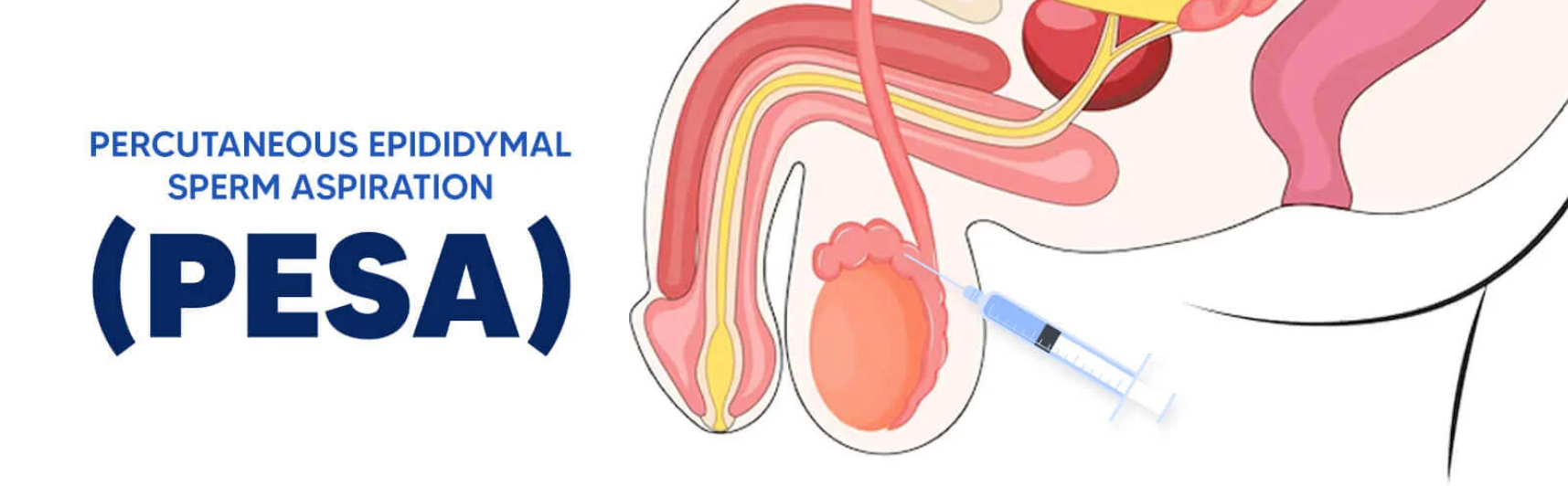
Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (PESA) is a medical procedure used to retrieve sperm directly from the epididymis (a coiled tube located behind the testicle) in men who are unable to ejaculate sperm naturally. This procedure is commonly employed in cases of male infertility where there is azoospermia (the absence of sperm in the ejaculate) or other issues preventing sperm from being ejaculated.
PESA is part of a broader set of surgical sperm retrieval techniques used in conjunction with assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). The sperm retrieved through PESA can be used for these procedures to help men who cannot produce viable sperm in their semen.
The PESA procedure is minimally invasive, involving the use of a fine needle to aspirate sperm from the epididymis. It is typically recommended for men with obstructive azoospermia (blockages in the male reproductive tract) or those with non-obstructive azoospermia (low sperm production) where sperm is present but cannot be ejaculated.
The advancement of ART and sperm retrieval techniques has greatly increased the success rates of male infertility treatments, offering hope for many men who otherwise would not be able to father biological children.
PESA is used primarily to address male infertility caused by various conditions, often related to sperm production or blockage. The following are the main causes and risk factors associated with needing PESA:
Causes for Needing PESA
-
Obstructive Azoospermia:
-
Obstructive azoospermia is a condition where sperm is produced normally in the testes but cannot pass through the reproductive tract due to blockages in the epididymis or vas deferens. This blockage can be due to genetic conditions, infections, previous surgeries, or trauma.
-
-
Congenital Absence of the Vas Deferens:
-
Some men are born without a vas deferens (the duct that carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra), often due to cystic fibrosis or other genetic disorders, leading to obstructive azoospermia and the need for PESA.
-
-
Post-Surgical Blockage:
-
After procedures such as vasectomy, there is a risk of sperm blockage in the epididymis or vas deferens, which can prevent sperm from being ejaculated. PESA can be performed to retrieve sperm for IVF or ICSI.
-
-
Trauma or Injury:
-
Physical trauma to the testes or reproductive organs can cause blockages or damage that affects sperm production or transport. PESA is often recommended for men who have experienced injuries that affect their fertility.
-
-
Non-Obstructive Azoospermia:
-
In non-obstructive azoospermia, sperm production in the testes is low or absent. While PESA can sometimes retrieve sperm in these cases, other sperm retrieval techniques like Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) may also be considered.
-
-
Infections and Inflammatory Conditions:
-
Infections like epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis) or orchitis (inflammation of the testicles) can cause damage to the sperm-producing organs, leading to obstruction or reduced sperm quality. PESA can help retrieve sperm when other options are not viable.
-
PESA itself does not have direct symptoms or signs, but the need for this procedure may arise from symptoms related to the underlying causes of male infertility.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for PESA
-
Absence of Sperm in Semen:
-
The primary indication for PESA is azoospermia, where no sperm is found in the ejaculate. This condition is usually diagnosed through a semen analysis, which is the first step in identifying male infertility.
-
-
Pain or Discomfort in the Testicles:
-
Men with certain conditions like epididymitis or testicular injury may experience pain, swelling, or discomfort in the testicles or epididymis, which may indicate an underlying issue that could be treated with PESA.
-
-
History of Vasectomy or Other Reproductive Surgery:
-
Men who have had a vasectomy or other surgeries in the reproductive tract may experience sperm blockage. In such cases, PESA can be used to retrieve sperm directly from the epididymis.
-
-
Failure of Previous Fertility Treatments:
-
Men who have failed fertility treatments, like IVF with their own sperm, may require PESA if the sperm issue is related to a blockage or low sperm production.
-
The diagnosis process for PESA involves evaluating male fertility and identifying the underlying causes of azoospermia or infertility. Several tests and assessments are used to determine whether PESA is the appropriate treatment option.
Key Diagnostic Steps:
-
Semen Analysis:
-
The first step in diagnosing azoospermia is a semen analysis, which tests for the presence of sperm in the ejaculate. If no sperm is found, further tests are conducted to determine if the cause is obstructive or non-obstructive.
-
-
Physical Examination:
-
A physical examination of the testicles and scrotum is performed to check for any abnormalities, swelling, or lumps that could indicate conditions like varicocele or epididymitis.
-
-
Hormonal Testing:
-
Blood tests to assess levels of testosterone, FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), and LH (luteinizing hormone) help evaluate sperm production and testicular function. These tests are important in diagnosing non-obstructive azoospermia.
-
-
Scrotal Ultrasound:
-
A scrotal ultrasound is often used to examine the testicles and epididymis for any structural issues, blockages, or cysts that could affect sperm transport.
-
-
Genetic Testing:
-
In some cases, genetic testing may be recommended to check for chromosomal abnormalities or genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis, which may cause azoospermia.
-
-
Vasography:
-
If the blockage is suspected in the vas deferens, a vasography (a special X-ray procedure) may be done to confirm the location of the obstruction.
-
PESA is a procedure used to retrieve sperm directly from the epididymis in men with azoospermia due to obstruction or other issues. The procedure is minimally invasive and generally involves the following steps:
Steps of PESA:
-
Preparation:
-
The male partner is given a local anesthetic or mild sedation to numb the area. This ensures minimal discomfort during the procedure.
-
-
Needle Aspiration:
-
A fine needle is inserted through the skin of the scrotum and into the epididymis to aspirate sperm. The needle is carefully guided to the epididymis, and sperm are collected through suction.
-
-
Sperm Retrieval:
-
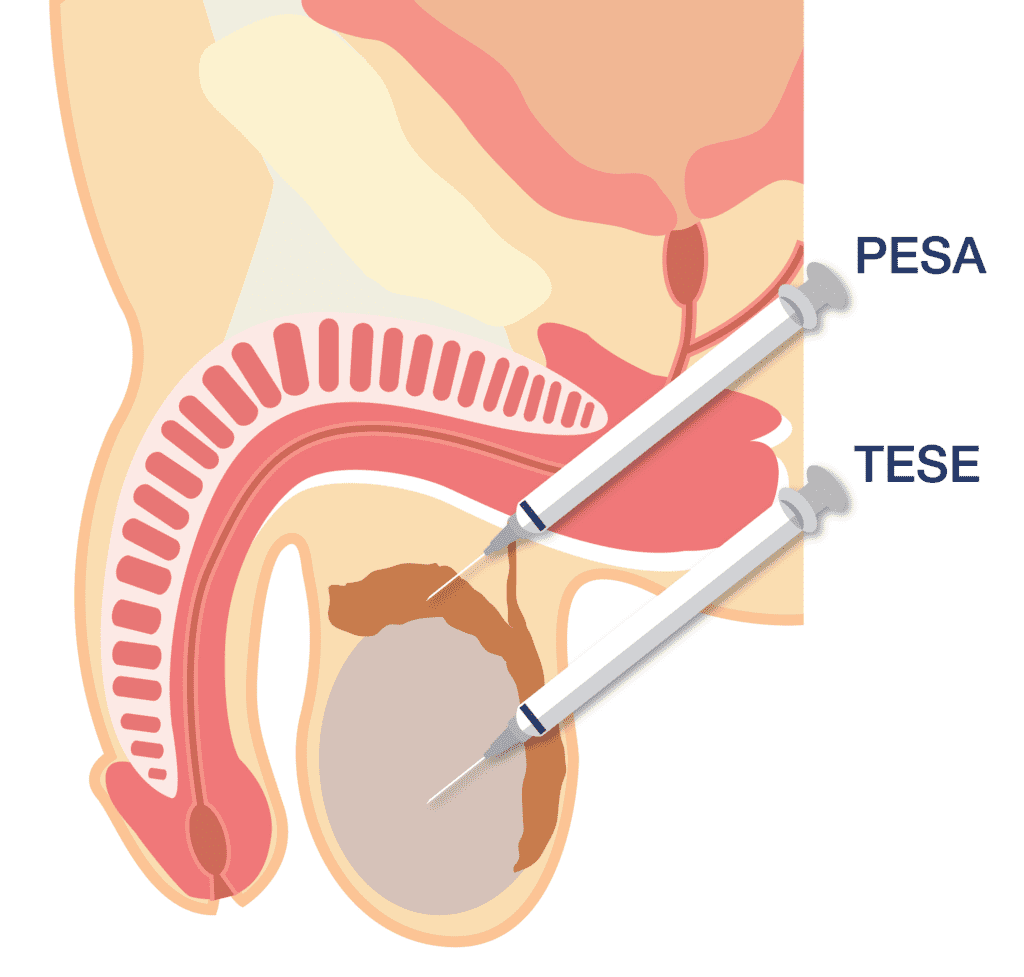
The retrieved sperm is then examined in the laboratory to ensure it is viable for use in IVF or ICSI. In cases where sperm cannot be retrieved from the epididymis, testicular sperm extraction (TESE) may be considered as an alternative.
-
-
Fertilization:
-
Once viable sperm is obtained, it is used to fertilize eggs through IVF or ICSI, depending on the specific fertility needs.
-
-
Embryo Transfer:
-
After fertilization, the resulting embryos are cultured for 3-5 days and transferred into the female partner’s uterus to achieve pregnancy.
-
Alternative Treatment:
-
If sperm retrieval via PESA is unsuccessful, other techniques like TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction) may be considered, where sperm is directly extracted from the testicles rather than the epididymis.
Although PESA is a relatively safe procedure, proper preparation, management, and post-procedure care are essential to ensure successful sperm retrieval and minimize risks.
Prevention Measures:
-
Fertility Preservation:
-
Men undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy can opt for sperm banking before treatment begins to preserve fertility for future use. This ensures that sperm is available for IVF or ICSI if required.
-
-
Managing Underlying Health Conditions:
-
Managing conditions such as epididymitis, testicular infections, or blockages can help prevent the need for PESA. Early intervention and treatment can preserve natural fertility.
-
-
Avoiding Harmful Lifestyle Factors:
-
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet can all contribute to fertility issues. Leading a healthy lifestyle can improve overall reproductive health.
-
Management During PESA:
-
Post-Procedure Care:
-
After the procedure, men should avoid heavy physical activity and refrain from sexual intercourse for a short period to allow the epididymis to heal.
-
-
Emotional Support:
-
Infertility treatments, including sperm retrieval procedures, can be emotionally challenging. Support from fertility counselors and healthcare providers can help manage any emotional distress.
-
While PESA is generally considered safe, there are a few potential risks and complications that should be considered:
-
Infection:
-
As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the puncture site. Proper sterile techniques are used to minimize this risk.
-
-
Bleeding:
-
There is a small risk of bleeding or hematoma formation at the needle insertion site. In rare cases, bleeding may occur inside the scrotum.
-
-
Damage to the Epididymis or Testicles:
-
Although the procedure is minimally invasive, there is a small risk of damage to the epididymis or testicles, which could affect future fertility.
-
-
Post-Procedure Pain or Swelling:
-
Mild pain, swelling, and bruising are common after PESA. These symptoms usually resolve within a few days to a week.
-
Living with the condition that necessitates PESA, or the emotional journey following the procedure, can be challenging. However, many men and couples find hope in the possibility of successful IVF or ICSI treatment.
For the Male Partner:
-
Emotional Support:
-
Sperm retrieval procedures can be emotionally challenging for men. Feeling a sense of helplessness or guilt is common, but seeking psychological support and fertility counseling can help manage these feelings.
-
-
Fertility After PESA:
-
PESA offers the possibility of biological parenthood, even for men with severe male infertility. If sperm are successfully retrieved, the chances of conception with IVF or ICSI are high.
-
For the Couple:
-
Understanding the IVF Journey:
-
Couples should be prepared for the IVF process, which involves emotional, physical, and financial challenges. The support of fertility specialists, psychologists, and support groups can help guide them through this journey.
-
1. What is Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (PESA)?
Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (PESA) is a minimally invasive procedure used to retrieve sperm directly from the epididymis (a tube that carries sperm from the testicles to the vas deferens). It is typically performed in men who have a blockage or obstruction in the reproductive tract, which prevents sperm from being present in the ejaculate, making natural conception impossible.
2. Why is PESA performed?
PESA is performed to retrieve sperm in cases where a man is unable to produce sperm through ejaculation due to various conditions, such as:
-
Congenital absence of the vas deferens (a genetic condition common in men with cystic fibrosis).
-
Obstructive azoospermia: A condition where sperm is produced but cannot pass through the reproductive tract due to blockages.
-
Previous vasectomy (if sperm retrieval is desired after a vasectomy).
-
In cases of failed sperm retrieval from other methods, such as testicular sperm extraction (TESE).
3. How is PESA performed?
PESA is a relatively simple and minimally invasive procedure. It is typically done under local anesthesia, though sedation may be used in some cases. A needle is inserted through the scrotum and into the epididymis to aspirate (suction) sperm. The sperm is then analyzed and, if viable, used for assisted reproductive techniques like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
4. Is PESA a painful procedure?
PESA is generally well-tolerated with minimal discomfort, especially since it is performed under local anesthesia. The procedure itself usually takes around 15-30 minutes. Most men experience only mild soreness or bruising in the area after the procedure, which typically resolves within a few days.
5. What are the success rates of PESA?
The success rates of PESA largely depend on the underlying cause of sperm retrieval and the quality of sperm retrieved. In cases of obstructive azoospermia, the procedure often has high success rates for obtaining viable sperm (up to 70-80%). However, the overall success of achieving a pregnancy depends on factors like sperm quality, the health of the woman, and the IVF or ICSI treatment that follows the sperm retrieval.
6. How is the sperm collected during PESA used?
Once sperm is successfully aspirated during PESA, it is assessed for viability and quality. The sperm can then be used in assisted reproductive technologies, such as:
-
In vitro fertilization (IVF): The sperm is combined with the egg in the laboratory for fertilization.
-
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into the egg to achieve fertilization, which is especially useful in cases where sperm quality is low.
7. What are the risks or complications associated with PESA?
PESA is generally safe, but like any medical procedure, it carries some risks, including:
-
Infection: Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the needle insertion site.
-
Bleeding or hematoma: There may be minor bleeding or bruising following the procedure.
-
Damage to surrounding tissues: Although uncommon, there is a small risk of injuring the epididymis or other nearby tissues.
However, these risks are minimized when the procedure is performed by an experienced specialist.
8. How long does it take to recover from PESA?
The recovery time for PESA is generally quick. Most men can resume normal activities within a couple of days, though they should avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for a week. Any soreness or bruising typically resolves within a few days. It’s important to follow any aftercare instructions provided by the physician to avoid complications.
9. Can PESA be used in all cases of male infertility?
PESA is effective in cases of obstructive azoospermia, where sperm is being produced but cannot pass through the reproductive tract due to blockages. However, it is not appropriate for men who have non-obstructive azoospermia, a condition in which sperm production is absent or very low in the testicles. In such cases, other sperm retrieval techniques like testicular sperm extraction (TESE) may be more appropriate.
10. What happens if PESA is unsuccessful?
If sperm is not successfully retrieved through PESA, alternative methods such as testicular sperm extraction (TESE) may be considered. TESE involves surgically extracting sperm directly from the testicles. While PESA is less invasive than TESE, TESE is often used if no sperm can be found in the epididymis.
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
- Cryopreservation of Gametes and Embryos
- Surgical sperm retrival … etc
- Thomson Fertility Centre
- Vibhavadi Hospital
- Apollo Fertility and IVF Center
- Jindal Heart Institute & Test Tube Baby Centre
- Lilavati Assisted Conception Unit
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.