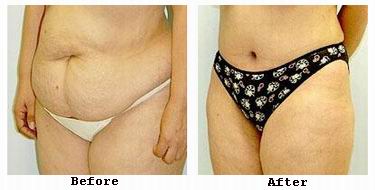
Abdominoplasty, commonly known as a tummy tuck, is a major cosmetic surgical procedure that addresses the contour and structural integrity of the abdominal region. It involves the removal of excess skin and fat, along with the tightening of underlying abdominal muscles, to achieve a firmer and flatter abdomen. This procedure is especially sought after by individuals who experience persistent sagging or protrusion of the abdominal wall that cannot be corrected through diet, exercise, or less invasive methods.
The popularity of abdominoplasty has risen dramatically over the past few decades, particularly due to increasing rates of massive weight loss from bariatric surgeries and the desire for post-pregnancy body restoration. The surgery offers not only aesthetic enhancement but also functional improvements, such as better posture and relief from back pain caused by weakened core muscles.
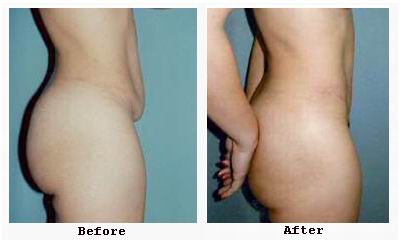
Unlike liposuction, which removes fat but does not correct loose skin or muscle separation, abdominoplasty provides a comprehensive approach that addresses all layers of the abdominal wall. It remains one of the most effective procedures to restore abdominal contour, and its benefits extend beyond appearance to overall quality of life.
Though abdominoplasty is a corrective surgical intervention rather than a treatment for a disease, various underlying physiological and lifestyle factors create conditions that prompt patients to seek this procedure.
Pregnancy and Childbirth Pregnancy imposes enormous mechanical stress on the abdominal muscles and skin. Multiple pregnancies often result in overstretched and separated rectus abdominis muscles (a condition known as diastasis recti), weakening the abdominal wall and causing a characteristic “pooch” or bulging belly. The overstretched skin may lose elasticity and fail to retract postpartum, leading to excess loose skin and stretch marks that are resistant to non-surgical treatments.
Significant and Rapid Weight Loss Massive weight loss, whether through dietary changes or bariatric surgery, frequently results in redundant, sagging skin that envelops the midsection. This loose skin can be uncomfortable, cause hygiene challenges, and restrict mobility. Unlike fat, excess skin cannot be removed by exercise or dieting, making surgical excision via abdominoplasty necessary.
Aging and Genetic Predisposition Natural aging diminishes collagen and elastin fibers, reducing skin’s resilience and contributing to laxity. Furthermore, genetics play a role in the distribution of body fat and the skin’s ability to retract, with some individuals predisposed to abdominal sagging regardless of lifestyle factors.
Prior Abdominal Surgeries and Scars Surgical scars and previous operations (e.g., C-sections, hernia repairs) can disrupt the abdominal wall’s integrity, contributing to muscle weakness or asymmetry. Abdominoplasty provides an opportunity to correct muscle defects and improve contour simultaneously.
Lifestyle Factors Poor posture, inadequate exercise, and prolonged sedentary behavior can exacerbate muscle weakness and poor abdominal tone. While these do not cause excess skin, they contribute to the overall unsatisfactory abdominal appearance and functional problems.
The decision to undergo abdominoplasty is often driven by a combination of physical, functional, and psychological symptoms.
Excess Skin and Fat Deposits Patients commonly complain about the presence of a panniculus—a significant overhanging fold of skin and fat that hangs over the lower abdomen. This excess tissue is not only aesthetically displeasing but also prone to irritation, infections, and discomfort during movement.
Abdominal Muscle Laxity and Bulging Visible bulging or protrusion of the abdomen, often resistant to diet and exercise, usually indicates diastasis recti or weakened abdominal muscles. This muscle separation reduces core strength, impacts posture, and can cause lower back pain.
Skin Irritation and Infection Persistent moisture trapped beneath skin folds can cause rashes, fungal infections, or ulcerations, which interfere with daily activities and personal hygiene.
Psychological Distress Many patients experience low self-esteem, social embarrassment, or dissatisfaction with their body image due to abdominal changes, impacting mental health and social life.
Functional Limitations Excess abdominal tissue can impair movement, limit exercise capacity, and cause discomfort during physical activities, which may decrease overall quality of life.
Abdominoplasty requires careful patient evaluation to optimize safety and outcomes. The diagnostic process is less about identifying a disease and more about comprehensive surgical planning and risk assessment.
Medical History and Risk Factor Identification Physicians evaluate patients’ overall health, pre-existing medical conditions (such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases), previous surgeries, medication usage, and lifestyle habits like smoking, all of which influence healing and surgical risk.
Physical Examination The surgeon assesses skin quality, elasticity, fat distribution, muscle tone, and the extent of muscle separation. The presence of hernias or asymmetries is evaluated, sometimes requiring imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans for detailed assessment.
Psychological and Social Evaluation Understanding the patient’s motivations, expectations, and psychological readiness is critical. Unrealistic expectations or psychological distress should be addressed before surgery.
Laboratory and Imaging Tests Routine blood work and possibly cardiac evaluations are performed to identify any underlying risks. Imaging helps in planning muscle repairs or detecting hidden defects.
Patient Counseling Detailed discussions are held regarding surgical options, expected results, risks, recovery timeline, and lifestyle modifications. Informed consent is obtained only after thorough education and answering patient questions.
Abdominoplasty techniques vary based on the degree of skin laxity, fat distribution, muscle separation, and patient goals.
Types of Abdominoplasty Procedures
- Full Abdominoplasty: A horizontal incision from hip to hip allows removal of significant skin and fat and repair of abdominal muscles. The belly button is repositioned for natural appearance.
- Mini Abdominoplasty: For patients with limited lower abdominal laxity, a smaller incision is used, usually without navel repositioning.
- Extended or Fleur-de-lis Abdominoplasty: This combines vertical and horizontal incisions to remove extensive skin, typically used in massive weight loss patients.
- Circumferential Abdominoplasty (Body Lift): Encompasses skin and fat removal around the waist, including the abdomen and back, for comprehensive contouring.
Surgical Steps
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia ensures patient comfort and safety.
- Incision and Flap Creation: Skin and fat are separated from the abdominal muscles.
- Muscle Repair: Rectus abdominis muscles are sutured to restore midline strength.
- Excision of Excess Skin and Fat: Removal tailored to patient’s anatomy.
- Umbilical Repositioning: The belly button is detached and reinserted through a new opening.
- Drain Placement: Prevents fluid accumulation post-surgery.
- Closure: Layered suturing minimizes tension and scarring.
- Postoperative Dressing and Compression Garment: Supports healing and reduces swelling.
Adjunct Procedures Sometimes combined with liposuction to enhance contour or hernia repair for abdominal wall defects.
Though the procedure itself cannot be “prevented,” optimal results depend heavily on pre- and postoperative care
Preoperative Management
- Achieving a stable, healthy weight.
- Cessation of smoking to improve circulation and healing.
- Optimizing nutrition to support tissue repair.
- Engaging in core strengthening exercises to enhance muscle tone pre-surgery.
Postoperative Care
- Adhering to wound care instructions to prevent infections.
- Using compression garments to reduce swelling and support tissue adaptation.
- Gradually resuming physical activity under medical guidance.
- Monitoring for and promptly addressing complications.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to sustain surgical results.
Despite advances in surgical technique, complications can occur.
Early Complications
- Seroma Formation: Fluid accumulation that may require drainage.
- Hematoma: Blood collection causing swelling and pain.
- Infection: Ranges from superficial wound infections to deeper abscesses.
- Delayed Wound Healing: Particularly in smokers or diabetics.
- Numbness or Sensory Changes: Usually temporary but sometimes permanent.
Late Complications
- Scarring: Hypertrophic or keloid scars may develop.
- Skin Necrosis: Rare but serious, due to impaired blood supply.
- Asymmetry: Unequal contouring may necessitate revision.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Potentially life-threatening but preventable with prophylaxis.
Recovery from abdominoplasty requires time and patience. Most patients experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort initially, which gradually resolve over weeks.
Physical Recovery
- Rest and limited activity for the first few weeks.
- Use of compression garments for 4 to 6 weeks.
- Gradual return to normal activities and exercise after medical clearance.
Psychological Impact
Many patients report improved body image and confidence. Supportive counseling may be helpful for adjusting to physical changes.
Long-Term Maintenance
- Maintaining stable body weight is essential to preserve results.
- Regular exercise and healthy diet support muscle tone and skin health.
- Scar care techniques like silicone sheets and sun protection improve appearance.
1. What is abdominoplasty (tummy tuck)?
Abdominoplasty, commonly known as a tummy tuck, is a surgical procedure designed to remove excess skin and fat from the abdomen and tighten the underlying muscles, resulting in a flatter and firmer abdominal profile.
2. Who is a good candidate for abdominoplasty?
Ideal candidates are individuals with excess abdominal skin or weakened muscles due to pregnancy, significant weight loss, or aging. It’s best suited for healthy adults close to their ideal weight who do not plan future pregnancies.
3. What types of abdominoplasty procedures are available?
There are mainly three types:
- Full abdominoplasty: Removes excess skin and tightens muscles from the entire abdomen.
- Mini abdominoplasty: Focuses on the lower abdomen below the navel.
- Extended abdominoplasty: Also addresses the flanks or love handles.
4. How long does the surgery take, and what is the recovery time?
Surgery usually takes 2 to 5 hours depending on the procedure extent. Recovery involves about 2 weeks of limited activity, with most patients returning to normal activities within 4 to 6 weeks.
5. What are the risks or complications of abdominoplasty?
Risks include infection, bleeding, scarring, fluid accumulation, and changes in skin sensation. Choosing a board-certified surgeon and following post-op instructions can minimize these risks.
6. Will abdominoplasty remove stretch marks?
Abdominoplasty can remove stretch marks located on the excess skin that is excised, especially those below the navel. However, stretch marks outside this area will remain.
7. How noticeable will the scars be after surgery?
Scars are usually located low on the abdomen, hidden beneath underwear or swimsuit lines. While scars fade over time, they will not disappear completely but often become less noticeable.
8. Can I combine abdominoplasty with other procedures?
Yes, abdominoplasty is often combined with liposuction or breast surgery in a "mommy makeover" to enhance overall body contouring results.
9. How much does abdominoplasty cost?
Costs vary widely based on geographic location, surgeon’s experience, and procedure complexity. It’s important to consider all fees, including anesthesia and facility costs, when budgeting.
10. How long do the results of abdominoplasty last?
With a stable weight and healthy lifestyle, the results can last for many years. Significant weight fluctuations or pregnancy after surgery can affect the outcome.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Abdominoplasty are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.