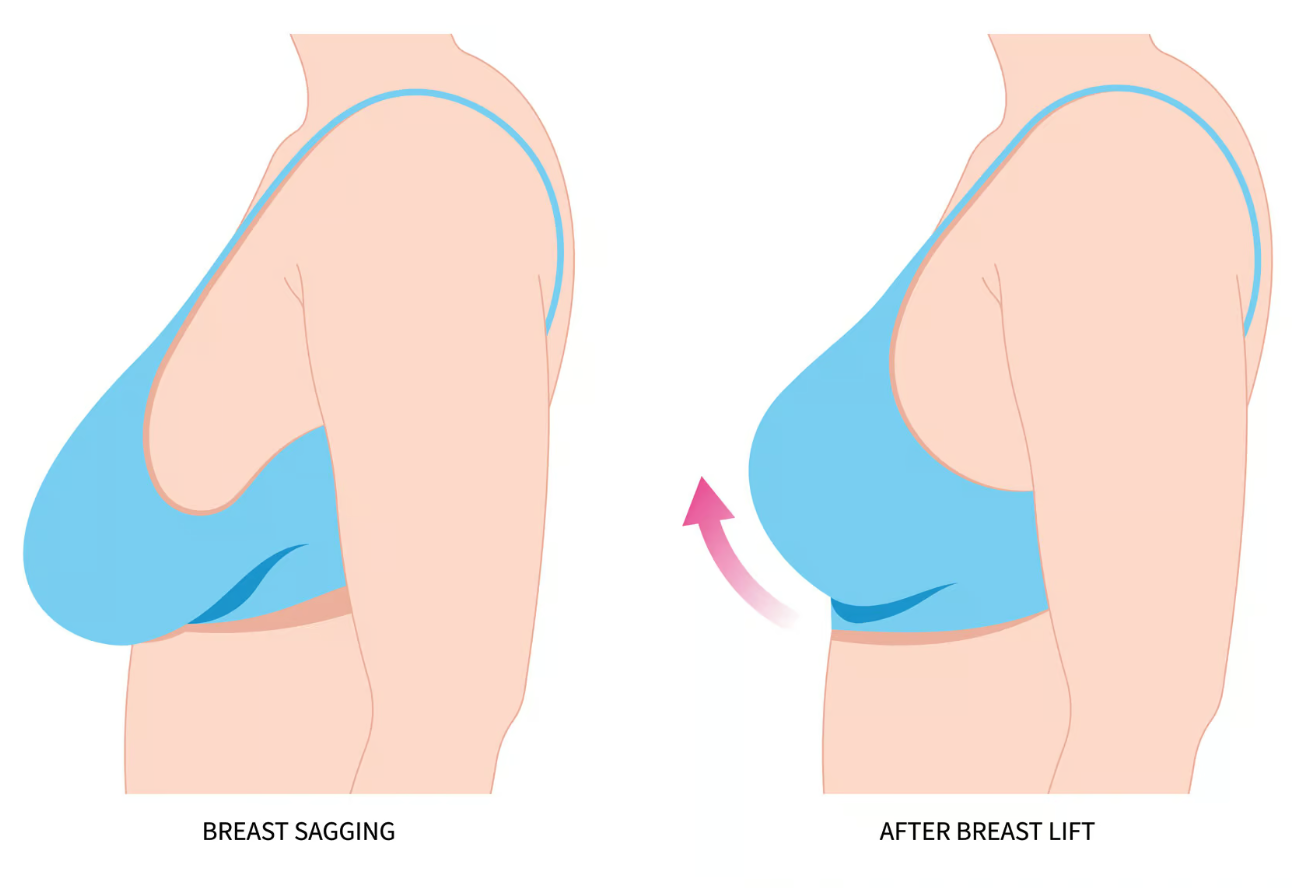
A breast lift, medically known as mastopexy, is a surgical procedure designed to raise and reshape sagging or drooping breasts. Over time, various factors such as aging, pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight fluctuations, and gravity cause the breasts to lose their youthful shape and firmness. A breast lift addresses these changes by removing excess skin, tightening the surrounding tissue, and repositioning the nipple and areola to a higher, more aesthetically pleasing position.
A breast lift, medically known as mastopexy, is a surgical procedure designed to raise and reshape sagging or drooping breasts. Over time, various factors such as aging, pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight fluctuations, and gravity cause the breasts to lose their youthful shape and firmness. A breast lift addresses these changes by removing excess skin, tightening the surrounding tissue, and repositioning the nipple and areola to a higher, more aesthetically pleasing position.
Advancements in surgical techniques have made breast lift procedures safer, more effective, and customizable based on individual anatomy and aesthetic goals.
Breast sagging, medically referred to as breast ptosis, is a common condition that many women experience as they age or go through certain life changes. This sagging occurs when the breast tissue, skin, and supporting ligaments lose their firmness and elasticity, causing the breasts to droop or appear deflated. Understanding the causes and risk factors behind breast sagging is essential to knowing why a breast lift (mastopexy) may be necessary.
Primary Causes of Breast Sagging
1. Aging
- As you age, the skin naturally loses collagen and elastin, two proteins responsible for skin’s firmness and elasticity.
- Breast tissue also becomes less dense and more fatty, contributing to loss of shape and volume.
- Gravity over time pulls the breasts downward, stretching the skin and ligaments.
2. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- During pregnancy, hormonal changes cause breast enlargement due to increased glandular tissue and milk production.
- Post-pregnancy, breasts often shrink back but the skin and ligaments may remain stretched.
- Breastfeeding itself does not cause sagging but the volume fluctuations during and after pregnancy can lead to loose skin.
3. Weight Fluctuations
- Significant weight gain stretches the skin and breast tissue.
- Subsequent weight loss can leave excess, loose skin that contributes to sagging.
- Frequent or extreme fluctuations exacerbate this effect.
4. Genetics
- Some women are genetically predisposed to less elastic skin or breast tissue that is more prone to sagging.
- Breast size and shape inherited from family members also play a role.
5. Large Breast Size
- Heavier breasts exert more downward force on the skin and ligaments.
- This often leads to earlier or more severe sagging compared to smaller breasts.
6. Smoking
- Smoking reduces blood supply to the skin and damages collagen and elastin fibers.
- This accelerates skin aging and reduces its ability to snap back, increasing sagging.
7. Gravity
- Over time, gravity pulls breast tissue downward, stretching skin and ligaments.
- This process is gradual but cumulative over the years.
Additional Risk Factors
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays degrade collagen in the skin, speeding up aging and sagging.
- Poor Posture: Slouching can contribute to the appearance of sagging by changing breast position.
- Lack of Support: Not wearing supportive bras, especially during high-impact activities, can increase strain on breast tissue.
Breast sagging (ptosis) is a natural process that varies widely between individuals. While some degree of sagging is normal with age, certain symptoms and signs can indicate when a breast lift (mastopexy) might be beneficial. Recognizing these signs helps women decide if surgical intervention could improve both the appearance and comfort of their breasts.
Key Signs You May Need a Breast Lift
1. Visible Drooping or Sagging of the Breasts
- The most obvious sign is when the breasts visibly sag or hang lower on the chest than desired.
- The nipples may point downward or rest below the natural crease (inframammary fold) beneath the breast.
2. Nipple Position Below Breast Fold
- When nipples sit at or below the level of the breast crease when standing, this is a classic sign of ptosis.
- This nipple position can make breasts appear deflated or “droopy.”
3. Loss of Upper Breast Fullness
- Breasts may lose volume in the upper pole (the area above the nipple), making them look flat or saggy.
- This loss of fullness contributes to an aged or deflated breast appearance.
4. Excess, Loose, or Wrinkled Skin
- The skin covering the breasts may appear loose, stretched, or wrinkled.
- Excess skin can cause folds, creases, or a “bat-wing” effect.
5. Breast Asymmetry
- Noticeable differences in breast size, shape, or nipple position between the two breasts.
- Asymmetry can become more pronounced as sagging progresses.
6. Physical Discomfort or Skin Irritation
- Sagging breasts can cause skin irritation or rashes beneath the breast fold due to friction or moisture buildup.
- Some women experience discomfort during physical activity or difficulty finding supportive bras.
When to See a Plastic Surgeon
If you notice one or more of these signs and they affect your confidence, comfort, or quality of life, a consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon can help determine whether a breast lift is the best option. The surgeon will assess your breast anatomy, skin quality, and goals to recommend an individualized treatment plan.
The diagnosis of breast ptosis and candidacy for a breast lift involves a thorough evaluation by a qualified plastic surgeon, including:
Medical History
Review of general health, past surgeries, pregnancies, breastfeeding history, and lifestyle habits such as smoking.
Physical Examination
- Assessment of breast size, shape, skin quality, degree of sagging, and nipple position relative to the breast fold.
- Evaluation of skin elasticity and breast tissue volume.
- Identification of asymmetry and chest wall anatomy.
Photographic Documentation
- Standardized photographs to assist with surgical planning and postoperative comparison.
Patient Goals Discussion
- Detailed conversation to understand the patient’s expectations and desired outcomes.
Imaging Tests
- Mammography or breast ultrasound as indicated, especially for patients over 40 or with risk factors for breast disease.
The choice of breast lift technique depends on the severity of breast sagging, breast size, skin quality, and patient goals. Common treatment options include:
1. Crescent Lift
- Suitable for mild sagging.
- Removes a crescent-shaped section of skin above the areola to elevate the nipple.
- Results in minimal scarring but limited lift.
2. Periareolar (Donut) Lift
- Removes a ring of skin around the areola.
- Ideal for mild to moderate sagging with minimal volume loss.
- Leaves a scar limited to the areola border.
3. Vertical (Lollipop) Lift
- Removes skin around the areola and vertically down to the breast crease.
- Appropriate for moderate sagging with significant skin excess.
- Results in scars around the areola and vertically down the breast.
4. Inverted-T (Anchor) Lift
- For severe sagging or larger breasts.
- Removes skin around the areola, vertically down, and along the breast crease.
- Allows for maximum reshaping but results in more extensive scarring.
5. Combination with Breast Augmentation
- Some patients opt for simultaneous breast augmentation using implants to increase volume while lifting sagging tissue.
Non-Surgical Alternatives
- Skin tightening procedures such as radiofrequency and ultrasound treatments may benefit mild cases but are not substitutes for surgery.
While aging and genetics cannot be fully prevented, certain lifestyle and care measures help delay sagging and maintain breast appearance:
- Maintain Stable Weight: Avoid rapid weight fluctuations to reduce skin stretching.
- Wear Supportive Bras: Proper support minimizes ligament strain.
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthen pectoral muscles to improve breast support.
- Skin Care: Use moisturizers and sunscreen to protect skin elasticity.
- Avoid Smoking: Preserves skin collagen and promotes healing.
- Balanced Nutrition: Adequate vitamins and hydration support skin health.
- Post-Pregnancy Care: Supportive bras during pregnancy and breastfeeding reduce stretching.
Breast lift surgery is generally safe but carries risks that patients should be aware of:
- Scarring: Permanent scars that typically fade over time but may be hypertrophic or keloid in some individuals.
- Changes in Nipple Sensation: Temporary or permanent numbness or increased sensitivity.
- Asymmetry: Unequal breast shape or nipple position post-surgery.
- Delayed Wound Healing: More common in smokers and those with certain medical conditions.
- Infection: Usually treatable with antibiotics but may require further intervention.
- Bleeding or Hematoma: May necessitate surgical drainage.
- Loss of Nipple or Areola Tissue: A rare but serious complication related to blood supply.
- Unsatisfactory Aesthetic Outcome: Sometimes requires revision surgery.
- Anesthesia Risks: Rare but possible adverse reactions.
Patients generally experience high satisfaction and improved quality of life after breast lift surgery. Important considerations include:
- Recovery Period: Most patients return to daily activities within 1-2 weeks and resume strenuous exercise after 4-6 weeks.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Wearing supportive bras, avoiding heavy lifting, and protecting scars during healing.
- Long-Term Results: While the lift results are long-lasting, natural aging continues, and breasts may change over time.
- Self-Confidence: Many patients report enhanced body image and comfort in clothing.
- Follow-Up Care: Routine visits to monitor healing and scar management.
- Scar Management: Use of silicone gels, massages, and laser treatments can improve scar appearance.
1. What is a breast lift (mastopexy) and how does it work?
A breast lift, medically known as mastopexy, is a surgical procedure designed to elevate and reshape breasts that have sagged or lost firmness due to factors such as aging, pregnancy, breastfeeding, or significant weight loss. The surgery involves removing excess skin and tightening the surrounding breast tissue to restore a more youthful and uplifted breast contour. Unlike breast augmentation, which adds volume, a breast lift focuses on repositioning and reshaping the existing breast tissue.
2. Who is an ideal candidate for a breast lift?
Ideal candidates for a breast lift are women who are physically healthy, have realistic expectations, and are unhappy with the drooping or flattened appearance of their breasts. Common reasons for seeking a lift include breasts that have lost shape and volume, nipples that point downward or fall below the breast crease, and asymmetry between the breasts. Women who have finished childbearing and breastfeeding and maintain a stable weight are typically the best candidates.
3. How does a breast lift differ from breast augmentation or reduction?
Breast lift surgery primarily addresses sagging by removing loose skin and tightening breast tissue to raise the breasts. Breast augmentation adds volume using implants, making breasts larger, while breast reduction removes breast tissue to decrease size. Often, breast lift is combined with augmentation or reduction to achieve both improved shape and desired size.
4. What are the different types of breast lift techniques and incisions?
The type of breast lift technique depends on the amount of sagging and the patient’s anatomy. The most common incision patterns include:
- Periareolar (around the nipple): Suitable for mild sagging, leaves minimal scarring around the areola.
- Lollipop (around the areola and vertical down to the breast crease): For moderate sagging, allows more skin removal.
- Anchor or inverted-T (around the areola, vertical down, and along the breast crease): Used for severe sagging or when extensive reshaping is needed, but results in more noticeable scarring.
5. What happens during breast lift surgery?
Breast lift surgery typically takes 2-3 hours under general anesthesia. The surgeon first marks the incision sites, then carefully removes excess skin and repositions the nipple and areola to a higher, more youthful location. Breast tissue is reshaped to improve firmness and contour. The incisions are closed with sutures, often layered to provide support. Sometimes drains are placed to remove excess fluid.
6. What is the recovery process like after a breast lift?
Immediately after surgery, patients experience swelling, bruising, and tenderness in the chest and breast area. Compression garments or surgical bras are recommended to reduce swelling and support healing. Most patients can return to light activities within 1-2 weeks but should avoid heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, and raising arms above shoulder level for 4-6 weeks. Full healing of scars and final breast shape can take several months.
7. Will breast lift surgery affect nipple sensation or the ability to breastfeed?
Some patients experience temporary numbness or heightened sensitivity of the nipples post-surgery, but sensation usually returns within a few months. The ability to breastfeed after a lift depends on the surgical technique used. Procedures that preserve the nipple’s blood supply and milk ducts increase the likelihood of successful breastfeeding. Discuss your breastfeeding plans with your surgeon beforehand.
8. What are the risks and potential complications of breast lift surgery?
While generally safe, breast lift surgery carries risks such as infection, bleeding, scarring, asymmetry, delayed wound healing, and changes in nipple sensation. Rare complications include loss of nipple or areola tissue due to compromised blood supply. Smoking, poor health, or inadequate post-op care can increase risks. Selecting a board-certified plastic surgeon and following pre- and post-operative instructions significantly reduces complications.
9. How long do the results of a breast lift last?
The results of a breast lift can last many years, particularly if you maintain a stable weight and avoid significant fluctuations. However, natural aging, gravity, pregnancy, and lifestyle factors may gradually affect breast shape and position. In some cases, patients may choose to have a secondary lift later in life to maintain desired results.
10. Can a breast lift be combined with other procedures?
Yes, breast lift surgery is often combined with other procedures to enhance overall body contour and aesthetics. Common combinations include breast augmentation (implant placement) to restore volume lost with sagging, breast reduction to alleviate discomfort while lifting, and liposuction to contour surrounding areas such as the armpits or chest wall. Combined procedures can often be performed safely in a single surgery with appropriate planning.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Breast Lift Surgery are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


