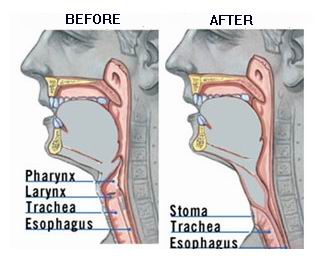
Laryngectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of the larynx, or voice box. It is most commonly performed to treat advanced laryngeal cancer but may also be necessary in cases of severe trauma, radiation failure, or certain benign conditions affecting the larynx. The surgery fundamentally alters the airway and vocal function by separating the airway from the mouth, nose, and esophagus.
While laryngectomy is a life-saving procedure, it profoundly impacts speech, breathing, and quality of life. Postoperative rehabilitation focuses on airway management, voice restoration, and adapting to new lifestyle challenges. Recent advances in surgical techniques and prosthetic devices have significantly improved outcomes and patient independence.
This detailed guide covers causes and risk factors leading to laryngectomy, symptoms and signs prompting the procedure, diagnostic processes, treatment options, prevention and postoperative management, potential complications, and living with a laryngectomy.
Common Causes Leading to Laryngectomy
-
Laryngeal Cancer:
The primary indication, particularly for advanced or recurrent tumors unresponsive to conservative treatments. -
Severe Laryngeal Trauma:
Injuries causing irreparable damage to the airway or vocal apparatus. -
Radiation Failure:
Tumors persisting or recurring after radiation therapy. -
Benign but Destructive Conditions:
Such as extensive papillomatosis or chronic infection causing airway compromise. -
Airway Obstruction:
From tumors or scarring impairing breathing.
Risk Factors for Laryngeal Cancer and Laryngectomy
-
Tobacco smoking, especially combined with alcohol consumption.
-
Exposure to occupational carcinogens like asbestos, wood dust.
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
-
Poor nutrition and low socioeconomic status.
-
Male gender and age over 50.
-
History of head and neck cancers.
-
Persistent Hoarseness or Voice Changes:
Often the earliest symptom of laryngeal cancer. -
Difficulty Breathing or Stridor:
Due to airway obstruction. -
Dysphagia:
Pain or difficulty swallowing. -
Chronic Cough or Hemoptysis:
Coughing up blood or persistent coughing. -
Neck Mass:
Enlarged lymph nodes indicating metastasis. -
Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue:
Signs of systemic illness. -
Failure to Respond to Conservative Treatments:
Persistent symptoms despite medical or radiation therapy.
Clinical Examination
-
Thorough head and neck examination including visualization of the larynx.
-
Flexible or rigid laryngoscopy to assess tumor extent and vocal cord mobility.
-
Palpation of cervical lymph nodes.
Imaging
-
CT Scan or MRI:
To evaluate tumor size, invasion of surrounding structures, and nodal involvement. -
PET Scan:
To detect metastasis or recurrent disease.
Biopsy and Histopathology
-
Tissue biopsy via direct laryngoscopy or office-based techniques confirms diagnosis.
Additional Tests
-
Pulmonary function tests to assess operative risk.
-
Blood tests and general medical evaluation.
Types of Laryngectomy
-
Partial Laryngectomy:
Removal of part of the larynx preserving voice and airway. -
Total Laryngectomy:
Complete removal of the larynx with permanent separation of airway and digestive tract. -
Supraglottic or Subglottic Laryngectomy:
Targeted resections depending on tumor location.
Surgical Procedure
-
Performed under general anesthesia.
-
Creation of a permanent tracheostoma (stoma) for breathing.
-
Removal of tumor-bearing tissues and often neck dissection for lymph nodes.
Adjuvant Therapies
-
Radiation or chemotherapy pre- or post-surgery to improve control.
-
Reconstructive surgeries for pharyngeal or esophageal defects.
Prevention
-
Smoking cessation programs.
-
Alcohol moderation.
-
Occupational safety and protective measures.
-
Early screening for high-risk individuals.
-
HPV vaccination.
Postoperative Management
-
Stoma care and airway hygiene education.
-
Voice rehabilitation with speech therapists (esophageal speech, electrolarynx, or tracheoesophageal puncture).
-
Nutritional support and swallowing therapy.
-
Psychological counseling to cope with changes.
-
Regular follow-up for cancer surveillance and management of complications.
Immediate Postoperative Complications
-
Bleeding and airway obstruction.
-
Wound infection or dehiscence.
-
Pharyngocutaneous fistula.
Long-Term Complications
-
Stoma stenosis or granulation tissue formation.
-
Voice prosthesis malfunction or displacement.
-
Swallowing difficulties or aspiration.
-
Psychological impact: depression, social isolation.
-
Respiratory infections due to altered airway.
Breathing and Airway Care
-
Learning stoma care to prevent infection and obstruction.
-
Avoidance of dust, smoke, and water entry into the stoma.
-
Use of humidifiers to keep mucosa moist.
Voice Rehabilitation
-
Electrolarynx: external device producing speech vibrations.
-
Esophageal speech: swallowing air to create sound.
-
Tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP): voice prosthesis enabling more natural speech.
Lifestyle Adjustments
-
Dietary modifications to aid swallowing.
-
Support groups and counseling for emotional wellbeing.
-
Workplace and social life adaptations.
-
Awareness of emergency procedures in case of stoma blockage.
1. What is a laryngectomy?
A laryngectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the larynx (voice box), typically performed to treat advanced laryngeal cancer or severe trauma.
2. Why is laryngectomy performed?
It is mainly done to remove cancerous tumors that affect the larynx and cannot be treated effectively with radiation or chemotherapy alone. It can also be necessary after severe injury or infection.
3. How does a laryngectomy affect breathing?
After laryngectomy, breathing is rerouted through a permanent opening in the neck called a stoma, bypassing the mouth and nose.
4. Will I be able to speak after a laryngectomy?
Speaking is affected because the vocal cords are removed. However, patients can learn alternative speech methods such as using an electrolarynx, esophageal speech, or tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP) voice prosthesis.
5. How is the laryngectomy surgery performed?
The surgery is done under general anesthesia and involves removing the larynx, creating a stoma for breathing, and sometimes reconstructing the surrounding tissues.
6. What is the recovery time after laryngectomy?
Hospital stay is typically 1 to 2 weeks, with full recovery taking several weeks to months, including rehabilitation for speech and swallowing.
7. Are there risks or complications associated with laryngectomy?
Risks include infection, bleeding, difficulty swallowing, changes in taste and smell, and complications related to the stoma. Proper care and follow-up help manage these risks.
8. How do I care for the stoma after laryngectomy?
The stoma requires regular cleaning to prevent infections, humidification to keep tissues moist, and protection from irritants such as dust and water.
9. Can laryngectomy patients eat and swallow normally?
Many patients can resume oral feeding but may require swallowing therapy and dietary modifications depending on the surgery extent.
10. How can I prepare for life after laryngectomy?
Preparation includes preoperative counseling, learning about speech rehabilitation options, stoma care training, and support from speech therapists and patient groups.
The other ENT Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Laryngectomy are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Laryngectomy | Doctors For Laryngectomy | Cost For Laryngectomy | Treatment For Laryngectomy | Destinations For Laryngectomy | Risks Laryngectomy | Laryngectomy In India | Laryngectomy Recovery | Laryngectomy Information | Laryngectomy Thailand | Laryngectomy In Malaysia | Laryngectomy Abroad | Laryngectomy Overseas | Laryngectomy Low Cost | Laryngectomy In Singapore | Laryngectomy In Argentina | Surgery Laryngectomy | Laryngectomy In Singapore General Hospital | Laryngectomy In Apollo Hospitals | Larynx Removal | Stoma | Tracheastomy | Radical Neck Dissection | Removal Of Lymph Nodes
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


