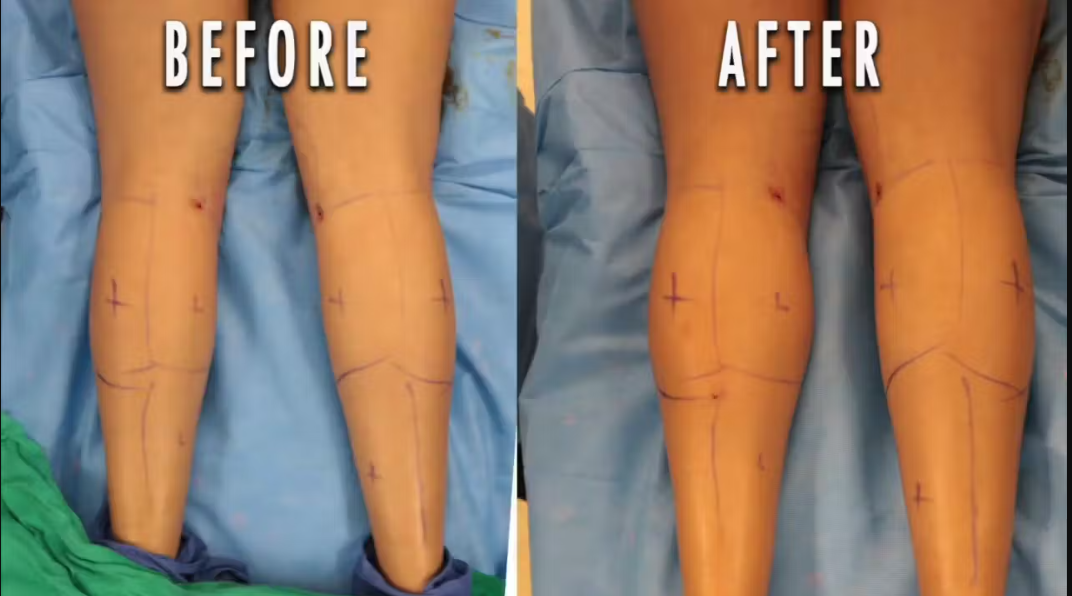
Calf augmentation is a specialized cosmetic surgical procedure designed to enhance the size, shape, and contour of the calves. This procedure is ideal for individuals who feel their calves are disproportionately small, underdeveloped, or asymmetrical due to genetics, muscle wasting, trauma, or age-related changes. Calf augmentation helps restore balance to the lower legs and improves overall body proportion and aesthetics.
Historically, concerns about calf size and shape have been addressed through exercise, but some individuals are unable to achieve their desired appearance due to factors beyond their control. With advancements in plastic surgery, calf augmentation now offers safe, reliable, and customizable solutions to these concerns, mainly through silicone implants or autologous fat transfer.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything from causes and risk factors to detailed treatment options, postoperative care, potential complications, and living with calf augmentation long-term.
Causes
-
Genetic Predisposition
Many people have naturally slim or underdeveloped calves. Genetics largely determine muscle size and fat distribution, making it difficult for some individuals to build calf muscle despite regular exercise. -
Muscle Atrophy Due to Injury or Disease
Conditions such as nerve injury, polio, muscular dystrophy, or peripheral neuropathy can cause significant wasting of the calf muscles. Trauma or surgeries involving the lower legs may also lead to calf atrophy and asymmetry. -
Congenital Deformities and Syndromes
Certain congenital conditions, such as Poland syndrome (characterized by absence or underdevelopment of muscles on one side of the body), can cause one calf to be underdeveloped. Clubfoot and other developmental anomalies can also alter calf muscle size. -
Age-Related Muscle Loss
Sarcopenia, the natural decline in muscle mass with aging, can lead to thinning and loss of muscle tone in the calves, making them appear smaller and less defined. -
Rapid or Significant Weight Loss
Weight loss can reduce both fat and muscle mass in the lower legs, leading to a deflated or disproportionate appearance. -
Body Proportion Imbalance
Some patients seek calf augmentation to improve body symmetry, especially when their upper legs or torso are muscular but calves appear disproportionately small. -
Post-Surgical or Post-Trauma Changes
Surgeries or injuries involving the lower leg that damage muscles or nerves can result in muscle volume loss and deformity.
Risk Factors
-
Smoking significantly impairs blood flow and delays wound healing.
-
Chronic illnesses, including diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and clotting disorders, increase risks of complications.
-
Poor skin quality or previous scarring may affect the surgical outcome.
-
Unrealistic expectations or psychological issues may affect satisfaction with the procedure.
-
High Body Mass Index (BMI) might increase surgical risks and affect contour results.
Calf augmentation is primarily pursued for aesthetic reasons rather than medical necessity. The following symptoms and signs typically motivate patients to consider the procedure:
-
Noticeably thin or flat calves that are out of proportion with the rest of the body.
-
Visible asymmetry where one calf is smaller or differently shaped than the other.
-
Muscle wasting or flattening due to injury, neurological conditions, or disuse.
-
Inability to increase calf size or shape despite regular physical exercise.
-
Self-consciousness and dissatisfaction with calf appearance affecting clothing choices and social confidence.
-
Rarely, functional impairment such as difficulty walking or instability due to muscle loss.
Medical History
-
Thorough collection of patient history focusing on:
-
Previous leg injuries or surgeries.
-
Neurological or muscular disorders.
-
Weight loss or gain history.
-
Lifestyle factors like exercise and smoking.
-
Any contraindications to surgery.
-
Physical Examination
-
Assessment of calf size, symmetry, muscle tone, and strength.
-
Skin quality evaluation including elasticity, thickness, and presence of scars.
-
Vascular and neurological assessment to ensure adequate blood flow and nerve function.
-
Measurement of calf circumference and photographic documentation for surgical planning.
Imaging Studies (If Necessary)
-
Ultrasound or MRI: For detailed evaluation of muscle and soft tissue, especially if previous trauma or disease is suspected.
-
X-rays: Occasionally needed to exclude bony abnormalities or deformities.
Psychological Evaluation
-
Assess patient’s motivation and expectations to confirm readiness for cosmetic surgery and avoid dissatisfaction.
Calf augmentation is performed using one or a combination of the following techniques:
1. Silicone Calf Implants
Overview:
Silicone implants specially designed to mimic the natural shape of the calf muscles are
surgically placed under the gastrocnemius muscle.
Surgical Procedure:
-
Incisions are usually made in the crease behind the knee or the calf crease to minimize visible scarring.
-
A pocket is carefully created beneath the calf muscle to house the implant without damaging nerves or blood vessels.
-
Implants come in various sizes and shapes, allowing customization based on patient anatomy and goals.
Advantages:
-
Immediate volume increase and long-lasting results.
-
Predictable and well-defined contour.
-
Suitable for patients with insufficient donor fat for fat grafting.
Recovery:
-
Moderate swelling and bruising for several weeks.
-
Light activity can resume in 1-2 weeks, with full recovery in 4-6 weeks.
Considerations:
-
Risk of implant displacement or capsular contracture.
-
Implants may feel firmer than natural muscle.
2. Autologous Fat Grafting (Fat Transfer)
Overview:
Fat is harvested via liposuction from donor areas such as the abdomen, thighs, or hips,
purified, and injected into the calves.
Advantages:
-
Uses the patient’s own tissue, avoiding foreign body reactions.
-
Dual benefit of contouring donor sites.
-
Creates a softer, more natural feel.
Limitations:
-
Volume gain per session is limited.
-
Fat resorption means some volume loss over time, often requiring multiple sessions.
-
Not suitable for patients with insufficient fat stores.
Recovery:
-
Shorter downtime compared to implants.
-
Mild swelling and bruising resolve over a few weeks.
3. Combination Approach
-
In some cases, implants are used for major volume enhancement, with fat grafting applied for refinement and improved contour softness.
4. Non-Surgical Methods (Limited)
-
Injectable fillers or muscle stimulators have minimal effectiveness and are not generally recommended for calf augmentation.
Preoperative Preparation
-
Stop smoking at least 4-6 weeks prior to surgery.
-
Manage underlying medical conditions for optimal health.
-
Maintain a healthy weight and balanced diet.
-
Discuss and set realistic expectations with your surgeon.
-
Engage in preoperative exercises to enhance circulation.
Postoperative Care
-
Wear compression stockings as recommended to reduce swelling and support tissues.
-
Keep legs elevated whenever possible during the initial recovery phase.
-
Avoid strenuous physical activities and prolonged standing for several weeks.
-
Follow wound care instructions strictly to prevent infection.
-
Attend all scheduled follow-up visits to monitor healing and intervene early if complications arise.
Although calf augmentation is generally safe, potential risks include:
-
Infection: May necessitate antibiotics or implant removal in severe cases.
-
Implant displacement or rotation: Causes contour irregularities and may require revision surgery.
-
Seroma or hematoma formation: Fluid or blood accumulation around the implant or graft site.
-
Nerve injury: Resulting in numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness.
-
Capsular contracture: Formation of tight scar tissue around implants, causing firmness or distortion.
-
Fat necrosis: Hard lumps or irregularities after fat grafting.
-
Visible or hypertrophic scarring: Though incisions are placed discreetly.
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Rare but serious risk of blood clots post-surgery.
-
Unsatisfactory aesthetic results: Asymmetry or unnatural appearance requiring revision.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
-
Initial swelling and discomfort typically subside within 2-3 weeks.
-
Gradual resumption of walking and leg exercises promotes circulation and muscle tone.
-
Patients should avoid heavy lifting or vigorous exercise for 4-6 weeks.
Long-Term Outcomes
-
Most patients enjoy a more balanced leg contour and enhanced confidence.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and balanced nutrition, is important to preserve results.
-
Implants may last many years but could require replacement or revision after 10-15 years.
-
Fat grafting results may fluctuate; some patients opt for additional treatments over time.
Psychological Benefits
-
Improved body image and self-esteem are common.
-
Support from counselors or support groups may be helpful for adjusting to new body
1. What is calf augmentation?
Calf augmentation is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to enhance the size, shape, and definition of the calves. This is commonly achieved through silicone implants or fat grafting to provide a more muscular and proportionate lower leg appearance.
2. Who is a good candidate for calf augmentation?
Good candidates are individuals with naturally thin or underdeveloped calves due to genetics, injury, or muscle loss. Candidates should be in good overall health, have realistic expectations, and want to improve their lower leg contour for aesthetic or reconstructive reasons.
3. What are the common methods used for calf augmentation?
The two main methods are:
- Calf Implants: Silicone implants surgically placed beneath the calf muscles.
- Fat Grafting: Fat is harvested from other areas of the body and injected into the calves to enhance volume.
4. How is the calf augmentation surgery performed?
The surgeon makes a small incision, usually behind the knee or in the natural crease, to insert the implants or inject fat. The procedure typically takes 1 to 2 hours and is performed under general or local anesthesia with sedation.
5. What is the recovery process like after calf augmentation?
Recovery involves rest, limited walking initially, and avoiding strenuous activities for several weeks. Swelling and bruising are common for the first 1-2 weeks. Most patients return to normal activities within 4 to 6 weeks.
6. Are there risks or complications associated with calf augmentation?
Risks include infection, bleeding, implant shifting, scarring, and nerve damage. Fat grafting carries risks of fat absorption or unevenness. Selecting a qualified surgeon and following postoperative instructions minimizes these risks.
7. Will calf augmentation scars be visible?
Incisions are typically small and placed in discreet locations like the back of the knee crease or behind the knee, making scars less noticeable. Proper scar care can help further reduce visibility.
8. How long do the results of calf augmentation last?
Results from calf implants are generally permanent, whereas fat grafting results depend on fat survival but can last several years with good care and stable weight.
9. Can calf augmentation be combined with other cosmetic procedures?
Yes, it can be combined with procedures like thigh lifts, liposuction, or overall body contouring to create balanced proportions and enhance overall leg aesthetics.
10. How should I prepare for calf augmentation surgery?
Preparation includes a thorough medical evaluation, stopping smoking several weeks before surgery, avoiding certain medications, and arranging for post-surgery care. Follow your surgeon’s detailed preoperative instructions closely.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Calf Augmentation are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



