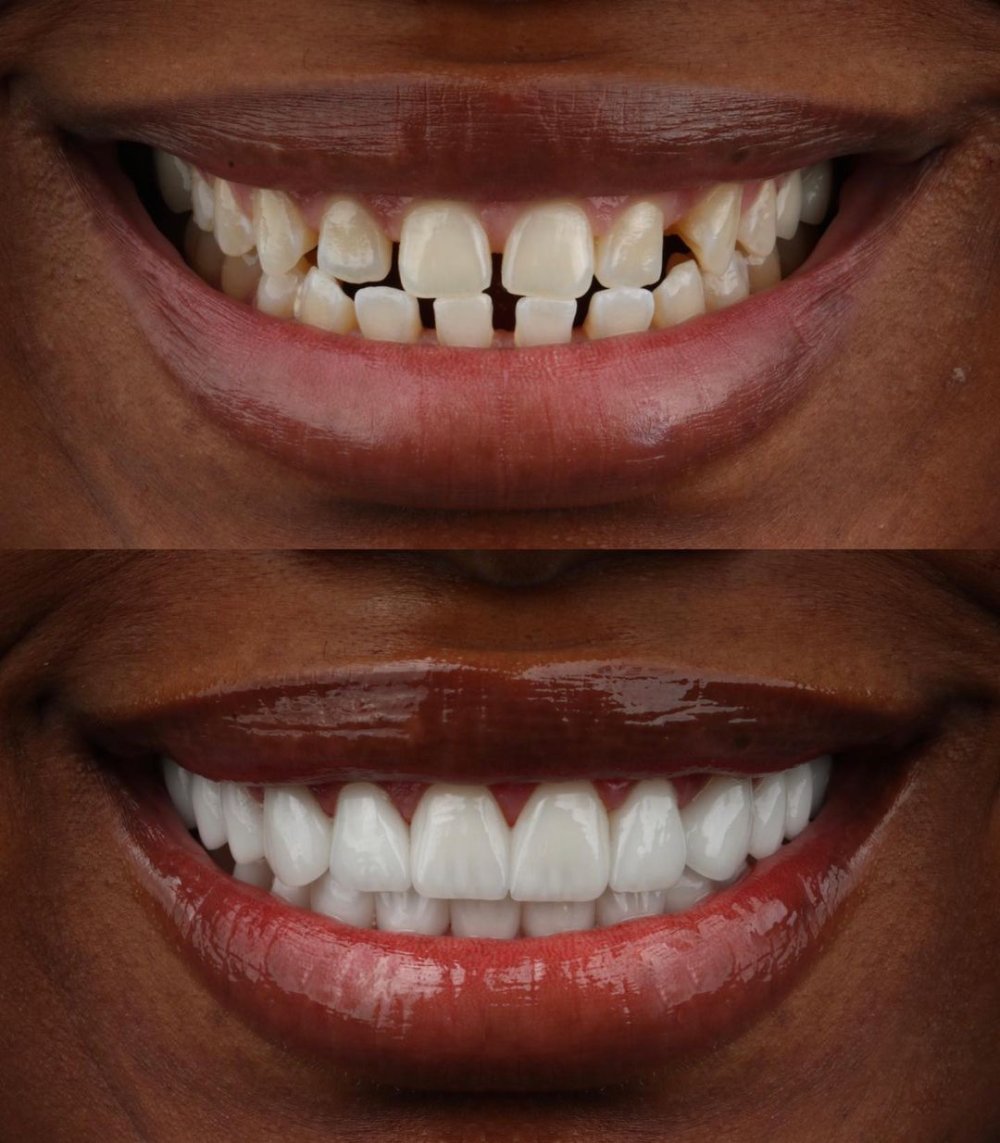
A captivating smile can transform your life—boosting confidence, improving social interactions, and contributing to overall well-being. However, many people face cosmetic dental challenges such as stained, chipped, uneven, or misshapen teeth that affect their smile aesthetics. Composite veneers provide an excellent minimally invasive option to address these issues with immediate results and less tooth preparation compared to traditional porcelain veneers.
Composite veneers are thin layers of tooth-colored resin applied directly to the teeth’s front surface. This resin is sculpted and hardened in the dentist’s office to reshape, cover imperfections, and create a harmonious, natural-looking smile. Due to advances in bonding agents and composite materials, modern composite veneers exhibit impressive durability, color stability, and aesthetic quality.
This article offers an in-depth overview of composite veneers—covering causes and risk factors prompting treatment, clinical signs, diagnostic techniques, treatment procedures, prevention and maintenance strategies, potential complications, and how to live well with your new veneers.
What Drives Patients to Composite Veneers?
-
Tooth Discoloration Resistant to Whitening: Intrinsic stains caused by antibiotics (tetracycline), fluorosis, trauma, or aging often cannot be removed by bleaching alone.
-
Minor Tooth Damage: Chips, cracks, or worn edges detract from smile aesthetics.
-
Gaps and Uneven Spacing: Diastemas between teeth can be closed quickly with composite veneers.
-
Irregular or Uneven Tooth Shape: Teeth that are asymmetrical, pointed, or too small.
-
Mild Malalignment: Slightly crooked or rotated teeth without severe crowding.
-
Enamel Erosion or Abrasion: From acid reflux, diet, or bruxism.
-
Aesthetic Replacement of Old Restorations: Stained or mismatched fillings.
Key Risk Factors
-
Lifestyle Habits: Smoking, heavy coffee, tea, or wine consumption lead to staining.
-
Parafunctional Habits: Teeth grinding causing wear and chips.
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Promoting decay and discoloration.
-
Dental Trauma: Past injuries affecting enamel integrity.
-
Genetics: Natural variations in enamel thickness and tooth shape.
-
Persistent Tooth Discoloration not resolved by whitening treatments.
-
Teeth showing small chips, cracks, or rough edges.
-
Visible gaps or uneven spacing between anterior teeth.
-
Teeth appearing uneven, short, or misshapen.
-
Mildly crooked or rotated teeth without severe orthodontic need.
-
Dissatisfaction with smile aesthetics due to shape or color.
-
Desire for immediate aesthetic enhancement without extensive treatment.
Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation
-
Comprehensive examination of teeth and gums to ensure health and suitability.
-
Assessment of occlusion (bite) to ensure veneers won’t interfere with function.
-
Checking for tooth decay or periodontal disease to treat before veneers.
-
Evaluation of enamel thickness critical for bonding success.
-
Digital photographs for smile analysis.
-
X-rays or 3D scans to assess roots and surrounding bone.
Digital Smile Design and Planning
-
Computer-aided simulation helps patients visualize potential outcomes.
-
Collaboration between dentist and patient to finalize aesthetics and function.
-
Planning restoration size, shape, and color to suit facial features.
Step 1: Initial Preparation
-
Minimal or no tooth reduction necessary; teeth cleaned and lightly roughened.
-
Local anesthesia rarely required due to non-invasive nature.
Step 2: Shade Matching
-
Selecting resin color to harmonize with natural dentition or desired brightness.
Step 3: Application of Composite Resin
-
Composite resin applied in layers, sculpted carefully to shape and contour teeth.
-
Each layer hardened with a curing light for durability.
Step 4: Finishing and Polishing
-
Polishing to mimic the natural enamel’s smoothness and shine.
-
Final adjustments ensure proper bite and comfort.
Advantages of Composite Veneers
-
Single-visit completion providing immediate results.
-
Cost-effective compared to porcelain veneers.
-
Easily repairable in case of chips or discoloration.
-
Reversible or adjustable compared to permanent enamel removal in porcelain veneers.
Complementary Treatments
-
Pre-treatment teeth whitening enhances final aesthetics.
-
Minor orthodontic treatment in some cases for optimal alignment.
Oral Hygiene Protocols
-
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush with non-abrasive fluoride toothpaste.
-
Daily flossing or interdental cleaning to prevent plaque build-up.
-
Use antibacterial mouth rinses if recommended.
Lifestyle Modifications
-
Avoid smoking and limit intake of staining foods and drinks.
-
Use a straw for acidic or pigmented beverages.
-
Nightguard use to protect veneers from bruxism-related damage.
Regular Dental Care
-
Professional cleanings and checkups every 6 months to maintain veneer health.
-
Early intervention if any veneer damage or gum issues develop.
Common Challenges
-
Surface Staining: Composite resin may discolor over time and require polishing or replacement.
-
Chipping and Wear: Less resistant than porcelain; avoid hard biting forces.
-
Sensitivity: Mild post-procedure sensitivity, usually temporary.
-
Debonding: Occasionally veneers may loosen and need rebonding.
-
Marginal Discoloration: Gum line stains if oral hygiene lapses.
Rare Complications
-
Allergic reactions (extremely rare).
-
Gum recession or inflammation if veneers improperly placed.
Management
-
Prompt dental visits for repairs or maintenance.
-
Professional polishing and cleaning to maintain appearance.
Longevity and Durability
-
Composite veneers typically last 5-7 years, sometimes longer with excellent care.
-
Repairs are simpler and less costly than replacing porcelain veneers.
Psychological Benefits
-
Enhanced smile aesthetics often lead to improved self-confidence.
-
Greater willingness to engage socially and professionally.
Long-Term Care Recommendations
-
Maintain excellent hygiene and avoid damaging habits.
-
Regular dental visits for maintenance.
-
Awareness of any new symptoms such as sensitivity or veneer damage.
1. What are composite veneers?
Answer: Composite veneers are thin, tooth-colored resin layers applied directly to the front surfaces of teeth to enhance their appearance. They are a conservative and cost-effective cosmetic dentistry option to correct imperfections like chips, gaps, discoloration, and minor misalignment.
2. Who is an ideal candidate for composite veneers?
Answer: Ideal candidates have healthy teeth and gums but want to improve the look of their smile due to minor dental flaws. Composite veneers are suitable for patients seeking a less invasive and quicker alternative to porcelain veneers.
3. How is the composite veneer procedure performed?
Answer: The dentist cleans the tooth surface, applies an acid etch to prepare it, then layers and sculpts the composite resin to the desired shape. The material is hardened with a special curing light, polished, and adjusted for a natural look—all typically done in a single appointment.
4. How long do composite veneers last?
Answer: Composite veneers generally last 5 to 7 years with proper care. They may require occasional repairs or touch-ups due to wear, chipping, or staining.
5. Do composite veneers look natural?
Answer: Yes, composite veneers can be color-matched to your natural teeth and shaped to blend seamlessly, providing a natural and attractive smile.
6. Are composite veneers reversible?
Answer: Since minimal enamel removal is involved, composite veneers are considered reversible or minimally invasive compared to porcelain veneers which require more tooth preparation.
7. How do I care for composite veneers?
Answer: Good oral hygiene is essential—brush twice daily, floss regularly, and avoid biting hard objects. Avoid foods and drinks that stain and attend regular dental checkups for maintenance.
8. Can composite veneers fix crooked teeth?
Answer: Composite veneers can mask mild misalignment or uneven teeth, but severe cases may require orthodontic treatment for optimal results.
9. How much do composite veneers cost?
Answer: Composite veneers are generally more affordable than porcelain veneers, typically costing between $250 and $1,500 per tooth depending on the location and dentist expertise.
10. What are the advantages and disadvantages of composite veneers?
Answer: Advantages include lower cost, quicker application, and less enamel removal. Disadvantages include shorter lifespan, potential for staining, and less durability compared to porcelain veneers.
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.