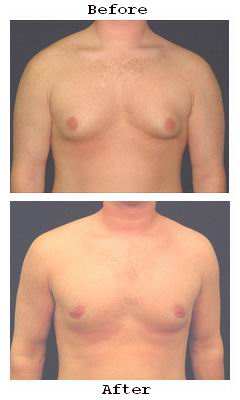
Gynecomastia is the benign enlargement of male breast tissue, a condition affecting a substantial proportion of the male population at various stages of life. While not life-threatening, gynecomastia often results in significant psychological distress, social embarrassment, and decreased quality of life. Men experiencing gynecomastia may feel self-conscious about their chest appearance, avoid activities such as swimming or exercising shirtless, and sometimes suffer from physical discomfort.
Gynecomastia correction surgery is a well-established, effective procedure designed to restore a natural, masculine chest contour. Through a combination of liposuction and glandular tissue excision, surgeons can significantly reduce breast volume and reshape the chest for improved aesthetics and confidence.
This comprehensive guide will cover the underlying causes and risk factors of gynecomastia, clinical signs that indicate the need for correction, detailed diagnostic steps, a review of modern treatment options, preventive and postoperative care strategies, possible complications, and lifestyle adaptations for living with gynecomastia correction.
Understanding the Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia arises primarily due to an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Estrogen promotes breast tissue growth, while testosterone inhibits it. When this balance tilts in favor of estrogen or when testosterone levels drop, gynecomastia develops.
-
Physiological Causes:
-
Neonatal gynecomastia: Seen in newborn boys due to maternal estrogen exposure.
-
Pubertal gynecomastia: Common during adolescence due to temporary hormonal imbalance; often resolves spontaneously within 6–12 months.
-
Senescent gynecomastia: Occurs in older men as testosterone declines naturally with age.
-
-
Pathological Causes:
-
Endocrine disorders: Hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism, pituitary tumors.
-
Liver and kidney diseases: Cirrhosis and renal failure disrupt hormone metabolism.
-
Tumors: Testicular, adrenal, or other hormone-secreting tumors increase estrogen levels.
-
Medications: Anti-androgens (e.g., spironolactone), anabolic steroids, antipsychotics, HIV medications, and some antibiotics.
-
Substance abuse: Alcohol, marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines.
-
-
Idiopathic: In many cases, no clear cause is identified.
Risk Factors for Developing Gynecomastia
-
Age: Peaks during puberty and older adulthood.
-
Genetics: Family history increases susceptibility.
-
Obesity: Increases peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogens, promoting breast tissue growth.
-
Hormonal Therapy: Use of testosterone blockers or estrogenic drugs.
-
Underlying systemic diseases: As noted above.
Men with gynecomastia typically notice:
-
Breast enlargement: Symmetrical or asymmetrical swelling beneath the nipple-areolar complex.
-
Firm or rubbery glandular tissue: Palpable behind the nipple, distinguishable from fatty tissue.
-
Breast tenderness or pain: Mild to moderate discomfort is common.
-
Nipple changes: Enlargement, puffiness, or increased prominence.
-
Psychosocial effects: Embarrassment, reduced self-confidence, anxiety, social withdrawal.
Clinical examination focuses on:
-
Measuring breast volume and consistency.
-
Differentiating true gynecomastia (glandular proliferation) from pseudogynecomastia (fat accumulation).
-
Checking for any suspicious masses requiring further investigation.
Stepwise Diagnostic Approach
-
Medical and Medication History:
Identify potential drug-induced causes or systemic illnesses. -
Physical Examination:
Evaluate breast tissue, differentiate glandular versus fatty enlargement, and check testicular size. -
Laboratory Investigations:
-
Hormonal panel: testosterone, estradiol, luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), prolactin, thyroid function.
-
Liver and renal function tests.
-
Tumor markers if malignancy suspected.
-
-
Imaging:
-
Breast ultrasound: Assess glandular tissue, exclude tumors or cysts.
-
Mammography: Rare but used if cancer suspected.
-
-
Biopsy:
Reserved for atypical presentations or when malignancy cannot be ruled out.
Psychological Assessment
-
Assess impact on mental health.
-
Screen for body dysmorphic disorder.
-
Ensure patient motivation aligns with realistic expectations.
Non-Surgical Treatments
-
Observation: Especially during puberty; spontaneous resolution is common.
-
Medical Therapy:
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen.
-
Aromatase inhibitors to reduce estrogen production.
-
Testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men.
-
These treatments have variable efficacy and are most effective early in gynecomastia development.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery remains the definitive treatment for persistent or severe gynecomastia, especially when glandular tissue predominates.
Liposuction Alone
-
Suitable when excess fatty tissue is the main cause.
-
Minimally invasive with small incisions.
-
Rapid recovery.
Excisional Surgery
-
Removal of dense glandular tissue via periareolar or inframammary incisions.
-
Allows contouring and correction of nipple protrusion.
-
May be combined with liposuction for optimal results.
Combined Approach
-
Liposuction plus gland excision is the most common and effective technique for
mixed-type gynecomastia.
Skin Excision
-
Required in cases with significant skin excess and ptosis.
-
Involves more extensive incisions and longer recovery.
Suitable when excess fatty tissue is the main cause.
Minimally invasive with small incisions.
Rapid recovery.
Removal of dense glandular tissue via periareolar or inframammary incisions.
Allows contouring and correction of nipple protrusion.
May be combined with liposuction for optimal results.
Liposuction plus gland excision is the most common and effective technique for mixed-type gynecomastia.
Required in cases with significant skin excess and ptosis.
Involves more extensive incisions and longer recovery.
Prevention Strategies
-
Avoiding causative medications when possible.
-
Limiting alcohol and drug use.
-
Maintaining healthy body weight through diet and exercise.
-
Monitoring and treating hormonal imbalances early.
Preoperative Preparation
-
Comprehensive evaluation and counseling.
-
Smoking cessation to improve healing.
-
Optimization of medical comorbidities.
Postoperative Care
-
Wearing compression garments to minimize swelling.
-
Managing pain with prescribed analgesics.
-
Avoiding strenuous activity for 2–4 weeks.
-
Follow-up visits for wound care and monitoring healing.
-
Scar care including silicone gels or sheets if needed.
Common Minor Complications
-
Swelling, bruising, and tenderness.
-
Temporary numbness or altered sensation around the nipples.
-
Minor asymmetry.
Serious Complications
-
Hematoma or seroma formation requiring drainage.
-
Infection at incision sites.
-
Poor wound healing or noticeable scarring.
-
Nipple necrosis (very rare).
-
Recurrence or residual breast tissue.
-
Unsatisfactory aesthetic outcome requiring revision.
Recovery Timeline
-
Initial swelling and bruising resolve in 2–3 weeks.
-
Most patients resume normal activities in 1–2 weeks.
-
Final chest contour becomes apparent after 3–6 months.
Psychological Impact
-
Dramatic improvement in self-image and confidence.
-
Greater participation in social and physical activities.
-
Some may benefit from psychological counseling during adjustment.
Long-Term Management
-
Maintaining a stable healthy weight.
-
Avoiding medications or substances that may trigger recurrence.
-
Regular self-examination and follow-up.
1. What is gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of male breast tissue caused by hormonal imbalance, genetics, medication, or health conditions, resulting in a feminine chest appearance.
2. What is gynecomastia correction surgery?
Gynecomastia correction surgery is a procedure that removes excess breast tissue and fat to restore a flatter, more masculine chest contour.
3. Who is a good candidate for gynecomastia correction?
Good candidates are men with persistent breast enlargement causing discomfort or self-consciousness, who are in good health and have realistic expectations.
4. How is gynecomastia surgery performed?
The procedure typically involves liposuction to remove excess fat and excision of glandular tissue through small incisions around the areola or chest.
5. What is the recovery time after gynecomastia surgery?
Most patients return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks, with full recovery and optimal results visible after several months.
6. Are there risks or complications?
Risks include infection, bleeding, scarring, asymmetry, and changes in nipple sensation, which are minimized by choosing an experienced surgeon.
7. Will the surgery leave scars?
Scars are usually small and strategically placed around the areola or in natural skin folds, fading over time.
8. Is gynecomastia correction surgery permanent?
Yes, results are typically permanent if a stable weight and healthy lifestyle are maintained.
9. Can gynecomastia recur after surgery?
Recurrence is rare but possible, especially if underlying hormonal imbalances or weight gain occur.
10. How should I prepare for gynecomastia surgery?
Preparation includes medical evaluation, avoiding blood thinners, quitting smoking, and following your surgeon’s pre-operative instructions.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Gynecomastia Correction are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



