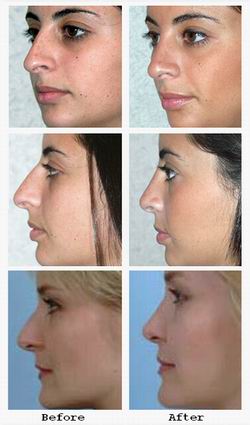
Rhinoplasty, often referred to as a "nose job," is a surgical procedure designed to reshape and restore both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the nose. As the most prominent facial feature, the nose plays a vital role in overall facial harmony and breathing efficiency. Rhinoplasty can correct structural abnormalities, repair trauma, address congenital defects, and enhance appearance to improve self-confidence.
While rhinoplasty is commonly associated with cosmetic improvements such as refining a dorsal hump or narrowing a broad nasal bridge, it equally addresses critical functional problems like septal deviation, nasal valve collapse, and airway obstruction that significantly impact quality of life.
Advancements in surgical techniques and a better understanding of nasal anatomy have enabled surgeons to customize rhinoplasty for each patient, balancing artistic vision with structural integrity for natural, long-lasting results.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of rhinoplasty, including causes and risk factors, clinical symptoms, diagnostic strategies, surgical and non-surgical treatments, preventive care, potential complications, and postoperative living.
Common Causes for Seeking Rhinoplasty
-
Congenital Nasal Deformities: These include asymmetry, wide nasal bones, flattened nasal bridges, and poorly defined tips.
-
Traumatic Nasal Injuries: Fractures, cartilage damage, or soft tissue injury from accidents, sports, or violence leading to deformity or breathing difficulties.
-
Age-Related Changes: Loss of skin elasticity, cartilage weakening, and gravity effects causing tip drooping and lengthening.
-
Functional Impairments: Deviated septum, nasal valve collapse, or turbinate hypertrophy causing nasal obstruction.
-
Dissatisfaction with Previous Rhinoplasty: Revision procedures to correct aesthetic or functional failures.
Risk Factors That May Affect Outcomes
-
Medical Comorbidities: Diabetes, hypertension, bleeding disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
-
Smoking: Impairs wound healing and increases risk of complications.
-
Skin Thickness: Thick skin can mask fine surgical refinements; thin skin reveals imperfections more readily.
-
Psychological Factors: Body dysmorphic disorder or unrealistic expectations can lead to dissatisfaction.
-
Ethnicity and Nasal Anatomy: Different ethnic backgrounds require customized surgical approaches to maintain ethnic identity.
-
Visible Nasal Irregularities: Bumps, humps, wide nostrils, bulbous or drooping tips, or crooked noses.
-
Nasal Obstruction: Difficulty breathing through one or both nostrils, often worsened by congestion.
-
Recurrent Sinus Infections: Linked to poor nasal drainage due to structural abnormalities.
-
Noisy Breathing or Snoring: Resulting from compromised nasal airflow.
-
Frequent Nosebleeds: Due to mucosal irritation from abnormal airflow.
-
Pain or Tenderness: Though rare, can indicate infection or trauma.
-
Post-Trauma Deformities: Noticeable changes in nose shape after injury.
Clinical Evaluation
-
Patient History: Duration and nature of symptoms, history of trauma, previous surgeries, allergies, and expectations.
-
Physical Examination: External inspection, palpation of nasal bones and cartilage, assessment of nasal airway.
-
Anterior Rhinoscopy: Visualizes nasal septum and internal structures.
-
Nasal Endoscopy: Offers detailed visualization of nasal passages and sinus openings.
Imaging
-
CT Scan: Essential for complex deformities, trauma assessment, or when planning combined sinus surgery.
-
3D Imaging and Computer Simulations: Used in advanced centers for preoperative planning and patient communication.
Psychological Assessment
-
Screen for psychological readiness and realistic goals.
Surgical Techniques
-
Open Rhinoplasty: Incision across the columella allowing full exposure; preferred for complex reconstructions and revision cases.
-
Closed Rhinoplasty: Incisions confined to inside nostrils; suitable for minor reshaping and less invasive.
-
Septoplasty: Correction of deviated septum to improve breathing; often performed simultaneously.
-
Tip Plasty: Focused reshaping of nasal tip cartilage.
-
Osteotomies: Controlled bone cuts to narrow or straighten nasal bones.
-
Cartilage Grafting: Using septal, ear, or rib cartilage to reinforce or augment nasal structure.
-
Alar Base Reduction: Reduces nostril width if excessive.
Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty
-
Dermal Fillers: Temporary reshaping of nasal contours without surgery; ideal for small irregularities.
-
Not a substitute for correcting functional issues.
Anesthesia
-
Typically general anesthesia; local anesthesia with sedation in select minor cases.
Prevention
-
Avoid nasal trauma.
-
Proper management of nasal allergies and infections.
-
Smoking cessation prior to surgery.
Preoperative Management
-
Thorough patient counseling and surgical planning.
-
Address medical comorbidities.
-
Psychological preparation and expectation management.
Postoperative Management
-
Head elevation and cold compresses to reduce swelling.
-
Nasal splints and packing for support.
-
Pain control with prescribed medications.
-
Avoid nose blowing and strenuous activities.
-
Follow-up visits for monitoring healing.
Common Side Effects
-
Swelling, bruising, and mild pain.
-
Temporary nasal congestion.
-
Mild numbness or altered sensation.
Potential Complications
-
Infection: Rare but treatable.
-
Septal Perforation: Hole in septum causing crusting and bleeding.
-
Unsatisfactory Aesthetic Outcome: Requires revision surgery in some cases.
-
Nasal Obstruction: Due to scarring or inadequate correction.
-
Skin Necrosis: Very rare.
-
Anesthesia Risks: As with all surgeries.
Minimizing Complications
-
Choose an experienced board-certified surgeon.
-
Follow pre- and postoperative care instructions strictly.
-
Early intervention if complications arise.
Recovery Timeline
-
Initial swelling and bruising peak within 48-72 hours.
-
Most patients return to work in 1-2 weeks.
-
Swelling continues to subside over months; final results apparent after 6-12 months.
Psychological Impact
-
Improved self-confidence and body image.
-
Positive social and professional interactions.
Long-Term Care
-
Protect nose from trauma.
-
Use sunscreen to prevent pigmentation changes.
-
Maintain follow-up for ongoing assessment.
1. What is rhinoplasty?
Rhinoplasty, commonly known as a nose job, is a surgical procedure designed to reshape or resize the nose for cosmetic or functional purposes, such as improving appearance or correcting breathing difficulties.
2. Who is a good candidate for rhinoplasty?
Ideal candidates are individuals who are physically healthy, have realistic expectations, and seek to improve nasal appearance or function. Candidates should have completed facial growth, typically after age 16-18.
3. How is rhinoplasty performed?
The surgery can be done via an open approach (small external incision) or closed approach (incisions inside the nostrils). The surgeon sculpts the bone and cartilage to achieve the desired shape.
4. What is the recovery time after rhinoplasty?
Initial recovery usually takes 1 to 2 weeks, with swelling and bruising subsiding gradually. Most patients resume normal activities within 2 weeks, but full results may take up to a year.
5. Are there risks or complications?
Risks include bleeding, infection, scarring, nasal obstruction, asymmetry, and dissatisfaction with results. Selecting an experienced, board-certified surgeon reduces these risks.
6. Will rhinoplasty affect my breathing?
If done correctly, rhinoplasty can improve breathing by correcting structural issues. However, some patients may experience temporary nasal congestion post-surgery.
7. Can rhinoplasty be combined with other procedures?
Yes, it is often combined with septoplasty (to correct a deviated septum), chin augmentation, or other facial surgeries for balanced facial aesthetics.
8. How long do the results of rhinoplasty last?
Results are typically permanent, but natural aging and trauma can alter nasal appearance over time.
9. Will there be visible scars after rhinoplasty?
Open rhinoplasty leaves a small scar on the columella (between the nostrils), which usually fades and becomes barely noticeable. Closed rhinoplasty leaves no external scars.
10. How much does rhinoplasty cost?
Costs vary widely based on surgeon experience, location, and complexity, ranging from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. It is usually considered a cosmetic procedure and not covered by insurance unless medically necessary.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Reshaping Septal deviation correction are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



