Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open narrowed or blocked arteries that supply blood to the heart, also known as coronary arteries. This procedure is most commonly performed to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), which is caused by the buildup of plaque (fatty deposits) in the arteries. Angioplasty improves blood flow to the heart muscle, relieves symptoms such as chest pain (angina), and reduces the risk of heart attacks. In an angioplasty procedure, a balloon catheter is inserted into the blocked artery and inflated to widen the artery, thereby improving blood flow. In many cases, a stent (a small mesh tube) is placed to help keep the artery open after the procedure. Angioplasty can be performed in a catheterization lab (also called a cardiac catheterization lab or angiography suite). Angioplasty is a commonly performed procedure, with high success rates. It is often used in patients who have significant blockages in the coronary arteries but do not require open-heart surgery. It can also be used as a bridge to surgery in patients who are not suitable candidates for coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
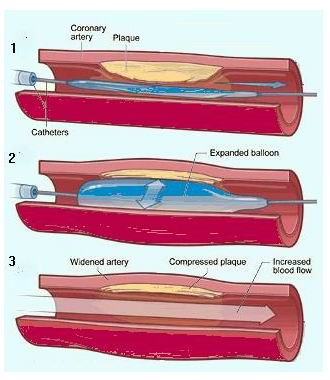
The primary cause of the need for angioplasty is coronary artery disease (CAD), which occurs when plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. There are several factors that contribute to this process:
-
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of coronary artery disease. It occurs when cholesterol and fatty deposits accumulate in the arteries, causing them to harden and narrow. This reduces the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart. -
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
High blood pressure can damage the arteries over time, making them more prone to plaque buildup and narrowing. Elevated blood pressure puts extra stress on the heart and can accelerate the development of coronary artery disease. -
High Cholesterol
High levels of LDL cholesterol (often referred to as "bad cholesterol") can lead to plaque formation in the arteries. This increases the risk of blockages and narrowing, which may require angioplasty. -
Diabetes
People with diabetes are more prone to developing coronary artery disease. High blood sugar levels contribute to plaque buildup, inflammation in the arteries, and overall heart dysfunction. -
Smoking
Smoking accelerates the process of atherosclerosis and increases the risk of heart disease by causing inflammation in the arteries, increasing blood pressure, and reducing levels of good cholesterol (HDL). -
Obesity
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes—all of which are risk factors for coronary artery disease. -
Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity contributes to heart disease by leading to poor circulation, higher cholesterol levels, and weight gain. -
Family History
A family history of heart disease can increase the risk of developing coronary artery disease. Genetic factors play a role in plaque buildup and other cardiovascular issues.
Angioplasty is typically performed when patients experience significant symptoms due to coronary artery disease or when diagnostic tests reveal narrowed or blocked arteries. Common symptoms that may require angioplasty include:
-
Chest Pain (Angina)
Angina is a common symptom of coronary artery disease, where the heart muscle is not getting enough oxygenated blood. Angina may present as a crushing or tightness in the chest, and it may be triggered by physical activity or emotional stress. -
Shortness of Breath
Difficulty breathing or feeling winded, especially during physical exertion, is a common symptom when the heart is not able to pump oxygenated blood efficiently due to blocked arteries. -
Fatigue
Unexplained tiredness or fatigue, especially during physical activity, can occur when the heart cannot supply enough oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues. -
Dizziness or Fainting
Blockages in the coronary arteries can reduce blood flow to the brain, causing dizziness or fainting (syncope). -
Swelling in the Legs or Abdomen
Poor circulation due to blocked arteries can cause fluid retention, resulting in swelling in the lower extremities (legs and feet) or the abdomen. -
Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
If a coronary artery becomes completely blocked, it can cause a heart attack. Symptoms of a heart attack may include severe chest pain, pain radiating to the left arm, sweating, nausea, and shortness of breath.
To diagnose coronary artery disease and determine if angioplasty is appropriate, several diagnostic tests may be used:
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart. It can detect abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and signs of a previous heart attack or ischemia (lack of blood flow). -
Stress Test
A stress test involves monitoring the heart’s function while the patient is engaged in physical activity or stimulated with medication. It helps doctors assess how well the heart responds to exertion and whether there is reduced blood flow to the heart. -
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart’s structure and function. It can help assess how well the heart is pumping blood and check for any areas affected by coronary artery disease. -
Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography is the gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease. It involves inserting a catheter into the coronary arteries and injecting a contrast dye to make the arteries visible on X-ray images. This allows doctors to visualize any blockages or narrowings in the arteries. -
Cardiac CT or MRI
A CT angiogram or cardiac MRI can provide detailed images of the heart and blood vessels, helping to assess the extent of any blockages and guide treatment planning.
When a coronary artery is narrowed or blocked, angioplasty may be recommended to restore normal blood flow. Treatment options include:
-
Balloon Angioplasty
During balloon angioplasty, a catheter with a small balloon at the tip is inserted into the blocked artery. The balloon is inflated at the site of the blockage to compress the plaque and widen the artery. This helps restore blood flow. -
Stent Placement
In most cases, a stent is placed in the artery during or after angioplasty. A stent is a small mesh tube that acts as a scaffold to keep the artery open and prevent it from narrowing again. Drug-eluting stents (DES) are coated with medication that helps prevent new blockages. -
Atherectomy
Atherectomy is a procedure used to remove plaque from the artery walls. A catheter with a rotating blade or laser is used to shave or vaporize the plaque, which is then removed or broken up into small pieces. -
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG)
If the blockages are severe or widespread, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be recommended. CABG involves bypassing the blocked arteries using grafts from other blood vessels, ensuring that blood can flow freely to the heart. -
Medications
After angioplasty, patients may be prescribed medications to help manage their heart health. These may include antiplatelets to prevent blood clots, cholesterol-lowering medications, and beta-blockers to reduce heart strain.
Although angioplasty can treat blockages, lifestyle changes and proper management of risk factors are essential to prevent further issues. Key preventive measures include:
-
Healthy Diet
A low-fat, high-fiber diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce cholesterol levels and prevent plaque buildup. -
Exercise
Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, improves circulation, and reduces the risk of further arterial blockages. -
Blood Pressure Control
Managing high blood pressure through medication, dietary changes, and exercise is crucial to reduce the strain on the heart and arteries. -
Cholesterol Management
Lowering LDL cholesterol through diet, medications (like statins), and exercise helps reduce the risk of future blockages. -
Quitting Smoking
Smoking cessation is one of the most important lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and further heart disease. -
Diabetes Management
Proper management of blood sugar is essential to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in people with diabetes.
While angioplasty is generally safe and effective, there are some risks and potential complications, including:
-
Re-narrowing of the Artery (Restenosis)
In some cases, the artery may narrow again after angioplasty. The use of drug-eluting stents can reduce the risk of restenosis. -
Blood Clots
Blood clots can form in the artery or stent, which may lead to a heart attack or stroke. Blood-thinning medications are often prescribed to reduce this risk. -
Arrhythmias
Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) may develop during or after angioplasty. In most cases, these arrhythmias are temporary and can be managed with medications or electrical therapy. -
Infection
In rare cases, an infection may occur at the catheter insertion site or within the heart, requiring antibiotics or additional intervention.
After angioplasty, most patients can return to normal activities with improved quality of life. However, ongoing care is necessary to maintain heart health:
-
Regular Follow-up Visits
After angioplasty, patients should have regular follow-up visits with their cardiologist to monitor heart function and manage medications. -
Physical Activity and Rehabilitation
Participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program can help patients recover fully, improve heart function, and reduce the risk of future heart problems. -
Medication Adherence
It is essential for patients to take prescribed medications, such as blood pressure-lowering drugs, cholesterol medications, and antiplatelets, to manage heart health and prevent complications. -
Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through dietary changes, exercise, and stress management plays a crucial role in preventing further heart problems.
The other major cardiac procedures are:
| 1. Heart Valve Replacement |
| 2. Abdominal or Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery |
| 3. VSD (Ventricular Septal Defect) Closures etc |
Popular hospitals for Angioplasty are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals for Coronary Angioplasty | Doctors for Coronary Angioplasty | Cost of Coronary Angioplasty | Treatment Coronary Angioplasty | Destinations for Coronary Angioplasty | Coronary Angioplasty in India | Coronary Angioplasty in Thailand | Coronary Angioplasty in Malaysia | Coronary Angioplasty Information | Recovery Coronary Angioplasty | Coronary Angioplasty in Singapore | Coronary Angioplasty Argentina | Coronary artery | PTCA | Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary angioplasty | Cad | angina | shortness of breath | heart attack | cardiac arrest | blockage | cardiac catheterization | catheter | angiogram | atheroma | plaque | coronary blockage | cardiac procedures done in Thailand | heart surgeons in Malaysia | Coronary Angioplasty overseas treatment | Coronary Angioplasty abroad | Coronary Angioplasty at low cost
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


