Cardiac catheterization is a medical procedure used to diagnose and treat heart conditions. It involves inserting a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into a blood vessel and guiding it to the heart. This technique provides doctors with a direct view of the heart's blood vessels and chambers, allowing them to evaluate the heart's function and detect any abnormalities.
Cardiac catheterization is typically performed to diagnose or treat various heart conditions. Some of the leading causes for needing this procedure include:
-
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): The most common cause, CAD occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, limiting the blood supply to the heart muscle.
-
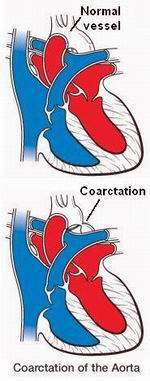
Congenital Heart Defects: Some people are born with structural heart problems, such as holes in the heart or abnormal heart valves, which can be assessed using cardiac catheterization.
-
Heart Valve Diseases: Conditions such as aortic stenosis or mitral valve regurgitation may require cardiac catheterization to assess the severity and guide treatment.
-
Heart Attack: After a heart attack, catheterization helps determine the extent of damage to the heart and can identify blocked arteries that may need to be treated with angioplasty or stents.
-
Pericardial Disease: Conditions affecting the lining around the heart, such as pericarditis or pericardial effusion, may also necessitate cardiac catheterization to assess the heart's function and the fluid around it.
Patients may present with a variety of symptoms that prompt doctors to recommend cardiac catheterization for a closer look at the heart. These include:
-
Chest Pain (Angina): Pain or discomfort in the chest is a common symptom of coronary artery disease. It often occurs with physical activity or stress and is typically relieved by rest.
-
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical exertion or at rest, can indicate heart failure or other cardiovascular issues.
-
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak, even after minimal activity, may be a sign of reduced heart function.
-
Swelling in Legs or Abdomen: Fluid buildup in the legs, ankles, or abdomen can signal heart failure, which may require catheterization to assess the underlying cause.
-
Irregular Heartbeats (Arrhythmia): Abnormal heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation, may lead to cardiac catheterization to evaluate the heart's electrical system.
-
Fainting or Dizziness: Syncope or lightheadedness may occur when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to the brain, often due to underlying heart conditions.
Cardiac catheterization serves as a key diagnostic tool for various heart conditions. Here's how it's used in the diagnostic process:
-
Angiography: During the procedure, a contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries to make them visible on an X-ray. This helps detect any blockages or narrowing of the arteries.
-
Pressure Measurements: Catheterization allows doctors to measure the pressure inside the heart's chambers, which is important for diagnosing conditions like heart failure or valve issues.
-
Oxygen Levels: The procedure can measure the oxygen levels in the blood to assess whether the heart is receiving enough oxygenated blood.
-
Cardiac Biopsy: In certain cases, a biopsy of the heart tissue may be performed during catheterization to diagnose conditions like myocarditis or heart muscle diseases.
Cardiac catheterization can be both diagnostic and therapeutic. Some of the treatment options it enables include:
-
Angioplasty: A balloon is used to open blocked coronary arteries, allowing blood to flow freely again. In some cases, a stent is inserted to keep the artery open.
-
Stent Placement: If a blockage is found during catheterization, a small mesh tube (stent) may be inserted into the artery to hold it open and prevent future blockages.
-
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): In cases where angioplasty and stenting are not possible, bypass surgery may be recommended to reroute blood around blocked arteries.
-
Valve Repair or Replacement: Catheterization can be used to repair or replace damaged heart valves in certain cases, especially in minimally invasive procedures like TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement).
-
Balloon Valvuloplasty: This technique is used to widen a narrowed heart valve. A balloon catheter is inserted into the valve and inflated to open it.
While some conditions may be unavoidable due to genetics, there are steps individuals can take to lower the risk of developing heart disease and requiring cardiac catheterization:
-
Healthy Diet: A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
-
Regular Exercise: Physical activity strengthens the heart and improves circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease.
-
Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular conditions.
-
Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Regular monitoring and treatment of high blood pressure and cholesterol levels can help prevent the development of heart disease.
-
Manage Diabetes: Proper management of diabetes can prevent complications like heart disease and stroke.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress contributes to heart disease. Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help reduce stress.
Although cardiac catheterization is a generally safe procedure, like any medical intervention, it comes with potential risks. These include:
-
Bleeding or Bruising: The insertion site may bleed, or a hematoma (blood clot) may form at the site of the catheter insertion.
-
Infection: Any invasive procedure carries a risk of infection, although this is rare with cardiac catheterization.
-
Allergic Reactions to Contrast Dye: Some people may be allergic to the contrast dye used during angiography, leading to symptoms such as hives or difficulty breathing.
-
Damage to Blood Vessels or Heart: In rare cases, the catheter may cause damage to blood vessels, heart valves, or other structures.
-
Kidney Problems: The contrast dye can sometimes affect kidney function, especially in individuals with preexisting kidney issues.
-
Arrhythmias: Cardiac catheterization can occasionally trigger abnormal heart rhythms, which may require treatment.
For those who have undergone cardiac catheterization, it's important to follow certain lifestyle changes and medical recommendations for a healthy recovery:
-
Post-Procedure Care: After catheterization, patients are typically monitored for several hours to ensure there are no immediate complications. Recovery time is relatively short, but it is essential to follow the doctor’s instructions regarding rest and activity.
-
Medication Adherence: Patients may be prescribed medications to prevent blood clots, lower cholesterol, or control blood pressure. It’s important to take medications as directed.
-
Cardiac Rehabilitation: A structured rehabilitation program that includes exercise, education, and counseling can help patients recover physically and emotionally after a heart procedure.
-
Long-Term Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with a cardiologist are necessary to monitor heart health, adjust medications, and prevent future problems.
-
Emotional Support: Living with heart disease can be stressful. Joining a support group or seeking counseling can be beneficial for emotional well-being.
Few popular hospitals for Coarctation of the Aorta Repair are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Coarctation Of Aorta Repair | Destinations For Coarctation Of Aorta Repair | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair In Thailand | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair In Malaysia | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair In Singapore | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair In India | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair In Argentina | Doctors For Coarctation Of Aorta Repair | Surgeons For Coarctation Of Aorta Repair | Cost Of Coarctation Of Aorta Repair | Treatmnet For Coarctation Of Aorta | Recovery After Coarctation Of Aorta Repair | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair Information | Left Ventricle | Aorta | Congestive Heart Failure | Aortic Arch | Ascending Aorta | Bleeding | Stroke | Bacterial Endocarditis | Coronary Arteries | Pulmonary Artery | Pulmonary Hypertension | Pale Skin | Sweating | Heavy / Rapid Breathing | Loss Of Appetite | Weight Loss | Heart Murmur | Cramps In Lower Section Of The Body | Cardiac Catheterization | Surgical Repair | Catheter | Balloon | Cardiology | Cardiac Procedures In Thailand | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair Overseas | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair Abroad | Coarctation Of Aorta Repair Low Cost
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


