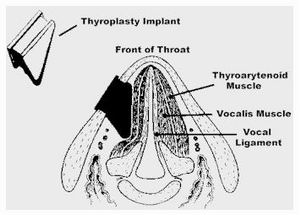
Voice restoration surgery, also known as thyroplasty, is a specialized surgical procedure designed to restore or improve the function of the voice in individuals who suffer from voice disorders. This surgery is particularly useful for people who have difficulty speaking due to vocal cord paralysis, voice strain, or other structural abnormalities affecting the voice box (larynx). The procedure helps in restoring the vocal cords' position or function, allowing for improved voice quality, volume, and clarity.
Thyroplasty was originally developed to address issues such as vocal cord paralysis or vocal cord insufficiency, which can occur as a result of nerve damage, aging, or trauma. Thyroplasty works by adjusting the position or tension of the vocal cords, improving their ability to produce sound. In some cases, it may also involve the implantation of a prosthesis to assist with vocal cord movement.
The goal of voice restoration surgery is not only to help individuals regain the ability to speak but also to enhance the quality of life for those whose careers or daily activities depend on clear and strong speech. It is often recommended for patients with vocal cord paralysis, presbyphonia (age-related voice changes), and other disorders that impair vocal cord function.
Voice disorders requiring thyroplasty often stem from structural issues in the vocal cords or damage to the nerve that controls them. Understanding the causes and risk factors that lead to the need for voice restoration surgery can help patients recognize early signs of voice problems and seek medical attention promptly.
Common Causes Leading to Thyroplasty:
-
Vocal Cord Paralysis:
-
One of the leading causes of vocal dysfunction is vocal cord paralysis, which occurs when the nerve that controls the vocal cords (recurrent laryngeal nerve) is damaged. This condition may be caused by surgery (especially neck or thyroid surgery), tumors, trauma, or neurological conditions. When the vocal cords cannot move correctly, it can result in a weak or breathy voice, or complete loss of voice.
-
-
Age-related Voice Changes (Presbyphonia):
-
As people age, the vocal cords tend to lose elasticity and strength, which can lead to a weaker, hoarser voice. This condition, known as presbyphonia, may cause difficulty in speaking clearly, especially in high-pitched or loud voices. Thyroplasty can be used to restore vocal cord function and improve the voice quality in elderly individuals.
-
-
Vocal Cord Atrophy:
-
Vocal cord atrophy occurs when the vocal cords lose muscle mass and become thin or weak. This condition can be exacerbated by long-term smoking, excessive alcohol use, or overuse of the voice. Thyroplasty can help reposition or augment the vocal cords to restore their function.
-
-
Vocal Cord Scarring:
-
Scarring of the vocal cords due to surgery, radiation therapy, or chronic inflammation (such as in cases of chronic laryngitis) can lead to a loss of flexibility and an inability to produce a clear sound. In these cases, thyroplasty can help by inserting a prosthesis or adjusting the vocal cords to improve sound production.
-
-
Neurological Conditions:
-
Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and multiple sclerosis can affect the nerves that control the vocal cords. This can lead to hoarseness, breathiness, or other voice impairments. Thyroplasty may be performed to improve the voice by restoring proper vocal cord movement.
-
-
Trauma or Injury to the Larynx:
-
Accidents or injuries to the neck, throat, or larynx can lead to damage of the vocal cords. In cases where the injury results in vocal cord paralysis or dysfunction, surgery may be necessary to restore voice function.
-
Risk Factors for Voice Disorders Requiring Thyroplasty:
-
Surgical Procedures Involving the Neck or Throat:
-
People who have undergone surgeries involving the neck, thyroid, or vocal cords are at risk of vocal cord damage due to unintended nerve injury.
-
-
Chronic Smoking and Alcohol Use:
-
Smoking irritates the vocal cords, leading to inflammation and scarring, while alcohol can dry out the throat, leading to long-term damage to vocal tissues. These habits increase the risk of developing voice issues.
-
-
Overuse of the Voice:
-
Professions that require heavy voice use, such as teaching, singing, or public speaking, can contribute to vocal cord fatigue and damage, making individuals more likely to need surgical intervention over time.
-
-
Age:
-
As individuals age, the laryngeal muscles and vocal cords naturally weaken. The elderly population is at a higher risk of developing voice disorders, including presbyphonia and vocal cord atrophy, which can often be improved through thyroplasty.
-
The need for voice restoration surgery is often recognized when a person begins to experience difficulty with speaking or has noticeable changes in their voice. If these symptoms persist or worsen over time, they may indicate the need for medical intervention, including thyroplasty.
Common Symptoms of Voice Disorders:
-
Hoarseness:
-
Hoarseness, or a raspy, breathy, or strained voice, is one of the most common symptoms that lead to thyroplasty. It can occur due to several underlying issues, such as vocal cord paralysis, scarring, or muscle weakness in the larynx.
-
-
Breathy or Weak Voice:
-
A weak or breathy voice, especially when speaking softly or for extended periods, may be caused by a lack of tension or movement in the vocal cords. This symptom can result from nerve damage or muscle atrophy.
-
-
Voice Fatigue:
-
Individuals who experience voice fatigue after speaking for a short period may suffer from vocal cord insufficiency. This can be caused by improper vocal cord closure, which may necessitate surgical intervention to restore proper function.
-
-
Difficulty Speaking at Higher Pitch:
-
A common symptom in elderly individuals with presbyphonia is the inability to speak in a higher pitch or reach certain vocal registers. This occurs when the vocal cords lose their ability to stretch and vibrate properly.
-
-
Loss of Voice:
-
A complete loss of voice (aphonia) can occur when the vocal cords are paralyzed or severely weakened. In cases of paralysis due to nerve damage, thyroplasty can help restore some degree of movement to the affected vocal cord.
-
-
Throat Clearing:
-
Frequent throat clearing may indicate an issue with vocal cord function, such as inflammation, scarring, or vocal cord paralysis. Individuals with these symptoms should consult an ENT specialist for evaluation.
-
-
Pain or Discomfort While Speaking:
-
Pain or discomfort when speaking or swallowing can suggest a problem with the vocal cords or surrounding structures. This is often a sign that surgical intervention, such as thyroplasty, may be needed.
-
Diagnosing the need for voice restoration surgery typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including an assessment of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and the underlying cause of the voice disorder. An ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist will conduct a comprehensive evaluation and may use several diagnostic tests to assess the function and condition of the vocal cords.
Diagnostic Process:
-
Medical History and Symptom Review:
-
The doctor will ask detailed questions about the patient’s symptoms, including the onset, duration, and severity of voice changes. A history of recent surgeries, trauma, or illnesses that may affect the vocal cords is also important.
-
-
Laryngoscopy:
-
Laryngoscopy is the primary diagnostic test used to visualize the vocal cords and surrounding structures. A flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the throat, allowing the doctor to directly observe the vocal cords’ movement, tension, and appearance. This procedure helps identify issues like vocal cord paralysis, scarring, or lesions.
-
-
Stroboscopy:
-
Stroboscopy is a specialized test used to assess the vibration and movement of the vocal cords. This technique involves using a strobe light to capture slow-motion images of the vocal cords in action, providing insight into their function and any irregularities in their movement.
-
-
Voice Evaluation:
-
A speech-language pathologist may perform a thorough voice evaluation, including assessing the patient’s vocal quality, pitch, resonance, and speaking patterns. This evaluation helps determine the impact of the voice disorder on communication and guides the need for surgery.
-
-
Imaging Studies:
-
In certain cases, CT scans or MRI may be used to assess the structures surrounding the larynx, particularly if there is concern about tumors, cysts, or other abnormal growths that may require surgical intervention.
-
The treatment for voice disorders that require thyroplasty varies based on the specific condition being treated. Thyroplasty is typically recommended when conservative treatments, such as voice therapy or medications, have not provided sufficient improvement.
Treatment Options:
-
Voice Therapy:
-
Before opting for surgery, voice therapy with a speech-language pathologist is often the first line of treatment for many vocal issues. Voice therapy aims to improve vocal cord function through exercises that strengthen the muscles of the larynx and improve breathing techniques.
-
-
Thyroplasty (Voice Restoration Surgery):
-
Thyroplasty involves surgically altering the vocal cords to improve their function. This may include adjusting the position of the vocal cords, adding volume or support, or removing tissue to restore normal movement. There are different types of thyroplasty, such as type I thyroplasty (vocal cord medialization) and type II thyroplasty (vocal cord repositioning).
-
-
Injections for Vocal Cord Paralysis:
-
In some cases of vocal cord paralysis, injections of collagen, fat, or hyaluronic acid may be used to plump up the paralyzed vocal cord, allowing for better closure during speech. These injections can improve vocal quality, although they may not provide long-term solutions.
-
-
Medications:
-
Medications, such as steroids or anti-inflammatory drugs, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation or treat underlying conditions like laryngitis or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) that contribute to voice problems.
-
-
Surgical Repositioning or Augmentation:
-
In cases where vocal cord repositioning is needed due to paralysis or atrophy, surgery may involve inserting an implant or prosthesis to improve vocal cord closure. Medialization thyroplasty, for example, is performed to reposition the vocal cords toward the midline to restore normal voice production.
-
Although not all voice disorders can be prevented, several lifestyle and health factors can reduce the risk of developing conditions that require thyroplasty.
Prevention and Management Strategies:
-
Avoid Overuse of the Voice:
-
Individuals who use their voice extensively should avoid vocal strain by taking regular breaks, staying hydrated, and using proper vocal techniques. This is especially important for teachers, singers, and public speakers.
-
-
Stop Smoking:
-
Smoking irritates the vocal cords and can lead to long-term damage, including vocal cord cancer, chronic laryngitis, and vocal cord paralysis. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of developing voice disorders.
-
-
Hydrate the Vocal Cords:
-
Staying hydrated is essential for vocal health. Drinking plenty of water keeps the vocal cords moist and flexible, preventing irritation and strain during speech.
-
-
Proper Voice Care:
-
Practicing good vocal hygiene, such as warming up before speaking or singing, avoiding whispering (which strains the voice), and limiting throat clearing, can help maintain vocal health.
-
Although thyroplasty is generally a safe procedure, like any surgery, it carries some risks. Potential complications include:
-
Infection:
-
As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site. Infections can usually be controlled with antibiotics if caught early.
-
-
Bleeding:
-
Bleeding can occur during or after the surgery, especially if the blood vessels in the vocal cords are damaged.
-
-
Voice Changes:
-
While the goal of thyroplasty is to improve the voice, there is a risk of unintended voice changes, such as a higher or lower pitch, or a different resonance.
-
-
Implant Rejection:
-
If a prosthetic implant is used to reposition the vocal cords, there is a slight risk of the body rejecting the implant or the implant shifting over time.
-
-
Damage to Surrounding Structures:
-
In rare cases, surrounding structures such as the nerves that control the vocal cords or the larynx may be injured during surgery, leading to further voice issues.
-
After undergoing thyroplasty or any other voice restoration surgery, patients must take steps to ensure a successful recovery and manage their voice health in the long term.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery:
-
Resting the Voice:
-
After surgery, it’s important to rest the voice to allow for healing. This may involve refraining from speaking, whispering, or singing for a specified period as advised by the doctor.
-
-
Voice Therapy:
-
Following surgery, voice therapy with a speech-language pathologist can help strengthen the vocal cords, improve technique, and ensure proper use of the voice.
-
-
Follow-up Appointments:
-
Regular follow-up visits with the ENT specialist are important to monitor recovery, check for any complications, and ensure that the desired improvements in voice quality have been achieved.
-
-
Lifestyle Adjustments:
-
Continued hydration, avoiding smoking, and minimizing vocal strain can help maintain the improvements made through surgery.
-
1. What is voice restoration surgery (thyroplasty)?
Voice restoration surgery, also known as thyroplasty, is a surgical procedure that aims to improve or restore the voice. It is performed to treat voice disorders caused by vocal cord paralysis, scarring, or structural abnormalities in the larynx (voice box). Thyroplasty involves altering the position or function of the vocal cords to improve sound production.
2. Why is thyroplasty performed?
Thyroplasty is performed to treat various conditions that affect voice quality, including vocal cord paralysis, weakness, or atrophy. It is often done when non-surgical treatments, such as speech therapy or vocal rest, have not been successful in improving voice function.
3. How is thyroplasty performed?
The surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision in the neck to access the thyroid cartilage and the vocal cords. The procedure may involve the insertion of a small implant or the repositioning of vocal cord structures to improve sound production and restore normal voice function.
4. Is thyroplasty painful?
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, so there is no pain during the procedure. Afterward, mild pain, throat soreness, or discomfort is common but usually resolves within a few days. Most patients can manage any discomfort with prescribed pain medications.
5. What is the recovery time after thyroplasty?
Recovery time generally varies from person to person, but most patients can resume normal activities within 1 to 2 weeks. Voice rest is crucial for the first few days to allow the vocal cords to heal. Full recovery and optimal voice quality may take a few months.
6. Are there risks or complications associated with thyroplasty?
Although rare, potential risks include infection, bleeding, voice changes, scarring, or damage to surrounding structures, such as the vocal cords, nerves, or the thyroid gland. The procedure is considered safe when performed by an experienced surgeon.
7. How should I prepare for thyroplasty?
Preparation involves a thorough medical evaluation, which may include imaging studies (such as a CT scan or laryngoscopy) and a voice assessment. You may need to avoid certain medications, such as blood thinners, prior to surgery. Fasting for several hours before the procedure is typically required.
8. Will my voice improve after thyroplasty?
For most patients, the procedure significantly improves voice quality, restoring clarity and strength to the voice. It can also reduce hoarseness or breathiness caused by vocal cord issues. However, the extent of improvement depends on the underlying condition and the type of surgery performed.
9. How long do the results of thyroplasty last?
The results of thyroplasty are typically long-lasting. In many cases, patients experience permanent improvements in their voice. However, in some instances, additional treatments or revisions may be needed, especially if there are changes to the vocal cords over time.
10. Can thyroplasty be repeated if necessary?
Yes, if the initial surgery does not fully restore voice function or if the vocal cords experience further issues, a secondary thyroplasty may be performed. Your doctor will assess your condition and recommend the best course of action.
The other ENT Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Voice Restoration Surgery (Thyroplasty) are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Voice Restoration Surgery| Doctors For Voice Restoration Surgery| Cost For Voice Restoration Surgery| Treatment For Voice Restoration Surgery| Destinations For Voice Restoration Surgery| Risks Voice Restoration Surgery| Voice Restoration Surgery In India | Voice Restoration Surgery Recovery | Voice Restoration Surgery Information | Voice Restoration Surgery Thailand | Voice Restoration Surgery In Malaysia | Voice Restoration Surgery Abroad | Voice Restoration Surgery Overseas | Voice Restoration Surgery Low Cost | Voice Restoration Surgery In Singapore | Voice Restoration Surgery In Argentina | Surgery Voice Restoration Surgery| Voice Restoration Surgery In Singapore General Hospital | Voice Restoration Surgery In Apollo Hospitals | Thyroplasty | Vocal Cord Weakness | Laryngeal Nerve
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



