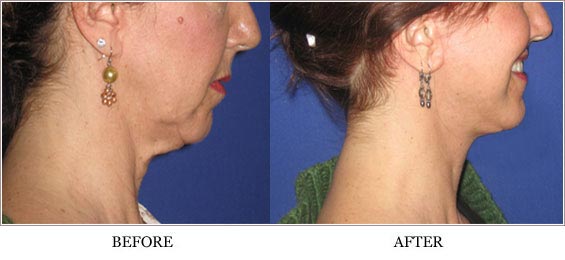
Platysmaplasty is an advanced cosmetic surgical procedure that specifically targets the platysma muscle of the neck to correct sagging, vertical banding, and loss of youthful contour. The platysma is a thin, superficial muscle spanning from the chest and shoulder region to the lower jaw. Over time, due to aging, genetics, weight fluctuations, and environmental factors, this muscle can weaken and separate, causing vertical bands or "turkey neck" appearance, contributing to an aged and fatigued look.
While many patients seek general facial rejuvenation, platysmaplasty is unique in directly addressing the structural cause of neck laxity. Often performed in conjunction with facelifts or submental liposuction, this procedure restores a smoother jawline, tightens muscle tone, and removes excess skin and fat, creating a balanced, youthful profile.
Platysmaplasty requires precise anatomical understanding and surgical skill to safely reposition and suture the muscle while minimizing scarring and complications. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of platysmaplasty—from causes and risk factors to recovery and long-term management.
Causes of Neck Aging and Platysma Muscle Laxity
-
Intrinsic Aging: The primary cause of platysma bands is age-related decline in collagen and elastin production, leading to skin sagging and muscle laxity.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Family history of early neck aging or prominent platysma bands often influences timing and severity.
-
Weight Fluctuations: Significant gain or loss of weight stretches skin and weakens muscle support.
-
Sun Exposure: Chronic UV exposure accelerates dermal collagen degradation.
-
Posture: Forward head posture places continuous strain on neck muscles, accelerating sagging.
-
Smoking: Nicotine decreases tissue perfusion and collagen synthesis.
-
Other Factors: Hormonal changes, dehydration, and poor nutrition may contribute.
Risk Factors Impacting Surgical Outcomes
-
Age and Skin Quality: Patients with good skin elasticity fare better postoperatively.
-
Degree of Muscle Separation: Severe platysma diastasis may require more extensive intervention.
-
Overall Health: Comorbidities like diabetes or vascular disease increase complication risk.
-
Previous Neck Surgery or Radiation: Scar tissue complicates dissection and healing.
-
Smoking and Lifestyle Habits: Affect healing and long-term results.
-
Visible Vertical Bands: Noticeable cord-like muscle bands in the anterior neck, particularly when talking or swallowing.
-
Loose or Sagging Skin: Excess neck skin creating folds or jowling.
-
Blurring of Jawline: Loss of crisp jaw contour and definition.
-
Submental Fullness: Fat accumulation causing a “double chin” appearance.
-
Patient Complaints: Aged, tired, or heavy neck appearance leading to self-consciousness.
-
Physical Exam Findings: Palpable platysma bands, skin laxity, fat deposits, and degree of muscle separation.
Clinical Evaluation
-
Detailed history exploring onset and progression of neck aging, prior cosmetic procedures, lifestyle factors.
-
Physical examination includes inspection and palpation of platysma muscle bands, skin elasticity testing, and assessment of neck fat volume.
-
Photographic documentation to guide surgical planning.
-
Evaluation of neck skin redundancy and cervical spine posture.
Imaging and Ancillary Tests
-
Usually not required for straightforward cases.
-
Ultrasound may be used to evaluate fat thickness and muscle anatomy.
-
Nerve conduction studies in rare cases if muscle function is compromised.
Surgical Procedures
-
Direct Platysma Plication: Suturing the separated muscle edges to recreate a tight, supportive sheet, eliminating vertical bands.
-
Submental Approach: Small incision under the chin allows muscle tightening and fat removal via liposuction.
-
Extended Neck Lift: Combines skin excision and muscle tightening with facelift techniques for comprehensive rejuvenation.
-
Liposuction: Targeted removal of submental fat to enhance contour.
-
Platysmal Band Transection: In select cases, selective muscle division combined with plication for optimal contour.
-
Botulinum Toxin: Temporary relaxation of platysma bands; adjunctive but not definitive treatment.
Non-Surgical Adjuncts
-
Ultrasound Therapy (Ultherapy): Stimulates collagen for mild skin tightening.
-
Radiofrequency Treatments: Improve skin laxity but do not address muscle.
-
Injectables: Fillers can improve jawline definition but cannot correct muscle laxity.
Prevention Strategies
-
Maintain stable healthy weight.
-
Avoid smoking and minimize sun exposure.
-
Regular hydration and balanced nutrition.
-
Maintain good posture to reduce neck muscle strain.
-
Early skin care with antioxidants and retinoids.
Preoperative Management
-
Thorough medical evaluation and optimization of chronic conditions.
-
Smoking cessation at least 4 weeks prior.
-
Psychological counseling to set realistic expectations.
-
Pre-surgical imaging or testing as indicated.
Postoperative Care
-
Use of neck compression garment for 1-2 weeks.
-
Pain control with prescribed medications.
-
Avoid strenuous neck movements and heavy lifting for 4-6 weeks.
-
Follow-up visits to monitor wound healing, scar management, and muscle function.
Common Mild Side Effects
-
Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort.
-
Temporary numbness or tingling.
-
Minor scarring, usually hidden under the chin or behind ears.
Potential Serious Complications
-
Hematoma requiring drainage.
-
Infection necessitating antibiotics.
-
Injury to marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve causing temporary asymmetry.
-
Skin necrosis or poor wound healing.
-
Unsatisfactory cosmetic outcome with persistent bands or laxity.
-
Scar hypertrophy or keloid formation.
Risk Reduction
-
Performed by board-certified plastic surgeons with detailed anatomical knowledge.
-
Strict sterile surgical technique.
-
Patient adherence to postoperative instructions.
-
Early detection and management of complications.
Recovery Process
-
Most patients experience noticeable improvement within 2-3 weeks as swelling resolves.
-
Final muscle tone and neck contour established over 3-6 months.
-
Return to normal activities typically within 1-2 weeks, with gradual resumption of strenuous activities.
Psychological Impact
-
Significant enhancement of self-esteem and confidence due to youthful neck appearance.
-
Increased satisfaction with facial profile and overall aesthetic harmony.
Long-Term Maintenance
-
Continued sun protection and skin care.
-
Healthy lifestyle to maintain weight and skin quality.
-
Periodic skin tightening treatments as needed.
-
Regular follow-up with surgeon for assessment.
1. What is platysmaplasty?
Platysmaplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at tightening and repairing the platysma muscles in the neck to reduce sagging skin, improve neck contour, and diminish the appearance of neck bands.
2. Who is a good candidate for platysmaplasty?
Ideal candidates are adults experiencing neck skin laxity, muscle banding, or a "turkey wattle" appearance, often due to aging or significant weight loss. Candidates should be in good health and have realistic expectations.
3. How is platysmaplasty performed?
The surgeon makes small incisions under the chin and/or behind the ears to access the platysma muscles, which are then tightened with sutures. Excess skin may be removed for enhanced contouring.
4. What is the recovery time after platysmaplasty?
Recovery usually takes 1 to 2 weeks for most swelling and bruising to subside. Patients may need to wear a compression garment and should avoid strenuous activity for several weeks.
5. Are there risks or complications associated with platysmaplasty?
Risks include infection, bleeding, nerve injury, asymmetry, scarring, and dissatisfaction with results. Choosing a board-certified surgeon helps minimize these risks.
6. Will platysmaplasty improve both muscle tone and skin tightness?
Yes, platysmaplasty specifically targets muscle laxity, but is often combined with skin tightening procedures like a neck lift for comprehensive rejuvenation.
7. How long do the results last?
Results can last for many years, often 7 to 10 years, depending on factors like aging and lifestyle.
8. Can platysmaplasty be combined with other procedures?
Yes, it is frequently combined with facelift, neck lift, or liposuction to achieve more balanced facial and neck rejuvenation.
9. Will there be visible scars after surgery?
Incisions are typically placed in inconspicuous areas, such as under the chin and behind the ears, minimizing visible scarring.
10. How much does platysmaplasty cost?
Costs vary based on surgeon, location, and procedure complexity but generally range from several thousand to over ten thousand dollars. The procedure is usually cosmetic and not covered by insurance.
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


