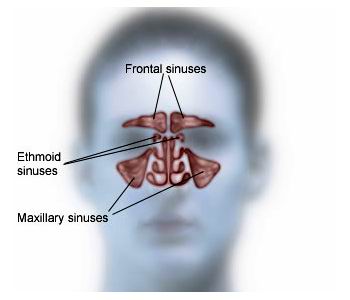
The ethmoid sinuses, a complex network of small air cells located between the nose and the eyes, play a crucial role in humidifying inhaled air, filtering pathogens, and maintaining normal nasal physiology. When these sinuses become inflamed or infected, often due to chronic sinusitis or nasal polyps, they can severely affect breathing, cause facial pain, and reduce quality of life.
Ethmoidectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at removing diseased ethmoid air cells and restoring proper drainage and ventilation of the sinuses. Traditionally performed via an external approach, modern advancements now favor the endoscopic ethmoidectomy, a minimally invasive surgery done through the nostrils with no external scars.
Ethmoidectomy is indicated when conservative medical therapies fail to resolve symptoms, or when anatomical obstructions prevent effective sinus drainage. This comprehensive guide will walk you through causes and risk factors necessitating ethmoidectomy, symptoms, diagnostic modalities, detailed treatment options, prevention and postoperative management, potential complications, and lifestyle adaptations following surgery.
Causes
-
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Ethmoid Involvement: Persistent mucosal inflammation leading to blockage and infection.
-
Nasal Polyposis: Benign mucosal growths originating often from ethmoid sinuses, causing obstruction.
-
Anatomical Variations: Deviated septum, concha bullosa (pneumatized middle turbinate), or narrow ethmoid infundibulum impairing drainage.
-
Fungal Sinusitis: Particularly allergic fungal sinusitis causing thick mucin and bony remodeling.
-
Mucocele Formation: Cystic mucus retention leading to expansion and erosion of surrounding bone.
-
Sinonasal Tumors: Rare benign or malignant growths requiring surgical resection.
-
Refractory or Recurrent Sinusitis: Failure of medical management necessitating surgery.
Risk Factors
-
History of allergies and asthma.
-
Cigarette smoking and exposure to irritants.
-
Previous sinus infections or surgeries.
-
Immunocompromised states (e.g., diabetes, HIV).
-
Occupational exposures to dust or chemicals.
-
Chronic Nasal Congestion: Persistent blockage unresponsive to medication.
-
Facial Pressure or Pain: Especially localized between the eyes or on the bridge of the nose.
-
Recurrent or Persistent Purulent Nasal Discharge: Often foul-smelling.
-
Hyposmia or Anosmia: Reduced or lost sense of smell.
-
Headache and Fatigue: Due to ongoing infection and inflammation.
-
Obstructive Sleep Symptoms: Snoring or breathing difficulties.
-
Postnasal Drip and Cough: Mucus drainage irritating the throat.
-
On endoscopic exam: nasal polyps, mucosal edema, or purulent secretions.
Clinical History and Physical Examination
-
Detailed symptom assessment including duration, severity, triggers.
-
Endoscopic nasal examination to visualize mucosa, polyps, drainage pathways.
Radiological Imaging
-
High-resolution CT Scan: Essential for detailed anatomy of ethmoid air cells, obstruction sites, and relation to orbital and skull base structures.
-
MRI: Useful when soft tissue differentiation is needed, especially for tumors or fungal infections.
Ancillary Tests
-
Allergy testing to identify contributing allergic rhinitis.
-
Microbiological cultures for resistant infections.
-
Blood tests to rule out systemic disease.
Conservative Medical Management (First Line)
-
Nasal corticosteroid sprays or drops.
-
Nasal saline irrigation to clear mucus.
-
Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
-
Antihistamines and leukotriene modifiers for allergic components.
-
Short-term oral steroids to reduce severe inflammation.
Surgical Intervention: Ethmoidectomy
-
Endoscopic Ethmoidectomy:
-
Performed under general or local anesthesia.
-
Utilizes nasal endoscope to access ethmoid air cells.
-
Diseased air cells and obstructive tissue removed with minimal trauma.
-
Aims to restore drainage, reduce polyp burden, and improve ventilation.
-
-
Extended Procedures: Sometimes combined with maxillary antrostomy, frontal sinusotomy, or septoplasty.
Postoperative Protocols
-
Nasal saline irrigations to promote healing and crust clearance.
-
Use of topical steroids to reduce inflammation and polyp recurrence.
-
Regular endoscopic debridement by ENT specialist during recovery.
Preventive Strategies
-
Ongoing allergy control and avoidance of irritants.
-
Smoking cessation to promote mucosal healing.
-
Prompt treatment of upper respiratory tract infections.
-
Maintenance of nasal hygiene with daily saline sprays.
Management of Chronic Conditions
-
Continued surveillance for recurrence of polyps or sinusitis.
-
Long-term use of topical corticosteroids.
-
Pulmonary or allergist collaboration if comorbid asthma exists.
-
Lifestyle adjustments including humidification and air quality control.
Early Postoperative Complications
-
Bleeding: Minor bleeding common; severe hemorrhage rare but possible.
-
Infection: Sinus or nasal cavity infection.
-
Orbital Injury: Due to proximity of ethmoid sinuses to the eye, potential for orbital hematoma or injury to optic nerve.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Leak: Rare but serious, from skull base breach.
-
Pain and Swelling: Usually temporary.
Late Complications
-
Adhesion Formation: Scar tissue causing nasal obstruction.
-
Recurrent or Persistent Sinus Disease: Possibly requiring revision surgery.
-
Altered Sense of Smell: Temporary or permanent hyposmia/anosmia.
-
Crusting and Dryness: Requiring ongoing care.
-
Anesthesia Risks: Depending on patient health.
Recovery Expectations
-
Initial nasal congestion and crusting expected for 2-4 weeks.
-
Gradual improvement in breathing and reduction in sinus symptoms.
-
Return to normal activities usually within 1-2 weeks.
Long-Term Outlook
-
Significant symptom relief and enhanced quality of life.
-
Ongoing nasal care important to prevent recurrence.
-
Some patients may require maintenance medications lifelong.
Lifestyle Recommendations
-
Avoid smoke, dust, and strong chemical exposures.
-
Use humidifiers in dry environments.
-
Maintain nasal hygiene routines.
-
Attend regular ENT follow-ups.
-
Manage allergies aggressively to reduce polyp formation.
1. What is ethmoidectomy?
Ethmoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove diseased or infected ethmoid sinus cells located between the nose and the eyes. It is commonly performed to treat chronic sinusitis or nasal polyps affecting the ethmoid sinuses.
2. Why is ethmoidectomy performed?
The surgery is done to relieve chronic sinus infections, nasal obstruction, facial pain, and pressure caused by inflamed or blocked ethmoid sinuses, especially when medical treatments have failed.
3. How is ethmoidectomy performed?
Ethmoidectomy is typically performed endoscopically through the nostrils using a thin, flexible scope. The surgeon removes the affected sinus tissue to improve drainage and ventilation without external incisions.
4. Is ethmoidectomy painful?
The procedure is done under general or local anesthesia, so it is painless during surgery. Postoperative discomfort like nasal congestion, mild pain, or swelling is common but manageable with medications.
5. What is the recovery time after ethmoidectomy?
Recovery usually takes one to two weeks. Patients may experience nasal congestion, mild bleeding, and nasal crusting, which gradually improve with proper care.
6. Are there risks or complications associated with ethmoidectomy?
Risks include bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding structures like the eyes or brain, cerebrospinal fluid leak, and changes in smell. Serious complications are rare with experienced surgeons.
7. How should I prepare for ethmoidectomy?
Preparation includes preoperative evaluation, imaging studies (CT scan), stopping certain medications like blood thinners, and fasting before surgery as advised by your doctor.
8. What should I expect after the surgery?
Expect nasal congestion, mild pain, and nasal discharge or crusting. Follow-up visits are important for nasal cleaning and monitoring healing.
9. Can ethmoidectomy cure chronic sinusitis?
Ethmoidectomy significantly improves symptoms by restoring sinus drainage and reducing infections but may not completely cure chronic sinusitis in all cases.
10. How long do the benefits of ethmoidectomy last?
Most patients experience long-term relief from sinus symptoms, though some may require additional treatments or surgeries depending on their condition.
The other ENT Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Ethmoidectomy are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Ethmoidectomy | Doctors For Ethmoidectomy | Cost For Ethmoidectomy | Treatment For Ethmoidectomy | Destinations For Ethmoidectomy | Risks Ethmoidectomy | Ethmoidectomy In India | Ethmoidectomy Recovery | Ethmoidectomy Information | Ethmoidectomy Thailand | Ethmoidectomy In Malaysia | Ethmoidectomy Abroad | Ethmoidectomy Overseas | Ethmoidectomy Low Cost | Ethmoid Sinuses | Ethmoid Sinus Cells | Sinus Problems | Ethmoidectomy in Singapore | Ethmoidectomy in Argentina | Surgery Ethmoidectomy | Ethmoidectomy in Singapore General Hospital | Ethmoidectomy in Apollo Hospitals
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


