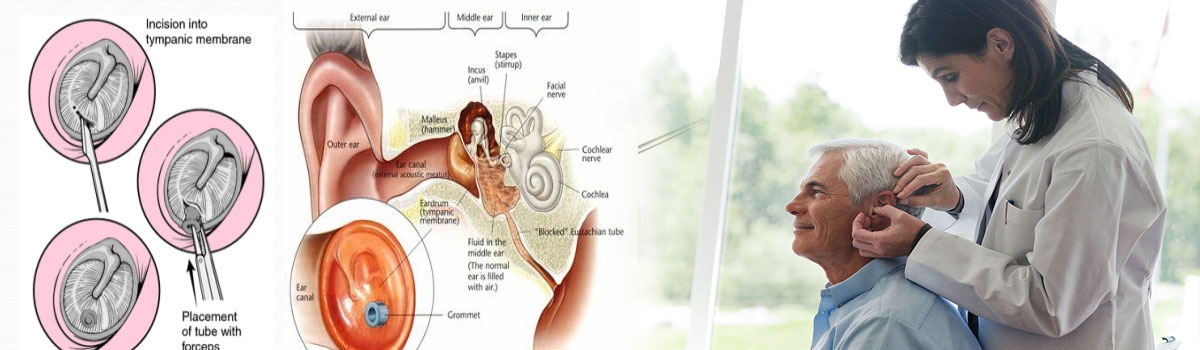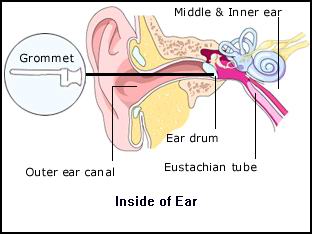
Grommet insertion, also known as tympanostomy tube placement or ventilation tube insertion, is a common surgical procedure used to treat persistent middle ear problems such as recurrent ear infections (otitis media) or chronic fluid accumulation behind the eardrum (otitis media with effusion). Grommets are tiny tubes placed through a small incision in the eardrum (tympanostomy) to ventilate the middle ear, equalize pressure, and facilitate drainage.
This procedure is widely performed in children but can also benefit adults with chronic ear problems. When the grommet has served its purpose, or complications arise, removal may be necessary. Understanding when grommets are needed, the procedure involved, potential complications, and living with grommets can help patients and caregivers make informed decisions.
This guide covers causes and risk factors for grommet insertion or removal, symptoms and signs warranting treatment, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, complications, and living with or after grommet surgery.
Indications for Grommet Insertion
-
Recurrent Acute Otitis Media (AOM): Multiple episodes of ear infection within a short time frame affecting quality of life.
-
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME): Persistent fluid in the middle ear lasting beyond 3 months causing hearing impairment.
-
Chronic Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Leading to poor middle ear ventilation and fluid build-up.
-
Hearing Loss: Conductive hearing loss from middle ear fluid affecting speech and language development in children.
-
Barotrauma: Middle ear pressure problems due to frequent flying or diving.
-
Chronic Middle Ear Infections: Resistant to medical management.
Risk Factors
-
Young age, especially children aged 1-3 years.
-
Family history of ear infections.
-
Exposure to tobacco smoke.
-
Attendance at daycare centers.
-
Allergic rhinitis or upper respiratory infections.
-
Craniofacial abnormalities (e.g., cleft palate).
-
Ear Pain or Discomfort: Persistent or recurrent earache.
-
Hearing Difficulties: Reduced hearing, delayed speech in children.
-
Ear Fullness or Pressure: Sensation of blocked ears.
-
Balance Problems or Dizziness: Occasionally related to middle ear issues.
-
Drainage from Ear (Otorrhea): Especially if persistent or foul-smelling.
-
Frequent Ear Infections: Despite antibiotics.
-
Visible Fluid or Retraction on Otoscopy: During examination by ENT.
-
Grommet Problems: Blockage, extrusion, or infection causing symptoms after insertion.
Clinical Evaluation
-
Comprehensive history of ear infections, hearing issues, and prior treatments.
-
Otoscopic examination: Assess eardrum mobility, presence of fluid, or grommet status.
-
Tympanometry: Objective test measuring middle ear pressure and eardrum compliance.
-
Audiometry: Hearing assessment especially important in children.
Additional Tests
-
Nasopharyngeal examination to exclude adenoidal hypertrophy or other obstructive causes.
-
Imaging (rarely needed) such as CT scan for complicated or recurrent cases.
Grommet Insertion Procedure
-
Usually performed under general anesthesia in children; local anesthesia may be used in adults.
-
Small incision (myringotomy) made in the eardrum.
-
Fluid suctioned from middle ear if present.
-
Grommet tube inserted to ventilate the middle ear.
-
Procedure typically lasts 10-15 minutes; patient usually discharged same day.
Grommet Removal
-
Grommets often fall out spontaneously after 6-18 months.
-
Removal recommended if grommet persists beyond recommended duration, causes infection, or malfunction.
-
Removal performed in clinic under local anesthesia or under general anesthesia if necessary.
Alternative Treatments
-
Antibiotics and nasal steroids for infection and inflammation.
-
Watchful waiting in mild or resolving cases.
-
Adenoidectomy may be combined with grommet insertion in some cases.
Prevention of Ear Infections and Fluid Build-Up
-
Avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke.
-
Breastfeeding infants, if possible, to enhance immunity.
-
Limiting daycare exposure during peak infection seasons.
-
Vaccination including pneumococcal and influenza vaccines.
-
Treating allergies promptly.
Management After Grommet Insertion
-
Keep ears dry; avoid swimming without ear protection.
-
Regular follow-up with ENT specialist.
-
Prompt treatment of any ear discharge or discomfort.
-
Monitoring hearing and speech development in children.
Possible Complications
-
Persistent Ear Discharge: Due to infection or tube blockage.
-
Premature Extrusion or Retention of Tubes: Tubes may fall out too early or remain too long.
-
Perforation of Eardrum: Rarely, eardrum may not heal properly after tube falls out or removal.
-
Scarring (Tympanosclerosis): White patches on eardrum that rarely affect hearing.
-
Cholesteatoma Formation: Rare abnormal skin growth behind eardrum.
-
Hearing Loss: Usually temporary; persistent loss rare.
-
Anesthesia Risks: In rare cases, related to sedation or general anesthesia.
Life with Grommets
-
Most children and adults tolerate grommets well.
-
Improved hearing, reduced infections, and better quality of life expected after insertion.
-
Ear protection important during swimming or bathing to prevent infection.
-
Some noise or sensation in the ear from the tube is normal initially.
After Grommet Removal
-
Eardrum usually heals completely within weeks.
-
Regular hearing assessments continue as needed.
-
Some individuals may require repeat insertion if infections recur.
-
Continued attention to preventive measures helps maintain ear health.
1. What is a grommet?
A grommet, also known as a tympanostomy tube or ear tube, is a small tube inserted into the eardrum to allow air to enter the middle ear and prevent fluid buildup.
2. Why is grommet insertion needed?
Grommet insertion is commonly performed to treat recurrent ear infections or persistent middle ear fluid (otitis media with effusion) that causes hearing loss or discomfort.
3. How is grommet insertion performed?
The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia for children and local anesthesia for adults. A small incision is made in the eardrum, and the grommet is inserted to ventilate the middle ear.
4. Is grommet insertion painful?
The procedure is painless due to anesthesia. Some mild discomfort or a feeling of fullness may occur after the surgery but usually resolves quickly.
5. How long do grommets stay in the ear?
Grommets typically stay in place for 6 to 12 months and often fall out naturally as the eardrum heals.
6. When is grommet removal necessary?
Grommet removal is usually not required unless complications arise. If needed, it is a minor procedure performed by an ENT specialist.
7. Are there any risks or complications of grommet insertion?
Risks include persistent ear drainage, infection, scarring of the eardrum, or the grommet becoming blocked or falling out prematurely.
8. How should I care for ears after grommet insertion?
Keep ears dry and avoid water entry during bathing or swimming unless waterproof earplugs are used. Follow your doctor’s advice on ear care and attend follow-up visits.
9. Can grommet insertion improve hearing?
Yes, grommets help restore normal air pressure and drainage in the middle ear, improving hearing in most cases.
10. How soon can children return to normal activities after grommet surgery?
Most children recover quickly and can return to normal activities within a day or two, but swimming and water exposure should be limited until the doctor confirms it is safe.
The other ENT Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Grommet Insertion or Removal are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Grommet Insertion Or Removal | Doctors For Grommet Insertion Or Removal | Cost For Grommet Insertion Or Removal | Treatment For Grommet Insertion Or Removal | Destinations For Grommet Insertion Or Removal | Risks Grommet Insertion Or Removal | Grommet Insertion Or Removal In India | Grommet Insertion Or Removal Recovery | Grommet Insertion Or Removal Information | Grommet Insertion Or Removal Thailand | Grommet Insertion Or Removal In Malaysia | Grommet Insertion Or Removal Abroad | Grommet Insertion Or Removal Overseas | Grommet Insertion Or Removal Low Cost | Grommet Insertion Or Removal In Singapore | Grommet Insertion Or Removal In Argentina | Surgery Grommet Insertion Or Removal | Grommet Insertion Or Removal In Singapore General Hospital | Grommet Insertion Or Removal In Apollo Hospitals | Grommet | Hollow Plastic Tube | Ear Drum | Hole In The Ear Drum | Myringotomy
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.