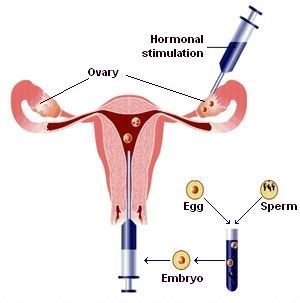
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a medical procedure that involves the fertilization of an egg outside the body, in a laboratory setting, and then transferring the fertilized egg (embryo) into the woman’s uterus to establish a pregnancy. IVF is one of the most well-known and effective treatments in assisted reproductive technology (ART), helping couples with infertility to achieve their dream of becoming parents.
IVF was first developed in 1978 and has since helped millions of couples worldwide. It is often recommended when other fertility treatments have not been successful or when there are specific health issues that prevent natural conception. IVF has revolutionized fertility treatments by offering a solution to individuals and couples facing a range of infertility challenges, including issues with ovulation, fallopian tube damage, male infertility, and unexplained infertility.
The IVF process typically involves the stimulation of the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, egg retrieval, fertilization outside the body, and the embryo transfer to the uterus. IVF can be done using a woman’s eggs and a partner's sperm, or donor eggs and sperm can be used when necessary.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is used to address various infertility issues caused by both male and female factors. The decision to pursue IVF treatment generally stems from difficulties in conceiving after trying for a certain period or when a medical condition impedes natural conception.
Causes of Infertility Leading to IVF
-
Female Infertility:
-
Ovulation Disorders: Women who do not ovulate regularly or at all due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hypothalamic dysfunction, or primary ovarian insufficiency.
-
Fallopian Tube Damage or Blockage: Women with blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, often due to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or past ectopic pregnancies, may not be able to conceive naturally.
-
Endometriosis: This condition can interfere with the function of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus, leading to infertility.
-
Age-related Infertility: As a woman’s age increases, the quantity and quality of her eggs decline, making natural conception more difficult.
-
Uterine or Cervical Issues: Conditions like fibroids, scar tissue, or abnormalities in the uterus or cervix can impact implantation or pregnancy.
-
-
Male Infertility:
-
Low Sperm Count (Oligospermia): A low sperm count can prevent the sperm from reaching and fertilizing the egg.
-
Poor Sperm Motility (Asthenozoospermia): When sperm cannot move efficiently, it becomes difficult for them to swim through the cervix and into the fallopian tubes.
-
Abnormal Sperm Morphology (Teratozoospermia): Abnormally shaped sperm may have difficulty penetrating the egg during fertilization.
-
Sperm DNA Fragmentation: Sperm with fragmented DNA may struggle to fertilize the egg and result in poorer embryo quality.
-
-
Unexplained Infertility:
-
In some cases, both partners may appear to have normal fertility, but conception does not occur. This unexplained infertility can often be treated with IVF.
-
-
Genetic Factors:
-
Genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, or hemophilia may prompt the use of genetic screening and IVF to avoid passing on hereditary conditions.
-
IVF itself does not have symptoms or signs, but there are several indicators that may lead someone to seek IVF treatment. These signs are usually related to infertility issues that prevent natural conception. The IVF process involves several steps, including ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, and embryo transfer, each of which can result in certain physical and emotional changes.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for IVF
-
Difficulty Conceiving:
-
Couples who have tried unsuccessfully to conceive for 12 months (or 6 months for women over 35) may be candidates for IVF. It is often recommended after other fertility treatments, such as medications or intrauterine insemination (IUI), have not worked.
-
-
Irregular or Absent Periods:
-
Women with irregular cycles or no periods at all may have difficulty ovulating. Ovulation problems are a common cause of infertility and may require IVF as part of a broader treatment plan.
-
-
Pelvic Pain or Endometriosis:
-
Women with a history of endometriosis or pelvic pain may face difficulty in getting pregnant. IVF is often recommended when other treatments, such as laparoscopy or medication, have not been successful.
-
-
Low Sperm Count or Poor Sperm Quality:
-
Men with low sperm count or poor sperm motility may find it difficult for the sperm to fertilize the egg naturally. IVF with ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) can help improve fertilization rates in these cases.
-
-
Age-Related Decline in Fertility:
-
As women age, fertility declines. IVF can be an option for women over 35 who may struggle to conceive naturally due to age-related changes in egg quality.
-
Before undergoing IVF, both male and female partners must undergo a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation to identify the cause of infertility and assess the suitability of IVF.
Diagnosis for IVF Treatment
-
Female Fertility Testing:
-
Ovarian Reserve Testing: Tests like Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) levels, Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), and ultrasound imaging can assess the quantity and quality of a woman’s eggs.
-
Hysterosalpingography (HSG): This imaging test evaluates whether the fallopian tubes are open and functional. It can also check for uterine abnormalities.
-
Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgery that allows the doctor to look inside the pelvic cavity for conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, or ovarian cysts.
-
-
Male Fertility Testing:
-
Semen Analysis: This is the first test for male infertility and checks sperm count, motility, and morphology.
-
Hormonal Evaluation: Blood tests can assess levels of testosterone, FSH, and LH to determine the cause of infertility.
-
Genetic Screening: This can identify any genetic issues, such as Y chromosome microdeletions or other hereditary conditions that may affect fertility.
-
-
Counseling and Psychological Evaluation:
-
Given the emotional and physical stress of infertility treatments, counseling may be recommended to help both partners manage the psychological aspects of IVF treatment.
-
IVF is a multi-step process that requires various medical interventions to stimulate the ovaries, retrieve eggs, fertilize them, and implant the resulting embryo. Here’s a detailed look at the IVF treatment process:
1. Ovarian Stimulation:
-
The first step in IVF involves stimulating the ovaries with hormonal injections to produce multiple eggs. The typical medications used are FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone). This process is carefully monitored through ultrasound and blood tests to track ovarian response.
2. Egg Retrieval (Aspiration):
-
Once the eggs are ready, they are retrieved in a procedure called egg aspiration. This is done under local anesthesia and involves using a needle to collect eggs from the ovaries.
3. Sperm Collection:
-
On the same day as egg retrieval, the male partner provides a sperm sample. If the sperm count or quality is low, ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) may be used, where a single sperm is directly injected into the egg to aid fertilization.
4. Fertilization:
-
In the laboratory, the eggs and sperm are combined for fertilization. If ICSI is used, a single sperm is injected directly into each egg.
5. Embryo Culture and Selection:
-
After fertilization, the embryos are cultured for 3 to 5 days in the laboratory. Embryologists monitor their development and select the best quality embryos for transfer.
6. Embryo Transfer:
-
The selected embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus using a thin catheter. This is a painless procedure, typically done under ultrasound guidance to ensure correct placement of the embryo(s).
7. Pregnancy Test and Follow-Up:
-
About 10 to 14 days after the embryo transfer, a blood test is done to check for pregnancy. If successful, an ultrasound will follow to confirm fetal development.
While IVF is a highly effective treatment for many, managing its risks and complications is crucial for success.
Prevention of IVF Failure:
-
Genetic Screening: Genetic testing can help identify potential genetic issues in both partners and avoid transferring embryos with genetic defects.
-
Embryo Screening (PGT): Pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT) can help ensure only healthy embryos are transferred, reducing the risk of miscarriage and improving the chances of success.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking, excessive alcohol, and stress can help improve IVF outcomes.
-
Emotional Support: IVF can be emotionally challenging. Psychological counseling for the couple can help them manage the emotional aspects of the process.
Management During IVF:
-
Hormonal Therapy: Hormonal injections are used to control the ovarian stimulation process. Careful monitoring and adjusting of medication dosages can help avoid Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS).
-
Post-Transfer Care: After embryo transfer, it’s essential to follow instructions regarding rest, activity levels, and medications to ensure the best chances of implantation.
Like any medical procedure, IVF carries risks and potential complications. These can range from mild to severe, and include:
-
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS):
-
This occurs when the ovaries over-respond to stimulation and become swollen, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and in severe cases, fluid accumulation.
-
-
Multiple Pregnancies:
-
IVF can increase the chances of multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets), which carry increased risks for both the mother and babies, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
-
-
Ectopic Pregnancy:
-
In rare cases, an embryo may implant outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube, which requires surgical intervention.
-
-
Infections and Bleeding:
-
As with any invasive procedure, there is a risk of infection or bleeding from the egg retrieval process or embryo transfer.
-
-
Emotional Stress:
-
IVF treatment can cause emotional strain due to the financial, physical, and psychological toll of the process.
-
Living with IVF treatment involves physical, emotional, and psychological adjustments for couples. While IVF offers a path to parenthood, it requires a significant commitment in terms of time, effort, and support.
Managing Expectations:
-
It’s important for couples to have realistic expectations about IVF success rates and understand that the process can be physically and emotionally demanding.
Support Systems:
-
Couples should consider engaging in support groups or counseling to share their experiences and receive emotional support throughout the IVF journey.
1. What is In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)?
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is an assisted reproductive technology (ART) in which an egg is fertilized outside the body, in a laboratory dish. The fertilized embryo is then transferred into the woman’s uterus to establish a pregnancy. IVF is commonly used to treat infertility and can be recommended for various reasons, including blocked fallopian tubes, male infertility, or unexplained infertility.
2. How does IVF work?
IVF involves several key steps:
-
Ovarian Stimulation: The woman undergoes hormone therapy to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
-
Egg Retrieval: Once the eggs are mature, they are collected from the ovaries using a needle under sedation.
-
Fertilization: The eggs are fertilized with sperm in the laboratory. This can be done traditionally by placing the sperm with the eggs or through ICSI (Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection) if there are sperm issues.
-
Embryo Culture: The fertilized eggs develop into embryos, which are cultured for several days.
-
Embryo Transfer: One or more healthy embryos are selected and transferred into the woman’s uterus in the hope of achieving a successful pregnancy.
3. Who is a good candidate for IVF?
IVF is commonly recommended for individuals or couples who have been unable to conceive through less invasive treatments. It can be suitable for:
-
Women with blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
-
Male infertility (low sperm count or motility)
-
Endometriosis or other reproductive health conditions
-
Unexplained infertility
-
Same-sex couples or single women who wish to have a biological child
4. What are the success rates of IVF?
Success rates for IVF vary depending on factors like the woman’s age, egg quality, and the clinic’s expertise. On average, the success rate for IVF ranges from 30% to 50% per cycle. Success rates tend to be higher for women under 35, with a gradual decline in success as age increases. Other factors, such as the quality of the sperm and embryos, also influence the outcome.
5. What are the risks and side effects of IVF?
IVF carries some risks and potential side effects, including:
-
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): Caused by an excessive response to hormone treatment, leading to swollen ovaries and fluid retention.
-
Multiple pregnancies: IVF increases the risk of twins or more, especially when multiple embryos are transferred.
-
Ectopic pregnancy: A pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tubes.
-
Emotional stress: IVF can be physically and emotionally taxing, with potential for anxiety, stress, and disappointment if the cycle fails.
6. How long does an IVF cycle take?
An IVF cycle typically takes about 4-6 weeks from start to finish. The first two weeks involve ovarian stimulation with hormones, followed by egg retrieval. After the fertilization process, embryo transfer typically occurs 3-5 days later. After the transfer, you will need to wait about 10-14 days before taking a pregnancy test to confirm if the procedure was successful.
7. How much does IVF cost?
The cost of IVF varies significantly depending on the location, clinic, and individual treatment requirements. On average, the cost of a single IVF cycle ranges from $10,000 to $15,000, excluding medication, consultations, and additional services like embryo freezing or sperm retrieval. Some insurance plans may cover part of the cost, but it's important to check with your provider to understand coverage options.
8. What is the difference between IVF and ICSI?
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) and ICSI (Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection) are both techniques used to help achieve pregnancy through assisted reproduction, but the difference lies in the fertilization process:
-
IVF: Eggs are fertilized by placing them in a dish with sperm, allowing fertilization to happen naturally.
-
ICSI: A single sperm is directly injected into an egg, typically used in cases of male infertility when sperm quality is poor or when previous IVF cycles have failed.
9. Can I undergo IVF if I’m over 40?
IVF is still an option for women over 40, but success rates tend to decrease as a woman’s age increases, especially after age 35. The quality of eggs declines with age, which can reduce the likelihood of a successful pregnancy. In some cases, egg donation from a younger donor may be recommended for women over 40 to increase the chances of success.
10. What are the ethical and legal considerations of IVF?
Ethical and legal issues surrounding IVF include decisions about the use of donor eggs or sperm, the number of embryos to transfer, and the fate of unused embryos. Some couples may also have concerns about the potential for selective reduction in the case of multiple pregnancies. Legally, the parents of the child born through IVF are typically the legal parents, though this can vary based on the country’s laws regarding gamete donation and surrogacy.
The other Infertility Treatment Procedures are:
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
- Zygote Intra-Fallopian Transfer
- Embryo Donation … etc
Few Major Hospitals for IVF are:
- Parkway Fertility Center
- Jinemed Hospital
- Jindal Heart Institute & Test Tube Baby Centre
- Apollo Fertility and IVF Center
- Malpani Infertility Clinic
- Thomson Fertility Centre
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



