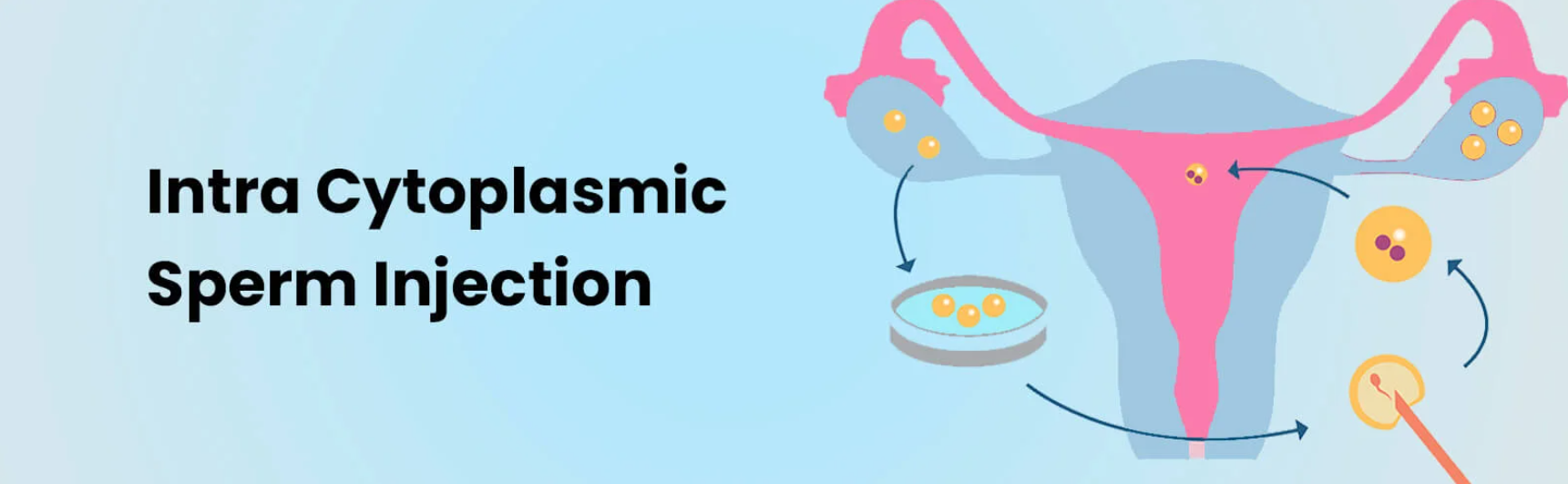
Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH) is a technique used in in vitro fertilization (IVF) to help embryos implant successfully in the uterus. During the IVF process, embryos are cultured in a lab after being fertilized outside the body. Once the embryos reach a certain developmental stage, they need to "hatch" from their protective outer shell, called the zona pellucida, in order to implant into the lining of the uterus and grow into a pregnancy.
However, in some cases, the zona pellucida may be too thick or difficult for the embryo to break through naturally. This can prevent successful implantation. Laser Assisted Hatching involves using a fine laser to make a small opening in the zona pellucida, allowing the embryo to hatch more easily and improving its chances of implantation.
LAH is typically recommended for women undergoing IVF with poor embryo quality, advanced maternal age, or recurrent IVF failure. It can also be helpful for embryos with thick zona pellucida, ensuring better chances of success in embryo transfer.
The development of LAH is a part of the ongoing efforts to improve IVF success rates, especially in cases where traditional methods of embryo transfer have failed. This procedure, though relatively simple, requires advanced technology and precise technique to minimize risks and optimize results.
Laser Assisted Hatching is primarily used in situations where an embryo may have difficulty hatching naturally. Below are the causes and risk factors that may lead to the need for LAH:
Causes for Using Laser Assisted Hatching
-
Thick Zona Pellucida:
-
The zona pellucida is a protective membrane surrounding the embryo. In some embryos, especially those from women of advanced maternal age, this membrane becomes thicker and more rigid. A thicker zona pellucida can make it difficult for the embryo to hatch and implant in the uterus.
-
-
Advanced Maternal Age:
-
Women over the age of 35 experience a decrease in egg quality, which can affect the ability of embryos to hatch naturally. LAH is often recommended in such cases to help embryos implant successfully.
-
-
Poor Embryo Quality:
-
Embryos that are poor quality may struggle to hatch, even if the zona pellucida is of normal thickness. LAH can help such embryos by enabling easier hatching, which can improve their chances of implantation.
-
-
Recurrent IVF Failures:
-
Women who have had several failed IVF attempts may be advised to undergo LAH. The procedure can be used to improve the chances of implantation for embryos that have previously failed to implant.
-
-
Male Infertility:
-
In cases where male infertility is a factor and embryos are of poor quality, LAH may be employed to assist the hatching process and improve embryo development.
-
Risk Factors for Needing Laser Assisted Hatching
-
Egg Quality:
-
Eggs that are retrieved from older women or those with ovarian issues may have a higher chance of producing embryos with a thick zona pellucida, increasing the likelihood of needing LAH.
-
-
Embryo Development Issues:
-
Embryos that do not develop normally, such as those with fragmentation or slow development, may benefit from LAH, as it helps them break out of the zona pellucida more easily.
-
-
Previous IVF Failures:
-
Patients who have undergone IVF previously but had failed attempts at embryo implantation may be candidates for LAH as an adjunct to increase the chances of success.
-
Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH) itself does not exhibit symptoms or signs, as it is a technical procedure performed during the IVF cycle. However, there are some indicators and concerns related to infertility or IVF treatment that may make LAH a beneficial procedure:
Symptoms Indicating the Need for LAH
-
Repeated IVF Failure:
-
Couples or individuals who have experienced repeated failed IVF cycles may benefit from LAH to enhance the chances of embryo implantation and success.
-
-
Age-related Fertility Decline:
-
Women over the age of 35 may face difficulties in egg quality and embryo implantation. LAH can be particularly beneficial for older women undergoing IVF.
-
-
Difficulties in Embryo Implantation:
-
If embryos fail to implant despite the IVF procedure being technically sound, the cause may be a thick zona pellucida. LAH can address this issue by assisting the embryo in breaking through its protective outer layer.
-
-
Low-Quality Embryos:
-
If the embryos formed during IVF are of low quality (e.g., fragmented or slow-growing embryos), LAH may improve their chances of implanting and establishing a pregnancy.
-
Post-LAH Symptoms
-
After undergoing Laser Assisted Hatching, mild cramping and spotting are normal for the surrogate or female partner as part of the general embryo transfer procedure. These symptoms are generally short-lived.
There isn’t a specific “diagnosis” for Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH) itself. However, IVF specialists and reproductive endocrinologists will assess whether LAH is needed based on various diagnostic factors:
Key Diagnostic Tests:
-
Embryo Assessment:
-
Embryos are examined for quality (shape, fragmentation, and rate of development). If the embryos appear poor quality or are slow-growing, LAH may be suggested to improve their chances of hatching.
-
-
Semen Analysis:
-
If male infertility is an issue, a semen analysis can help assess sperm quality. Poor sperm quality can lead to embryos that are less likely to hatch or develop properly.
-
-
Age and Ovarian Reserve Tests:
-
The woman’s age and ovarian reserve (measured through tests such as AMH levels and FSH testing) are evaluated to predict egg quality and how likely an embryo is to succeed in implantation. Advanced maternal age may warrant LAH as a potential treatment.
-
-
Previous IVF History:
-
If there have been previous failed IVF cycles, especially those with good-quality embryos, Laser Assisted Hatching may be recommended based on a suspected zona pellucida issue.
-
Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH) is a surgical procedure performed in conjunction with IVF. It requires advanced laser technology to create a small hole in the zona pellucida of the embryo.
Steps of the LAH Procedure:
-
Ovarian Stimulation and Egg Retrieval:
-
The IVF process begins with ovarian stimulation to produce multiple eggs. After the eggs are retrieved, they are fertilized either by using the partner's sperm or a sperm donor.
-
-
Embryo Development:
-
The fertilized embryos are cultured in a laboratory for 3-5 days. The embryologist monitors the development and quality of the embryos.
-
-
Laser Assisted Hatching:
-
When the embryos reach the appropriate stage of development, the embryologist uses a fine laser to create a small hole in the zona pellucida (the protective shell around the embryo). This allows the embryo to hatch and implant in the uterus more easily.
-
-
Embryo Transfer:
-
The embryo is then transferred into the woman’s uterus. This is typically a painless procedure, and ultrasound is used to guide the catheter during embryo placement.
-
-
Pregnancy Testing:
-
After 10-14 days, pregnancy tests are conducted to determine if the embryo has implanted successfully.
-
Laser Assisted Hatching is generally considered a safe procedure with a low risk of complications. However, proper preparation, monitoring, and post-treatment care are essential to ensure the best results.
Prevention Measures:
-
Genetic Screening:
-
Genetic screening of embryos can help identify healthy embryos for transfer, reducing the likelihood of miscarriage or genetic disorders.
-
-
Embryo Freezing:
-
Cryopreservation of embryos before or after the LAH procedure allows for future attempts if necessary, ensuring that healthy embryos are available for additional IVF cycles.
-
-
Optimizing Female Fertility:
-
Women considering IVF with LAH should focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, staying physically active, and reducing stress.
-
-
Regular Monitoring:
-
Monitoring during ovarian stimulation and after embryo transfer is essential to ensure the best chance of success. Blood tests and ultrasounds should be done to track progress.
-
Management During IVF with LAH:
-
Hormonal Management:
-
Hormonal medications, such as estrogen and progesterone, are prescribed to prepare the uterus for embryo implantation. Proper dosing and timing are critical for the procedure’s success.
-
-
Post-Transfer Care:
-
After the embryo transfer, the woman should follow rest instructions and avoid heavy physical activity to ensure the best chances of implantation.
-
While Laser Assisted Hatching is generally safe, it does come with some risks and complications, which are important to consider:
-
Embryo Damage:
-
The laser used in LAH can, in rare cases, cause damage to the embryo if not applied with precision. This can potentially lead to implantation failure.
-
-
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS):
-
Hormonal treatments used for egg retrieval can lead to OHSS, a condition where the ovaries become swollen and painful, causing fluid retention, nausea, and bloating.
-
-
Multiple Pregnancies:
-
Though only one or two embryos are typically transferred, multiple embryo transfers can result in multiple pregnancies, which carry risks such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
-
-
Ectopic Pregnancy:
-
In rare instances, an embryo may implant outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube, leading to an ectopic pregnancy, which requires surgical intervention.
-
-
Psychological Effects:
-
IVF and LAH procedures can be emotionally challenging for both the surrogate and the intended parents. Managing stress, anxiety, and depression during the process is crucial.
-
The journey of Laser Assisted Hatching and IVF can be emotionally and physically demanding for all involved parties. Support from medical professionals, family, and friends is essential.
For Intended Parents:
-
Emotional Adjustment:
-
The process of IVF and LAH may lead to feelings of hope, anxiety, and stress. It’s important to maintain realistic expectations and manage emotional well-being throughout the journey.
-
-
Legal Considerations:
-
In some cases, legal matters such as parental rights and embryo ownership need to be addressed, particularly for couples using egg donors or gestational carriers.
-
For Surrogates:
-
Emotional Connection:
-
Surrogates may experience emotional attachment to the baby they are carrying. Post-birth support and counseling can help with the emotional process of handing over the baby to the intended parents.
-
-
Physical Health:
-
Surrogates must be in good physical health throughout the IVF and pregnancy process. Regular check-ups and emotional support are important for a healthy outcome.
-
1. What is Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH)?
Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH) is a technique used in assisted reproductive technology (ART), specifically in IVF (in vitro fertilization), to help embryos implant in the uterus. The procedure involves using a fine laser to create a small hole in the outer layer of the embryo (the zona pellucida) to facilitate its hatching and enable it to implant into the uterine lining more easily.
2. Why is Laser Assisted Hatching done?
LAH is done to improve the chances of embryo implantation, especially in cases where the embryo’s outer shell is too thick, making it difficult for the embryo to hatch and implant. It can be particularly helpful in the following scenarios:
-
Older women (who may have embryos with thicker zona pellucida).
-
Failed IVF cycles where previous attempts at embryo transfer have not resulted in a successful pregnancy.
-
Embryos with a poor prognosis or those that are not hatching naturally.
3. How is Laser Assisted Hatching performed?
The LAH procedure is performed in the laboratory just before embryo transfer. Using a precise laser, the embryologist creates a small opening in the zona pellucida (the protective shell of the embryo). This procedure is minimally invasive and is done with extreme care to ensure the embryo is not harmed. After the procedure, the embryo is transferred into the woman’s uterus, where it will hopefully implant.
4. What are the benefits of Laser Assisted Hatching?
The main benefits of LAH include:
-
Improved implantation rates: By facilitating the embryo’s hatching process, LAH increases the likelihood that the embryo will implant successfully in the uterus.
-
Better outcomes for older women: Women over 35 may have embryos with thicker shells, and LAH can help overcome this barrier to implantation.
-
Higher chances of success for embryos that have previously failed to implant or resulted in a miscarriage.
5. What are the risks or disadvantages of Laser Assisted Hatching?
While LAH is generally considered safe, there are some potential risks, including:
-
Damage to the embryo: Although rare, the procedure can cause harm to the embryo, potentially affecting its development.
-
Not suitable for all embryos: Some embryos may not need LAH, and performing the procedure unnecessarily could reduce the success rate.
-
Cost: LAH is an additional procedure that increases the overall cost of IVF treatment.
6. When is Laser Assisted Hatching recommended?
LAH is typically recommended in the following cases:
-
Age-related infertility: Women over 35 may have embryos with a thicker zona pellucida, making it harder for the embryo to hatch.
-
Previous failed IVF attempts: If previous IVF cycles have not resulted in pregnancy, LAH may be considered to improve the chances of success.
-
Poor embryo quality: In cases where embryos are of lower quality, LAH can help increase the chances of implantation.
-
Thick zona pellucida: If an embryo has a thick outer shell, LAH can help the embryo hatch and implant more easily.
7. Is Laser Assisted Hatching safe?
Yes, Laser Assisted Hatching is generally considered safe when performed by experienced embryologists. The procedure is minimally invasive and uses precise lasers to avoid damaging the embryo. However, as with any medical procedure, there are some risks, which should be discussed with your fertility specialist beforehand.
8. Does Laser Assisted Hatching increase the chances of pregnancy?
LAH has been shown to increase the chances of pregnancy in some patients, particularly in cases where the embryo’s outer shell is too thick to allow natural hatching. Studies suggest that LAH can improve implantation rates, especially in women with advanced maternal age or those who have had failed IVF cycles.
9. How much does Laser Assisted Hatching cost?
The cost of Laser Assisted Hatching varies depending on the fertility clinic, but it typically adds an additional fee of $500 to $1,500 to the cost of an IVF cycle. It’s important to check with your fertility clinic for specific pricing details and determine whether this procedure is included in your IVF package.
10. Are there any alternatives to Laser Assisted Hatching?
Alternatives to Laser Assisted Hatching include:
-
Chemical hatching: Using a special solution to weaken the zona pellucida to facilitate hatching. This method is less common than laser hatching.
-
Natural hatching: In some cases, embryos may hatch naturally without the need for intervention.
Your fertility specialist can evaluate your specific situation and recommend the best option based on factors like embryo quality and previous IVF outcomes.
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.