Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is a congenital condition characterized by a narrowing of the aorta, the major artery responsible for transporting oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. This narrowing typically occurs near the ductus arteriosus, just beyond the arteries that supply the upper body. The constriction forces the heart to work harder to pump blood through the narrowed segment, leading to increased blood pressure before the constriction and reduced blood flow beyond it. If left untreated, CoA can result in severe cardiovascular complications, underscoring the importance of timely diagnosis and intervention.
The exact cause of coarctation of the aorta remains unclear, but it is predominantly a congenital defect, meaning it is present at birth. Several factors and associations have been identified:
-
Genetic Factors: CoA is often associated with certain genetic disorders, most notably Turner syndrome—a condition where a female is partly or completely missing an X chromosome.
-
Familial Patterns: There is evidence to suggest a hereditary component, as CoA can occur more frequently in certain families, indicating a potential genetic predisposition.
-
Associated Cardiac Anomalies: CoA frequently coexists with other congenital heart defects, such as bicuspid aortic valve (where the aortic valve has two leaflets instead of three), ventricular septal defects, and patent ductus arteriosus.
While CoA is primarily congenital, rare cases in adults can result from inflammatory conditions like Takayasu arteritis, which causes inflammation of the aorta and its branches.
The clinical presentation of CoA varies based on the severity of the narrowing and the age at diagnosis:
-
Infants: Severe narrowing can lead to symptoms shortly after birth, including:
-
Pale skin: Indicating poor perfusion.
-
Irritability: Due to discomfort or inadequate oxygenation.
-
Heavy sweating: A response to increased effort in feeding or breathing.
-
Difficulty breathing: Resulting from congestive heart failure.
-
Poor feeding and growth: Known as failure to thrive.
-
-
Older Children and Adults: Milder cases might not be detected until later in life, presenting with:
-
High blood pressure (hypertension): Particularly in the arms.
-
Headaches: Due to elevated blood pressure.
-
Muscle weakness or cramps: Especially in the legs, owing to reduced blood flow.
-
Cold feet or legs: Indicative of diminished circulation.
-
Nosebleeds: Associated with hypertension.
-
In some cases, individuals may remain asymptomatic, and CoA is only discovered during evaluations for hypertension or heart murmurs.
Diagnosing coarctation of the aorta involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging studies:
-
Physical Examination:
-
Blood Pressure Measurement: A significant difference between higher blood pressure in the arms and lower pressure in the legs can indicate CoA.
-
Pulse Evaluation: Weakened or delayed pulses in the femoral arteries (located in the groin) compared to the brachial arteries (in the arms) are suggestive of CoA.
-
Heart Murmurs: A physician may detect a murmur—a whooshing sound—indicative of turbulent blood flow across the narrowed segment.
-
-
Imaging Studies:
-
Echocardiography: Utilizes ultrasound waves to produce images of the heart and aorta, allowing visualization of the narrowing and assessment of heart function.
-
Chest X-ray: May reveal rib notching (caused by enlarged collateral vessels) or an enlarged heart.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) Angiography: Provide detailed images of the aorta and help in planning surgical or catheter-based interventions.
-
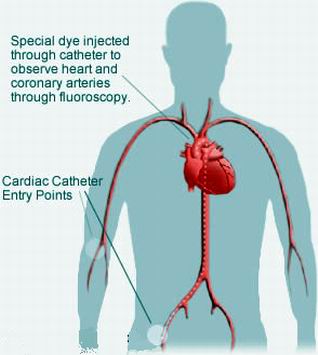
Cardiac Catheterization: Involves inserting a thin tube into a blood vessel leading to the heart to measure pressures and obtain detailed information about the aorta's anatomy.
-
Early detection is crucial to prevent complications, making awareness of the condition's signs and symptoms vital.
The primary goal in treating coarctation of the aorta is to relieve the narrowing and restore normal blood flow. Treatment options depend on factors such as the patient's age, the severity of the coarctation, and the presence of other heart defects:
-
Surgical Repair:
-
Resection with End-to-End Anastomosis: The narrowed segment is surgically removed, and the two healthy ends of the aorta are reconnected. This technique is commonly used in infants and children. Endovascular Today
-
Subclavian Flap Aortoplasty: A portion of the left subclavian artery (which supplies blood to the left arm) is used to enlarge the narrowed area. This method sacrifices some blood flow to the left arm but effectively widens the aorta.
-
Patch Aortoplasty: A patch, often made from synthetic material or the patient's own tissue, is sewn into the aorta to widen the narrowed segment.Home+4Wikipedia+4Endovascular Today+4
-
-
Transcatheter Interventions:
-
Balloon Angioplasty: A catheter with a balloon at its tip is threaded to the site of narrowing. Inflating the balloon stretches the a
-
While coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is primarily a congenital condition and thus not preventable, proactive management can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. Effective management strategies include:
Regular Medical Follow-ups: Routine check-ups and imaging tests (such as echocardiography and MRI) help monitor the condition and identify potential complications early.
Blood Pressure Management: Strict control of hypertension through medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications reduces stress on the heart and blood vessels.
Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, balanced nutrition, weight management, and avoidance of smoking is critical.
Preventing Endocarditis: Good oral hygiene and prophylactic antibiotics before dental or surgical procedures can prevent infections that could complicate heart conditions.
Without appropriate treatment, coarctation of the aorta can lead to several serious complications:
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Persistent hypertension can damage arteries and lead to conditions like stroke, heart failure, or kidney disease.
Aneurysm Formation: Weakening and bulging of the aorta may occur near the site of repair, posing a risk of rupture or life-threatening bleeding.
Heart Failure: Long-standing narrowing forces the heart to work harder, eventually leading to weakening and reduced heart function.
Stroke and Cerebral Hemorrhage: High blood pressure and weakened vessels can cause strokes or brain bleeds.
Endocarditis: Infections of the heart lining are more likely in patients with structural heart abnormalities.
Individuals with coarctation of the aorta who receive timely treatment often lead active, fulfilling lives. Key factors in successfully living with this condition include:
Ongoing Medical Care: Lifelong cardiology follow-ups ensure proper monitoring of heart function and early identification of complications.
Medication Adherence: Consistent use of prescribed medications helps manage blood pressure and reduces cardiovascular risks.
Physical Activity: Moderate, supervised exercise programs enhance overall cardiovascular health without placing undue stress on the heart.
Psychological Support: Emotional and psychological support from healthcare providers, family, and support groups can help individuals cope effectively with the condition.
Awareness and Education: Understanding the condition thoroughly empowers patients to actively participate in their care, recognize symptoms early, and seek timely intervention when necessary.
Advances in surgical and medical treatments have significantly improved prognosis and quality of life for patients managing coarctation of the aorta.
The other major cardiac procedures are:
Few popular hospitals for Cardiac Catheterization are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Cardiac Catheterization | Doctors Cardiac Catheterization | Cost Of Cardiac Catheterization | Destinations For Cardiac Catheterization | Cardiac Catheterization In India | Cardiac Catheterization In Thailand | Cardiac Catheterization In Malaysia | Recovery After Cardiac Catheterization | Risks Of Cardiac Catheterization | Cardiac Catheterization In Singapore | Cardiac Catheterization In Argentina | Catheter | Long Thin Tube | Coronary Angiography | Coronary Artery | Valvuoplasty | Angina Type Pain | Cardiac Procedures Done In India | Cardiac Procedures Done In Thailand And Malaysia | Angiogram | Blood Sampling | Arrhythmias | Catheter Ablation | Cardiology | Cardio-Thoracic Surgeons | Cardiac Catheterization Procedure | Side Effects Of Cardiac Catheterization | Cardiac Catheterization Abroad | Cardiac Catheterization Overseas | Cardiac Catheterization Low Costsurgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


