Breast implants are medical devices implanted under the breast tissue or chest muscles to enhance breast size, restore breast volume after weight loss or pregnancy, or reconstruct the breast after mastectomy or injury. Breast augmentation with implants is one of the most common cosmetic surgical procedures worldwide, designed to improve breast shape and symmetry, boost self-confidence, and restore body image.
There are two main types of breast implants: saline-filled and silicone gel-filled. Both have undergone significant improvements over the years, making the procedure safer and more effective. However, like any surgery, breast implantation carries risks, possible complications, and requires informed decision-making.
This guide provides detailed information on breast implants including causes and risk factors leading to implantation, symptoms related to implant issues, diagnosis, treatment options, preventive measures, possible complications, and living with breast implants.
The “causes” here refer to the reasons why patients may opt for breast implants, as well as risk factors related to complications.
Causes for Breast Implant Surgery:
1. Cosmetic Breast Augmentation:
Women seek implants to enhance breast size, improve shape, or balance asymmetry to meet aesthetic goals.
2. Breast Reconstruction:
After mastectomy (breast removal due to cancer or trauma), implants restore breast contour.
3. Congenital or Developmental Abnormalities:
Conditions like tuberous breasts or micromastia (underdeveloped breasts) may be corrected with implants.
Risk Factors Associated with Breast Implants:
- Implant Type: Silicone vs. saline implants carry different risk profiles.
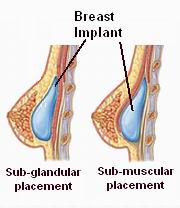
- Surgical Technique and Implant Placement: Subglandular vs. submuscular positioning affects outcomes.
- Patient Factors: Age, smoking status, immune system health, and history of breast disease impact healing and risk.
- Previous Breast Surgeries: Scar tissue or prior procedures may influence complications.
- Capsular Contracture History: Risk of hardening around implants.
- Lifestyle: Physical activity, trauma, or infection can affect implants.
- Duration of Implant: Risk of rupture or leakage increases with implant age.
While many patients with breast implants experience no problems, recognizing symptoms of potential complications is critical:
- Pain or Tenderness: Persistent or new breast pain around the implant.
- Swelling or Hardening: Breast becoming unusually firm, hard, or misshapen (possible capsular contracture).
- Visible Deformity or Asymmetry: Changes in breast shape or size.
- Skin Changes: Redness, rash, or thinning skin over the implant.
- Implant Rupture Signs:
- Saline implants: sudden deflation or loss of breast volume.
- Silicone implants: often silent rupture, sometimes breast changes or lumps.
- Lumps or Nodules: Around the implant or in the breast tissue.
- Seroma Formation: Fluid accumulation causing swelling.
- Infection Signs: Fever, redness, warmth, and pain.
- Systemic Symptoms: Rarely, symptoms like fatigue or joint pain may relate to breast implant illness (BII), an area under ongoing research.
Diagnosis involves a detailed clinical evaluation combined with imaging and laboratory tests when necessary.
Clinical Examination:
- Inspection for breast symmetry, skin condition, and signs of inflammation or deformity.
- Palpation to assess implant position, lumps, or fluid collections.
Imaging Studies:
- Mammography: Useful for breast cancer screening but may be limited by implants.
- Ultrasound: Effective for detecting implant rupture, fluid collections, and masses.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The gold standard for detecting silicone implant ruptures and detailed breast evaluation.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Occasionally used in complex cases.
Additional Tests:
- Aspiration and Culture: Fluid removal for suspected infections or seromas.
- Biopsy: For suspicious lumps or changes, including checking for Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL).
- Blood Tests: To rule out infection or systemic illness.
Treatment depends on the specific problem and ranges from conservative management to surgical intervention.
Conservative Treatments:
- Pain management with NSAIDs or analgesics.
- Antibiotics for infections if caught early.
- Observation for mild symptoms or silent rupture without clinical signs.
Surgical Treatments:
- Implant Removal (Explantation): Complete removal without replacement.
- Implant Replacement: Removing the old implant and inserting a new one.
- Capsulectomy: Removal of the fibrous capsule surrounding the implant, especially in capsular contracture cases.
- Seroma Drainage: Aspiration or surgical evacuation of fluid collections.
- Correction of Implant Malposition: Surgical adjustment of implant placement.
- Treatment for BIA-ALCL: En bloc capsulectomy and oncology referral.
Preventive strategies focus on minimizing risks before, during, and after surgery:
- Preoperative Evaluation: Thorough health assessment and counseling.
- Choice of Implant: Using FDA-approved implants suited to patient anatomy and preference.
- Surgical Technique: Sterile environment, minimal tissue trauma, and proper implant placement.
- Postoperative Care: Follow-up appointments, wound care, and monitoring.
- Patient Education: Recognizing symptoms, avoiding trauma, and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits.
- Regular Imaging: Periodic MRI or ultrasound for silicone implants as recommended.
Though breast implants are generally safe, potential complications include:
- Capsular Contracture: Hardening due to scar tissue tightening around implant.
- Implant Rupture or Leakage: Saline implants deflate; silicone ruptures may be silent.
- Infection: Can require implant removal.
- Seroma or Hematoma: Fluid or blood accumulation.
- Implant Malposition or Asymmetry: Implant shifting or rotation.
- Changes in Sensation: Numbness or hypersensitivity of the nipple or breast.
- Breast Implant Illness (BII): A set of systemic symptoms some patients report; under research.
- Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL): A rare lymphoma linked to textured implants.
- Scarring and Poor Cosmetic Outcome: Hypertrophic scars or unsatisfactory shape.
Patients with breast implants can live healthy, active lives with proper care and awareness:
- Lifestyle: No major restrictions, but avoid trauma to breasts and report unusual symptoms.
- Breast Cancer Screening: Regular mammograms with specialized techniques to visualize implants.
- Routine Follow-Up: Regular clinical exams and imaging as advised by the surgeon.
- Physical Activity: Most exercises are safe; some may require adjustments.
- Psychological Impact: Many report improved self-esteem but should have realistic expectations.
- Longevity: Implants are not lifetime devices; replacement or removal may be needed over time.
1. What are breast implants?
Breast implants are medical devices placed under the breast tissue or chest muscles to increase breast size (augmentation) or to reconstruct the breast after mastectomy or injury. They come in different shapes, sizes, and materials to suit individual needs.
2. What types of breast implants are available?
The two main types of breast implants are:
- Saline implants: Filled with sterile saltwater, these implants can be adjusted during surgery and tend to feel firmer.
- Silicone implants: Filled with silicone gel, they feel more like natural breast tissue and are preferred by many patients.
3. Who is a good candidate for breast implants?
Good candidates are women in good health who want to enhance breast size, improve symmetry, or reconstruct their breasts. They should have realistic expectations and be emotionally prepared for surgery and recovery.
4. How is the breast implant surgery performed?
The surgeon makes incisions in discreet locations (under the breast crease, around the areola, or under the arm), creates a pocket either under the breast tissue or muscle, and inserts the implant. The incision is then closed with sutures.
5. What is the recovery like after breast implant surgery?
Recovery typically involves swelling, bruising, and discomfort for the first few weeks. Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for 4-6 weeks. Follow-up visits help monitor healing and implant positioning.
6. Are breast implants safe?
Breast implants are generally safe, but like any surgery, they carry risks including infection, implant rupture, capsular contracture (scar tissue tightening), and changes in nipple sensation. Regular monitoring and follow-up care reduce these risks.
7. How long do breast implants last?
Breast implants are not lifetime devices. Many last 10-20 years, but some may require replacement sooner due to rupture, leakage, or cosmetic changes. Regular check-ups are important to ensure implant integrity.
8. Can breast implants affect breastfeeding?
Most women with breast implants can breastfeed successfully, especially if implants are placed under the muscle and incisions avoid the milk ducts. However, some women may experience difficulty, so it’s important to discuss plans with your surgeon.
9. What are the signs of breast implant complications?
Signs include unusual swelling, pain, changes in breast shape, lumps, hardness, or nipple sensitivity changes. If these occur, consult your surgeon immediately for evaluation.
10. Can breast implants be removed or replaced?
Yes, implants can be removed or replaced through a surgical procedure. Some patients opt for removal due to complications or cosmetic preferences. Revision surgery is common and can restore desired appearance.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Brachioplasty are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


