A Bone implants are an essential component of reconstructive surgery that helps restore bone integrity and function in patients suffering from bone loss, fractures, deformities, or defects. Bone tissue is vital not only for structural support and movement but also for protecting vital organs, producing blood cells, and storing minerals such as calcium and phosphorus.
In cases where bones are severely damaged due to trauma, disease, infection, or congenital abnormalities, natural healing might be insufficient or impossible. Bone implants offer a durable, biocompatible solution that supports regeneration, provides mechanical stability, and improves patients’ quality of life.
Over the last few decades, advancements in surgical techniques and biomaterial sciences have revolutionized bone implant technologies. From traditional autografts and allografts to state-of-the-art synthetic and bioengineered implants, there is now a wide range of options tailored to individual patient needs.This guide provides a detailed exploration of bone implants — from the causes that necessitate them, through symptoms and diagnosis, to the latest treatment options and long-term management strategies.
Bone implants are primarily required when the natural bone structure is compromised beyond the body’s ability to heal adequately. The causes can be categorized into traumatic, pathological, congenital, and surgical.
Traumatic Causes
- Severe fractures: High-energy impacts such as car accidents, falls from heights, or sports injuries can cause complex fractures where bones shatter into multiple pieces or large bone fragments are lost. In such cases, bone implants are necessary to reconstruct the defect and stabilize the skeleton.
- Crush injuries: These often cause extensive bone and soft tissue damage, resulting in segmental bone loss that requires reconstruction.
- Open fractures: When the broken bone pierces the skin, the risk of infection and bone necrosis is high, sometimes necessitating implants to replace infected or dead bone.
Pathological Causes
- Osteomyelitis (Bone Infection): Chronic bone infections can destroy large portions of bone tissue. Surgical removal of infected bone followed by implant placement helps restore function.
- Bone tumors: Benign or malignant bone tumors often require surgical excision of the affected bone. Bone implants fill the resultant defect.
- Osteoporosis: Severe osteoporosis causes fragile bones prone to fractures, sometimes requiring implants to stabilize bones or replace lost tissue.
- Metabolic Bone Disorders: Conditions such as Paget’s disease or rickets can weaken bones and create deformities needing reconstruction.
Congenital and Developmental Causes
- Congenital bone defects: Some patients are born with absent or malformed bones (e.g., cleft palate, limb deficiencies), necessitating implants to restore form and function.
- Growth abnormalities: Disorders affecting normal bone growth may require implant-assisted corrections.
Surgical Causes
- Bone resection surgeries: Removal of diseased or damaged bone segments during tumor excision or necrotic bone removal leaves defects that need implants.
- Revision surgeries: Failed prior implants or nonunion of fractures may require replacement or augmentation.
Risk Factors Increasing Need for Bone Implants
- Advanced age: Decreased bone density and slower healing.
- Smoking and alcohol: Impair blood supply and healing.
- Chronic illnesses: Diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, immune deficiencies.
- Malnutrition: Deficiency in calcium, vitamin D, and protein affects bone quality.
- Medications: Long-term corticosteroid use reduces bone formation.
- Previous radiation therapy: Damages bone vascularity.
Recognizing symptoms that may indicate severe bone damage or loss is crucial for timely intervention. Symptoms vary based on the underlying condition, bone involved, and extent of damage.
General Symptoms
- Severe or persistent bone pain: Pain localized to the affected bone, often worsening with movement or weight-bearing.
- Swelling and tenderness: Inflammatory response due to injury, infection, or tumor.
- Visible deformity or abnormal angulation: Misalignment or shortening of the affected limb or bone.
- Instability or inability to bear weight: Feeling that the bone or limb cannot support normal load.
- Limited range of motion: Especially around joints adjacent to damaged bones.
- Delayed healing or nonunion of fractures: Persistent pain and movement at the fracture site months after injury.
Symptoms of Specific Conditions Requiring Implants
- Osteomyelitis: Fever, redness, warmth, pus discharge from overlying skin.
- Bone tumors: Localized swelling, night pain, or systemic symptoms like weight loss.
- Dental bone loss: Loose teeth, difficulty chewing, jaw pain.
Determining the requirement for a bone implant involves a thorough assessment including clinical evaluation, imaging, and laboratory investigations.
Clinical Evaluation
- Detailed history focusing on trauma, symptoms duration, previous treatments.
- Physical exam assessing deformity, tenderness, range of motion, and signs of infection.
Imaging Modalities
- X-rays: Initial screening to identify fractures, bone loss, implant failure, or deformity.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Provides 3D reconstruction and precise assessment of complex fractures or bone defects.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Detects marrow involvement, soft tissue extension, or occult infections.
- Bone Scintigraphy: Useful for identifying bone infections or metastatic lesions.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): Measures bone density to evaluate osteoporosis risk.
Laboratory Tests
- Blood work: CBC, ESR, CRP for infection or inflammation.
- Microbiological cultures: In cases of suspected osteomyelitis.
- Biopsy: When malignancy or unclear lesions are present.
Treatment strategies for bone implants vary depending on the patient’s condition, location, size of bone defect, and overall health. The primary goal is to restore skeletal stability and enable bone healing.
Types of Bone Implants and Grafts
1. Autografts (Patient’s Own Bone):
- Gold standard due to osteogenic, osteoconductive, and osteoinductive properties.
- Common donor sites include iliac crest, fibula, and rib.
- Risks include donor site morbidity, increased surgical time, and pain.
2. Allografts (Donor Bone):
- Processed cadaveric bone used to fill large defects.
- Benefits include availability and no donor site complications.
- Risks involve slower integration and possible immune reaction.
3. Synthetic Bone Substitutes:
- Materials like hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, bioactive glass.
- Serve as osteoconductive scaffolds to promote new bone growth.
- Often used in combination with growth factors.
4. Metallic Implants:
- Titanium and stainless steel plates, rods, screws.
- Provide mechanical stability for fracture fixation and bone reconstruction.
5. Composite and Bioengineered Implants:
- Incorporate cells, growth factors, and scaffolds.
- Aim to enhance healing and reduce complications.
Surgical Techniques
- Internal Fixation: Plates, screws, and intramedullary nails used to align and stabilize bone segments.
- Bone Grafting and Reconstruction: Filling defects to facilitate new bone formation.
- 3D Printed Custom Implants: Designed from patient-specific imaging for complex defects, improving fit and functional outcomes.
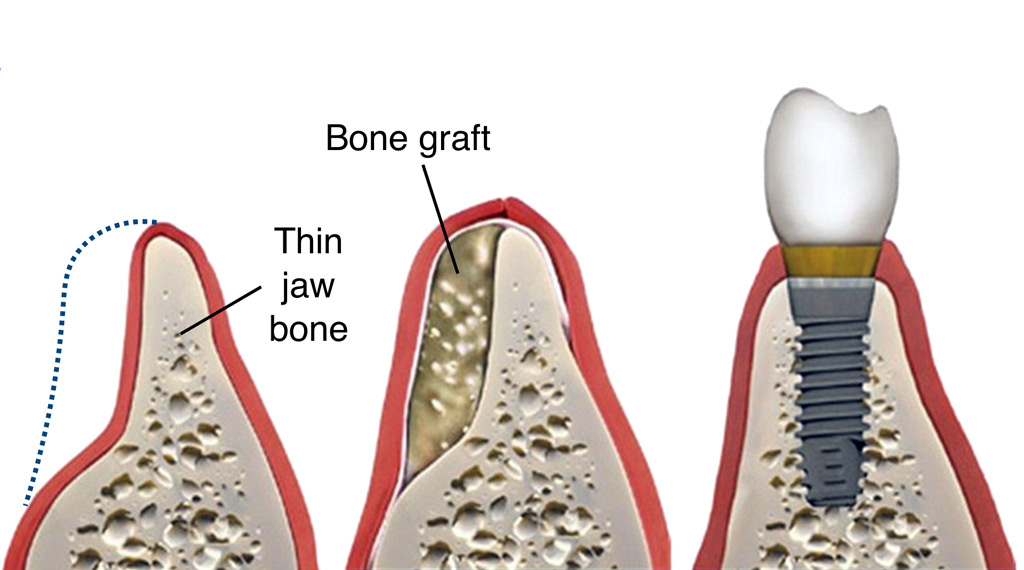
- Dental Implants: Titanium posts anchored in the jawbone to replace tooth roots.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
- Immobilization to allow initial healing.
- Pain control using NSAIDs, opioids if necessary.
- Early physiotherapy to restore strength and range of motion.
- Nutritional support with calcium, vitamin D, and protein supplements.
Prevention Strategies
- Optimal surgical techniques: Minimizing tissue trauma and ensuring sterile environments.
- Perioperative antibiotics: To reduce infection risk.
- Lifestyle modifications: Smoking cessation, balanced diet, and weight management.
- Bone health maintenance: Regular exercise, supplementation, and treatment of osteoporosis.
- Careful patient selection and implant choice: Based on individual risk profiles.
Management of Complications
- Infections: Require aggressive antibiotic therapy and sometimes implant removal.
- Nonunion or delayed healing: May need revision surgery, bone stimulators, or additional grafting.
- Implant loosening or failure: Revision with new implants or alternative fixation.
- Chronic pain management: Multimodal approaches including medications, physical therapy, and counseling.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Regular imaging and clinical evaluations to detect early issues.
Although bone implants are generally safe and effective, complications can occur, potentially affecting outcomes:
- Infection: The most common and serious complication, potentially leading to osteomyelitis and implant removal.
- Implant rejection or allergic reaction: Rare, but hypersensitivity to metals like nickel or titanium can occur.
- Mechanical failure: Loosening, bending, or breakage of implants due to stress or poor integration.
- Delayed union or nonunion: Failure of the bone to properly heal around the implant.
- Nerve and vascular injury: Damage during surgery leading to numbness, weakness, or bleeding.
- Chronic inflammation or pain: May persist despite successful surgery.
Adapting to life with a bone implant requires physical, emotional, and social adjustments.
Physical Adaptations
- Following rehabilitation protocols to regain function.
- Avoiding high-impact activities initially; gradual return to normal activities.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support bone health.
Psychological and Social Considerations
- Coping with changes in body image or function.
- Accessing support groups or counseling if needed.
- Understanding the importance of follow-up care to ensure implant longevity.
Long-term Follow-up
- Regular visits for X-rays and clinical assessment.
- Monitoring for late complications such as implant loosening or secondary fractures.
1. What is a bone implant, and how does it work?
A bone implant is a surgical device or material placed inside the body to repair, replace, or support damaged or missing bone tissue. These implants are designed to restore the structural integrity and functionality of bones affected by trauma, disease, or congenital defects. Bone implants may be used to fix fractures that won’t heal on their own, stabilize joints, or replace portions of bone lost to cancer or infection. The implant works by integrating with the surrounding bone tissue, providing mechanical support while the natural bone regenerates around it.
2. What are the most common reasons for needing a bone implant?
Bone implants are frequently required in several medical conditions:
- Complex or non-healing fractures (nonunions or malunions)
- Bone loss due to trauma, tumors, or infections like osteomyelitis
- Degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis needing joint replacements
- Spinal surgeries requiring fusion and stabilization
- Congenital bone deformities or defects
- Revision surgeries for previously failed implants or prosthetics
3. What materials are bone implants made from, and why?
Bone implants are crafted from materials that combine strength, biocompatibility, and durability:
- Titanium and titanium alloys: Popular for their strength, lightweight nature, and excellent compatibility with bone. They encourage bone growth around the implant (osseointegration).
- Stainless steel: Common in temporary implants like fracture fixation devices due to its toughness.
- Cobalt-chromium alloys: Used in joint replacements for wear resistance.
- Ceramics and bioactive glasses: Mimic natural bone mineral composition, often used as bone graft substitutes.
- Polymers: Sometimes used in combination with metals or ceramics for specific applications.
4. What does the bone implant surgery involve?
Bone implant surgery is typically done under general or regional anesthesia. The surgeon first exposes the affected bone area through an incision. Damaged bone or tissue is cleaned or removed if necessary. Then, the bone implant device is carefully positioned and fixed using screws, plates, or cement, depending on the implant type. The incision is closed with sutures or staples. The procedure’s duration varies from less than an hour for simple fractures to several hours for complex reconstructions.
5. How painful is the recovery from bone implant surgery, and what can I expect?
Pain after bone implant surgery varies by individual and procedure complexity. Patients usually experience soreness, swelling, and stiffness around the surgical site initially. Pain is managed with medications, including NSAIDs, opioids (short-term), and local anesthetics. Early physical therapy helps regain movement and strength, reducing long-term discomfort. Most patients see a significant reduction in pain once healing progresses and the implant stabilizes the bone.
6. How long does it take for the bone to heal with an implant in place?
Bone healing is a gradual process that can take several weeks to months:
- Initial healing phase (inflammatory and soft callus formation): 1-3 weeks
- Hard callus formation and remodeling: 6-12 weeks or longer
7. What are the potential risks and complications of bone implant surgery?
While bone implants have high success rates, complications can occur:
- Infection: At the surgical site or around the implant, requiring antibiotics or implant removal.
- Implant loosening or failure: Over time, implants can shift or break.
- Allergic reactions: Rare, but possible to implant materials.
- Nonunion or delayed union: Bone fails to heal adequately.
- Nerve or blood vessel injury: Caused during surgery.
- Blood clots: Deep vein thrombosis is a risk after surgery.
- Surgeons take steps to minimize risks, such as sterile techniques and post-operative care plans.
8. Can the body reject a bone implant?
Rejection of bone implants is uncommon because implant materials are chosen for biocompatibility. However, the body can sometimes react with inflammation or allergic responses, especially to metal ions released by corrosion or wear. Osteolysis, where bone around the implant deteriorates, can occur, especially with joint implants. Regular follow-up helps detect such issues early to prevent implant failure.
9. How should I care for my bone implant after surgery to ensure proper healing?
Post-operative care is critical for successful healing:
- Keep the surgical site clean and dry.
- Follow wound care instructions to prevent infection.
- Avoid weight-bearing or strain on the affected area as directed.
- Attend physical therapy to regain motion and strength safely.
- Take prescribed medications on schedule.
- Report any unusual symptoms like swelling, fever, or severe pain to your doctor immediately.
- Adhering to these guidelines maximizes the chances of implant success.
10. Can bone implants be replaced or removed if problems arise?
Yes. If a bone implant causes complications like infection, pain, or mechanical failure, revision surgery can remove or replace the implant. Advances in implant technology allow for easier revision procedures. In some cases, implants are removed once the bone fully heals and no longer requires internal support. Your surgeon will evaluate the implant’s condition during follow-ups to decide if intervention is necessary.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for a Bone Implant procedure are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.

