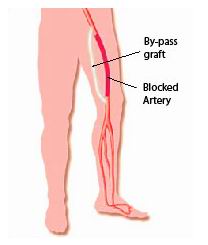
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) occurs when the arteries in the legs or other extremities become narrowed or blocked, often due to a buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis). This condition reduces blood flow to the limbs, leading to pain, cramping, and even more serious complications, such as ulcers or tissue death. Peripheral bypass surgery is a common treatment option for patients with severe PAD. The goal of this surgery is to reroute blood flow around the blocked arteries using a graft, restoring blood supply to the affected limb and preventing further complications, including the need for amputation. The procedure involves placing a graft—either from a vein in the patient’s body or a synthetic material—into the leg to bypass the blocked or narrowed artery. This allows blood to flow freely again and can significantly reduce symptoms like pain and leg weakness, while also improving overall quality of life.
The primary cause of PAD is atherosclerosis, where fatty plaque builds up inside the arteries, causing them to narrow and harden. However, several other conditions and lifestyle factors can increase the risk of developing PAD and its complications.
Common Causes:
-
Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the arteries, typically caused by a combination of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and other lifestyle factors.
-
Blood clots (thrombosis): A clot can block the blood vessels, leading to sudden loss of blood flow.
-
Vasculitis: Inflammation of the blood vessels can lead to narrowing or blockage of the arteries.
-
Diabetes: Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels, increasing the risk of PAD.
-
Chronic kidney disease (CKD): Poor kidney function is often associated with PAD.
Risk Factors for PAD:
-
Age: PAD risk increases with age, particularly for individuals over 50.
-
Smoking: Smoking is one of the leading causes of PAD and accelerates the progression of the disease.
-
High blood pressure (hypertension): Consistently elevated blood pressure damages the walls of blood vessels and can cause PAD.
-
High cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
-
Obesity: Excess weight puts strain on the heart and vascular system.
-
Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise and physical activity increase the risk of developing PAD.
-
Family history: A family history of heart disease or PAD increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
Managing these risk factors through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular medical checkups can help reduce the risk of developing PAD or slow its progression.
In its early stages, PAD may not cause noticeable symptoms, but as the disease progresses, it can lead to several key signs and symptoms. Recognizing these early symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and preventing further complications.
Common Symptoms of PAD:
-
Intermittent claudication: Pain or cramping in the legs or thighs during physical activity (e.g., walking or climbing stairs), which improves with rest.
-
Leg weakness: Difficulty walking or standing for long periods due to reduced circulation.
-
Numbness or coldness: The affected limb may feel cold to the touch or experience numbness due to poor blood flow.
-
Slow-healing wounds or ulcers: Open sores on the legs or feet that do not heal properly, due to lack of blood supply.
-
Shiny or discolored skin: The skin of the affected leg may appear shiny, thin, or pale because of poor circulation.
-
Rest pain: A more severe form of PAD that causes pain in the legs, even at rest, especially at night when lying down.
-
Hair loss on the legs: A reduction in circulation to the lower limbs can cause hair to stop growing in affected areas.
If any of these symptoms are present, it is important to seek medical advice to prevent the disease from advancing and to discuss potential treatment options like peripheral bypass surgery.
To accurately diagnose PAD and assess the extent of arterial blockage, a variety of diagnostic tests are used. These tests help doctors determine the severity of the condition and whether surgery is necessary.
Key Diagnostic Tests:
-
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): A non-invasive test that compares the blood pressure in the ankle with the blood pressure in the arm. A lower ABI score suggests the presence of PAD.
-
Ultrasound (Doppler Study): An imaging technique that uses sound waves to visualize blood vessels and check for blockages or narrowing.
-
Angiography (CT or MR Angiography): Detailed imaging tests that provide a clear picture of the arteries and identify areas of restriction or blockage.
-
Arteriography: A more invasive test in which a contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream to help visualize blockages on X-rays.
-
Blood tests: To check for underlying conditions such as high cholesterol, diabetes, or inflammation that may contribute to PAD.
These diagnostic procedures are crucial in determining the most appropriate course of treatment, including whether peripheral bypass surgery is needed.
The treatment of PAD depends on the severity of the disease. While lifestyle changes and medications are the first line of defense, in some cases, surgical intervention is necessary to improve blood flow and alleviate symptoms.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options:
-
Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, smoking cessation, and dietary changes can help improve circulation and slow the progression of PAD.
-
Medications: Drugs like antiplatelet medications (aspirin or clopidogrel) can help prevent blood clots, while statins may be prescribed to reduce cholesterol levels and prevent further plaque buildup.
-
Angioplasty and Stenting: In cases where arteries are narrowed but not fully blocked, angioplasty (using a balloon to widen the artery) and stenting (inserting a mesh tube to keep the artery open) can help improve blood flow.
Surgical Treatment:
When the above treatments are not effective, peripheral bypass surgery is the most common procedure used to bypass blocked arteries and restore blood flow to the affected limb.
-
Peripheral Bypass Surgery: A graft (usually taken from the patient’s own vein or a synthetic material) is used to bypass the blocked artery, creating a new pathway for blood flow. This surgery is typically recommended for patients with severe PAD or those who have not responded to other treatments.
Preventing PAD involves managing risk factors and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. While PAD is a progressive disease, early intervention and regular monitoring can significantly improve outcomes.
Prevention Tips:
-
Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days to improve circulation.
-
Eat a healthy diet: Follow a diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, and high in fiber and antioxidants.
-
Quit smoking: Smoking is one of the leading causes of PAD, and quitting can dramatically reduce the risk of disease progression.
-
Manage underlying conditions: Keep blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar under control through medications, diet, and lifestyle changes.
-
Regular check-ups: If you have risk factors for PAD, schedule regular visits with your healthcare provider to monitor the health of your arteries.
Post-Surgery Care:
After peripheral bypass surgery, patients must follow specific guidelines to ensure proper healing and avoid complications:
-
Take prescribed medications, such as antiplatelets or statins.
-
Participate in physical therapy to strengthen the muscles and improve circulation.
-
Attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor the success of the bypass and check for complications like graft failure or restenosis (narrowing of the artery).
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with peripheral bypass surgery. However, most complications can be minimized with careful surgical technique and post-operative care.
Possible Complications:
-
Infection: Surgical site infections are possible, and it is crucial to follow wound care instructions.
-
Graft failure: The bypass graft can become blocked or narrowed over time, requiring further intervention.
-
Blood clots: There is a risk of developing clots in the new graft or elsewhere in the body.
-
Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery may require medical intervention.
-
Restenosis: The recurrence of arterial narrowing may necessitate additional procedures.
For patients with peripheral artery disease, both before and after surgery, managing lifestyle factors and adhering to medical recommendations is crucial to long-term success. Post-Surgery Life: Most patients can return to normal activities after recovery, though it is important to avoid heavy physical strain initially. Continued monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol, and overall cardiovascular health is necessary to prevent further complications. With proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, patients can manage PAD effectively and enjoy improved mobility and quality of life.
The other major cardiac procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Peripheral Bypass Surgery are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Peripheral Arterial Disease | Pad | Peripheral Vascular Bypass | Lower Extremity Bypass | Plaque | Fatty Deposits | Graft | Saphenous Vein | Autogenous Graft | Synthetic Graft | Angioplasty | Bypass Surgery | Aortobifemoral Bypass | Iliac Arteries | Aorta | Femoropopliteal Bypass | Fempop Bypass | Femoral-Tibial Bypass | Atherosclerosis | Triglycerides | Hypertension | Hospitals Peripheral Bypass Surgery | Doctors Peripheral Bypass Surgery | Surgery Peripheral Bypass Surgery | Cost Peripheral Bypass Surgery | Treatment Peripheral Bypass Surgery | Destinations Peripheral Bypass Surgery | Peripheral Bypass Surgery India | Peripheral Bypass Surgery Recovery | Peripheral Bypass Surgeryinformation | Peripheral Bypass Surgery Thailand | Peripheral Bypass Surgery Malaysia | Peripheral Bypass Surgery Abroad | Peripheral Bypass Surgery Overseas | Peripheral Bypass Surgery Low Cost
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


