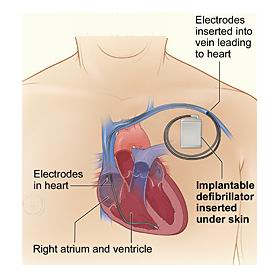
An Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) is a small medical device designed to monitor and correct abnormal heart rhythms. It is primarily used in patients who are at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, such as ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, which can lead to sudden cardiac arrest. The ICD continuously monitors the heart’s electrical activity and delivers shocks or pacing to restore normal heart rhythm when necessary.
ICD implantation is typically recommended for individuals with a history of serious arrhythmias, those with certain heart conditions like heart failure, or those at high risk of developing abnormal heart rhythms. The procedure is minimally invasive and has become a standard approach to preventing sudden cardiac death in high-risk patients.
An ICD is typically implanted in patients who have certain conditions that put them at a higher risk for life-threatening arrhythmias. These conditions disrupt the heart's electrical system and increase the likelihood of abnormal heart rhythms.
Conditions that may require ICD implantation:
-
Heart Failure: Patients with heart failure may experience abnormal heart rhythms, such as ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, due to weakened heart muscle. An ICD helps manage these risks.
-
Previous Heart Attack: A past heart attack can damage the heart tissue, leading to abnormal electrical pathways and increasing the risk of arrhythmias.
-
Idiopathic Ventricular Fibrillation: This condition occurs when the electrical system of the heart misfires and causes erratic rhythms that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest.
-
Congenital Heart Disease: People born with heart defects may be at higher risk for arrhythmias and may benefit from an ICD for protection.
-
Long QT Syndrome: A genetic condition that affects the heart’s electrical activity and can lead to arrhythmias.
-
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, disrupting normal electrical signals and increasing the risk of arrhythmias.
-
Brugada Syndrome: A rare genetic condition that causes abnormal electrical activity in the heart, leading to increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Risk factors for arrhythmias:
-
Age: The risk of arrhythmias increases with age, especially in individuals with heart disease or other underlying conditions.
-
Previous heart disease: Individuals with a history of heart attack or heart failure are at a higher risk for arrhythmias.
-
Family history: A family history of sudden cardiac arrest or arrhythmias increases the risk of these conditions.
-
Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, high blood pressure, and a sedentary lifestyle all contribute to the risk of heart disease and arrhythmias.
Having one or more of these risk factors may make ICD implantation a necessary preventive measure to protect against sudden cardiac arrest.
An ICD may be necessary when a person experiences certain symptoms that indicate an increased risk of serious arrhythmias or sudden cardiac arrest. In some cases, patients may not have any symptoms until an arrhythmia occurs. However, the following signs and symptoms could indicate the need for an ICD:
Common Symptoms Include:
-
Frequent or unexplained fainting (syncope): Loss of consciousness or feeling lightheaded, which can be caused by abnormal heart rhythms.
-
Palpitations: A sensation of rapid, irregular heartbeats or a fluttering in the chest, which may be caused by arrhythmias.
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness: This can occur when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to the brain due to arrhythmias.
-
Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling winded with minimal exertion due to heart rhythm disturbances.
-
Chest pain or discomfort: A sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest, which may be related to arrhythmias or heart disease.
-
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA): In extreme cases, arrhythmias can lead to sudden cardiac arrest, which is fatal if not treated immediately. An ICD is designed to prevent this outcome by delivering a shock to restore normal heart rhythm.
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially in the presence of risk factors for arrhythmias, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider who can evaluate your heart health and determine if an ICD is necessary.
Before an ICD is implanted, several diagnostic tests are used to assess the heart’s electrical activity and determine whether the device is appropriate. A thorough evaluation of the patient's health history, symptoms, and risk factors is also required.
Diagnostic Tests Include:
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG): A standard test that measures the heart's electrical activity and can help detect arrhythmias.
-
Echocardiogram: A non-invasive ultrasound test that helps visualize the heart’s structure and assess its function. This test is useful in determining whether the heart’s pumping ability is compromised.
-
Holter monitor: A portable ECG that records heart activity over 24-48 hours to detect intermittent arrhythmias.
-
Electrophysiological Study (EPS): A procedure in which catheters are inserted into the heart to map its electrical activity and identify abnormal pathways or areas prone to arrhythmias.
-
Stress Test: A test that monitors the heart’s response to exercise and helps identify arrhythmias that may occur with physical exertion.
-
Cardiac MRI: A more detailed imaging test that assesses heart structure and function, particularly useful for certain types of arrhythmias.
-
Blood tests: These may be conducted to assess the presence of underlying conditions such as heart failure, kidney function, and electrolyte imbalances.
Once these tests are completed, the doctor will review the results to determine whether an ICD is needed and which type of device is most appropriate for the patient.
ICD implantation is a relatively straightforward procedure that is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation. The procedure takes about 1-2 hours and is done in a hospital setting by a cardiac electrophysiologist or surgeon.
Steps Involved in ICD Implantation:
-
Preparation: The patient is positioned comfortably, and local anesthesia is administered to numb the area where the ICD will be implanted, typically near the collarbone.
-
Incision: A small incision is made just below the collarbone. In some cases, a minimally invasive approach may be used with smaller incisions.
-
Insertion of leads: Thin, flexible wires (leads) are inserted into a vein and threaded through to the heart. These leads are responsible for detecting abnormal heart rhythms and delivering electrical impulses or shocks when needed.
-
Placement of the ICD device: The pacemaker-sized ICD is then placed under the skin, near the collarbone, and the leads are attached to the device. The ICD is typically programmed to detect abnormal rhythms and deliver a shock when necessary to restore normal heart function.
-
Testing and closure: The device is tested to ensure proper function and that the leads are securely attached. Once confirmed, the incision is closed with sutures.
-
Post-operative care: The patient is monitored in the hospital for a few hours to ensure proper device function. Most patients can return home the same day or after a short stay.
As with any surgery, there are risks associated with ICD implantation. However, the procedure is generally safe, and complications are relatively rare.
Potential Risks Include:
-
Infection: An infection at the incision site or around the device can occur.
-
Lead dislodgement: The leads may become dislodged, requiring repositioning or re-implantation.
-
Bleeding or hematoma: Bleeding under the skin may occur at the insertion site.
-
Device malfunction: The ICD may fail to deliver therapy or may deliver inappropriate shocks.
-
Arrhythmias: In rare cases, the ICD may cause arrhythmias or alter the heart’s rhythm.
-
Pneumothorax: A punctured lung during the insertion of leads is a rare complication but can occur.
-
Blood clots: In rare cases, blood clots can form in the veins and travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism) or heart.
Recovery from ICD implantation is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a few days to weeks. However, there are some important aftercare instructions to follow:
Post-Surgery Care:
-
Follow-up appointments: Regular visits to the doctor are necessary to monitor the function of the ICD and adjust settings if needed.
-
Avoid heavy lifting: Patients should avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities for about 4-6 weeks to allow the leads and device to settle.
-
Wound care: The incision site should be kept clean and dry to prevent infection.
-
Limit arm movement: Patients may be advised to avoid certain arm movements on the side of the implant for several weeks.
Living with an ICD can be life-changing for many patients, as it offers protection from life-threatening arrhythmias. After recovery, most patients can return to their normal activities, including driving, exercise, and work, with some modifications.
Lifestyle Considerations:
-
Regular follow-up care: Patients will need regular follow-up appointments to monitor the ICD’s function and make any necessary adjustments.
-
Avoid strong magnets: Certain devices like MRI machines and metal detectors can interfere with the ICD, so it’s important to inform healthcare providers of the device.
-
Physical activity: Most patients can return to physical activity but should avoid contact sports or activities that could impact the device.
-
Medical alert: Wearing a medical ID card indicating the presence of the ICD is recommended in case of emergencies.
The other major cardiac procedures are:
Few popular hospitals for ICD IMPLANTATION are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Implantable Defibrillator | Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator | Rapid Heart Racing Attacks | Ventricular Tachycardia | Vt | Ventricular Fibrillation | Vf | Anti Tachycardia Pacing | Low Energy Synchronized Cardioversion | High Energy Defibrillation Shocks | Cardiac Death | Ventricular Arrhythmias | Hcm | Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy | Dilated Cardiomyopathy | Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy | Hospitals Icd Implantation | Doctors Icd Implantation | Surgery Icd Implantation | Cost Icd Implantation | Treatment Icd Implantation | Destinations Icd Implantation | Icd Implantation India | Icd Implantation Recovery | Icd Implantation Information | Icd Implantation Thailand | Icd Implantation Malaysia | Icd Implantation Abroad | Icd Implantation Overseas | Icd Implantation Low Cost
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


