing on trauma, symptoms duration, previous treatments.
- Physical exam assessing deformity, tenderness, range of motion, and signs of infection.
Imaging Modalities
- X-rays: Initial screening to identify fractures, bone loss, implant failure, or deformity.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Provides 3D reconstruction and precise assessment of complex fractures or bone defects.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Detects marrow involvement, soft tissue extension, or occult infections.
- Bone Scintigraphy: Useful for identifying bone infections or metastatic lesions.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): Measures bone density to evaluate osteoporosis risk.
Laboratory Tests
- Blood work: CBC, ESR, CRP for infection or inflammation.
- Microbiological cultures: In cases of suspected osteomyelitis.
- Biopsy: When malignancy or unclear lesions are present.
Treatment strategies for bone implants vary depending on the patient’s condition, location, size of bone defect, and overall health. The primary goal is to restore skeletal stability and enable bone healing.
Types of Bone Implants and Grafts
1. Autografts (Patient’s Own Bone):
- Gold standard due to osteogenic, osteoconductive, and osteoinductive properties.
- Common donor sites include iliac crest, fibula, and rib.
- Risks include donor site morbidity, increased surgical time, and pain.
- Processed cadaveric bone used to fill large defects.
- Benefits include availability and no donor site complications.
- Risks involve slower integration and possible immune reaction.
- Materials like hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, bioactive glass.
- Serve as osteoconductive scaffolds to promote new bone growth.
- Often used in combination with growth factors.
- Titanium and stainless steel plates, rods, screws.
- Provide mechanical stability for fracture fixation and bone reconstruction.
- Incorporate cells, growth factors, and scaffolds.
- Aim to enhance healing and reduce complications.
Surgical Techniques
- Internal Fixation: Plates, screws, and intramedullary nails used to align and stabilize bone segments.
- Bone Grafting and Reconstruction: Filling defects to facilitate new bone formation.
- 3D Printed Custom Implants: Designed from patient-specific imaging for complex defects, improving fit and functional outcomes.
- Dental Implants: Titanium posts anchored in the jawbone to replace tooth roots.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
- Immobilization to allow initial healing.
- Pain control using NSAIDs, opioids if necessary.
- Early physiotherapy to restore strength and range of motion.
- Nutritional support with calcium, vitamin D, and protein supplements.
Prevention Strategies
- Optimal surgical techniques: Minimizing tissue trauma and ensuring sterile environments.
- Perioperative antibiotics: To reduce infection risk.
- Lifestyle modifications: Smoking cessation, balanced diet, and weight management.
- Bone health maintenance: Regular exercise, supplementation, and treatment of osteoporosis.
- Careful patient selection and implant choice: Based on individual risk profiles.
Management of Complications
- Infections: Require aggressive antibiotic therapy and sometimes implant removal.
- Nonunion or delayed healing: May need revision surgery, bone stimulators, or additional grafting.
- Implant loosening or failure: Revision with new implants or alternative fixation.
- Chronic pain management: Multimodal approaches including medications, physical therapy, and counseling.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Regular imaging and clinical evaluations to detect early issues.
Although bone implants are generally safe and effective, complications can occur, potentially affecting outcomes:
- Infection: The most common and serious complication, potentially leading to osteomyelitis and implant removal.
- Implant rejection or allergic reaction: Rare, but hypersensitivity to metals like nickel or titanium can occur.
- Mechanical failure: Loosening, bending, or breakage of implants due to stress or poor integration.
- Delayed union or nonunion: Failure of the bone to properly heal around the implant.
- Nerve and vascular injury: Damage during surgery leading to numbness, weakness, or bleeding.
- Chronic inflammation or pain: May persist despite successful surgery.
Adapting to life with a bone implant requires physical, emotional, and social adjustments.
Physical Adaptations
- Following rehabilitation protocols to regain function.
- Avoiding high-impact activities initially; gradual return to normal activities.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support bone health.
Psychological and Social Considerations
- Coping with changes in body image or function.
- Accessing support groups or counseling if needed.
- Understanding the importance of follow-up care to ensure implant longevity.
Long-term Follow-up
- Regular visits for X-rays and clinical assessment.
- Monitoring for late complications such as implant loosening or secondary fractures.
1. What is an adrenalectomy?
Adrenalectomy is a surgical procedure to remove one or both adrenal glands, which sit above
the kidneys and produce important hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
2. Why would someone need an adrenalectomy?
It is typically performed to remove adrenal tumors, including benign growths, cancerous
tumors, or hormone-producing tumors causing conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or
pheochromocytoma.
3. What are the different types of adrenalectomy procedures?
There are mainly two approaches:
- Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: Minimally invasive, using small incisions and a camera.
- Open adrenalectomy: Traditional surgery with a larger incision, usually for larger tumors or complicated cases.
4. How long does the surgery take?
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy generally takes 2 to 3 hours, while open surgery can take longer
depending on tumor size and complexity.
5. What is the recovery time after adrenalectomy?
Recovery varies by surgery type: laparoscopic patients may return to normal activities
within 2 to 4 weeks, while open surgery patients may require 4 to 6 weeks or longer for full
recovery.
6. What are the risks and potential complications?
Risks include bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding organs, hormone imbalances, and
blood pressure fluctuations. Careful preoperative evaluation and postoperative care help
reduce these risks.
7. Will I need hormone replacement therapy after surgery?
If both adrenal glands are removed, lifelong hormone replacement is necessary. If only one
gland is removed, the remaining gland usually compensates, and hormone therapy may not be
needed.
8. How is adrenalectomy performed laparoscopically?
The surgeon makes small incisions to insert a camera and surgical tools to carefully detach
and remove the adrenal gland with minimal trauma and faster recovery.
9. What symptoms should I watch for after adrenalectomy?
Watch for signs of infection, severe pain, dizziness, fatigue, or symptoms of hormone
imbalance such as low blood pressure or unusual weakness, and report these promptly to your
doctor.
10. How effective is adrenalectomy in treating adrenal tumors?
Adrenalectomy is often very effective, especially for benign tumors and hormone-secreting
tumors, providing symptom relief and reducing risks related to tumor growth or hormone
excess.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Breast Augmentation are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


