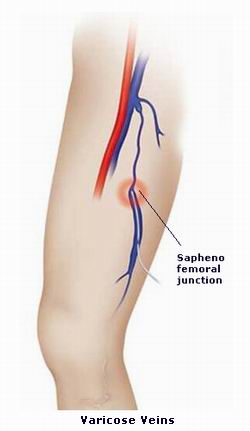
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted, and often painful veins, typically found on the legs and feet. These veins can become more prominent and may cause physical discomfort or aesthetic concerns. Although they are frequently associated with old age, varicose veins can affect anyone and may be exacerbated by lifestyle choices, underlying medical conditions, and hormonal changes.
In a healthy venous system, veins work by carrying deoxygenated blood from the body’s tissues back to the heart. Veins are equipped with one-way valves that ensure blood flows in the right direction. However, when these valves weaken or malfunction, blood begins to pool in the veins, causing them to stretch, bulge, and become visible under the skin. This is what leads to the characteristic appearance of varicose veins.
While varicose veins are typically not dangerous, they can lead to complications such as venous ulcers, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and chronic venous insufficiency if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and available treatment options is crucial for those suffering from the condition or at risk of developing it.
The formation of varicose veins is primarily attributed to vein valve malfunction , which can result from various causes and risk factors. Some of these factors are within our control, while others are linked to genetics or natural bodily processes.
Primary Causes of Varicose Veins:
-
Valve Dysfunction:
-
Healthy veins have one-way valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves become weak or damaged, blood can flow backward and pool in the veins, causing them to stretch and become varicose. This condition is often called venous reflux.
-
-
Increased Pressure on the Veins:
-
Increased pressure on the veins can occur due to prolonged standing or sitting, obesity, or pregnancy. This pressure can weaken the walls of the veins and lead to blood pooling, which worsens the appearance of varicose veins.
-
-
Hormonal Changes:
-
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can contribute to the development of varicose veins. Estrogen and progesterone relax the walls of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to damage.
-
-
Age:
-
As people age, the veins lose their elasticity, and the valves become weaker. This natural process increases the likelihood of developing varicose veins.
-
-
Pregnancy:
-
Pregnancy is a major risk factor for varicose veins due to increased blood volume and pressure from the growing uterus. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also relax vein walls, making them more prone to dilatation.
-
-
Genetics:
-
A family history of varicose veins increases the likelihood of developing them. Genetics can influence the strength of vein walls and valves, making some individuals more susceptible to vein problems.
-
-
Obesity:
-
Excess body weight places additional pressure on the veins, especially in the legs, and contributes to the development of varicose veins.
-
-
Prolonged Standing or Sitting:
-
Jobs or activities that require long periods of standing or sitting can contribute to the development of varicose veins. When standing, the pressure on the veins increases, causing blood to pool. Similarly, sitting for long periods can restrict circulation, worsening the condition.
-
-
Sedentary Lifestyle:
-
A lack of physical activity can lead to poor circulation, which is a risk factor for varicose veins. Regular movement, such as walking, helps blood circulation and reduces the risk of developing vein problems.
-
The symptoms of varicose veins vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. In many cases, varicose veins may cause no discomfort and are only a cosmetic concern. However, as the condition progresses, more severe symptoms can develop, affecting a person’s overall quality of life.
Key Symptoms and Signs:
-
Visible Swollen Veins:
-
The most obvious sign of varicose veins is the appearance of bulging, twisted veins under the skin, often appearing dark purple or blue. These veins are typically visible on the legs, especially behind the knees and along the inner thighs.
-
-
Pain, Heaviness, and Discomfort:
-
Many people with varicose veins experience aching or a feeling of heaviness in the affected legs, especially after long periods of standing or sitting. This discomfort can range from a dull, throbbing sensation to intense pain.
-
-
Leg Swelling:
-
Swelling (edema) in the legs and ankles is another common symptom. The swelling is often worse after prolonged periods of standing or sitting and may subside with rest or elevation.
-
-
Itchy Skin:
-
The skin over the varicose veins may become itchy or dry. This is often due to poor circulation, which can cause irritation and discomfort in the affected area.
-
-
Skin Discoloration:
-
Over time, the skin around the varicose veins may develop brownish or reddish discoloration, often near the ankles. This occurs due to the pooling of blood and poor circulation in the veins.
-
-
Restless Legs:
-
People with varicose veins may also experience restless leg syndrome (RLS), which causes an overwhelming urge to move the legs due to discomfort or tingling sensations, especially at night.
-
-
Throbbing or Burning Sensation:
-
Some individuals with varicose veins report a throbbing or burning sensation in the affected area, which can worsen with standing or walking.
-
-
Leg Cramps:
-
Muscle cramps in the legs, especially at night, are common in people with varicose veins due to poor circulation.
-
-
Bleeding:
-
In some cases, varicose veins can rupture and cause bleeding, especially when bumped or injured. This can occur with large, visible varicose veins that are located close to the skin's surface.
-
Varicose veins are typically diagnosed through a combination of a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic imaging. The doctor will evaluate the appearance of the veins, ask about symptoms, and may recommend additional tests to determine the extent of the condition and any associated complications.
Diagnostic Methods:
-
Physical Examination:
-
The doctor will begin by inspecting the legs and feet to check for visible varicose veins, swelling, and skin changes. They will also ask the patient about their symptoms, including pain, fatigue, and swelling in the legs.
-
-
Ultrasound:
-
The most common diagnostic test for varicose veins is doppler ultrasound. This non-invasive imaging technique uses sound waves to assess blood flow in the veins and detect problems such as venous reflux (backward blood flow) and vein wall damage.
-
-
Venography:
-
Venography is a diagnostic procedure that involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins and taking X-ray images to evaluate blood flow. This method is used in rare cases when more detailed images are needed or when ultrasound results are inconclusive.
-
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
-
In some cases, an MRI may be performed to examine the veins in greater detail, particularly if the varicose veins are large or involve deeper veins.
-
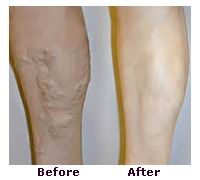
The treatment for varicose veins depends on the severity of the condition, symptoms, and the presence of any complications. Mild varicose veins may be managed with lifestyle changes and conservative treatments, while more severe cases may require medical or surgical intervention.
Conservative Treatment:
-
Compression Stockings:
-
Compression stockings are the most common non-invasive treatment for varicose veins. These stockings provide gentle pressure on the legs, which helps improve circulation, reduce swelling, and alleviate pain. They come in different compression levels and can be purchased over the counter or prescribed by a doctor.
-
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, helps improve circulation and prevent blood from pooling in the veins.
-
Leg Elevation: Elevating the legs above the heart can reduce swelling and improve circulation. Aim to elevate the legs for 20 minutes a few times a day.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the pressure on your veins, preventing the development or worsening of varicose veins.
-
Avoiding Prolonged Standing or Sitting: If your job or lifestyle involves standing or sitting for long periods, take breaks every 30-60 minutes to move around and promote circulation.
-
Minimally Invasive Treatments:
-
Sclerotherapy:
-
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a special solution into the varicose veins, which causes the veins to collapse and eventually fade. This procedure is commonly used for smaller veins or spider veins.
-
-
Laser Treatment:
-
Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT) uses laser energy to close off the affected veins. The laser is delivered through a small catheter inserted into the vein, and the heat from the laser causes the vein to collapse and be absorbed by the body.
-
-
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA):
-
Radiofrequency ablation is similar to laser therapy, but it uses radiofrequency energy to heat and close the varicose veins. This minimally invasive procedure is highly effective and has a quick recovery time.
-
Surgical Treatment:
-
Vein Stripping:
-
Vein stripping is a traditional surgical procedure where the affected vein is removed through small incisions. This method is typically reserved for large varicose veins that cannot be treated with minimally invasive techniques.
-
-
Ambulatory Phlebectomy:
-
Ambulatory phlebectomy is a procedure where small incisions are made in the skin to remove large surface veins. It is done under local anesthesia and is suitable for veins that are too large for sclerotherapy or laser treatment.
-
While varicose veins cannot always be prevented, there are several lifestyle adjustments and interventions that can help reduce the risk of developing the condition or minimize symptoms for those already affected.
Preventive Measures:
-
Stay Active:
-
Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, promotes healthy circulation and helps prevent blood from pooling in the veins. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
-
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
-
Excess body weight places added pressure on the veins, particularly in the legs. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the strain on the veins and prevent varicose veins.
-
-
Elevate Your Legs:
-
Elevating your legs above the level of your heart can reduce swelling and improve circulation. Try elevating your legs for 20 minutes a few times a day.
-
-
Avoid Prolonged Standing or Sitting:
-
If you have a job that requires standing for long periods, take breaks every 30 minutes to move around. Similarly, avoid sitting with your legs crossed for long periods, as this can restrict blood flow.
-
-
Wear Compression Stockings:
-
Compression stockings can help prevent varicose veins and manage symptoms in individuals who are at risk.
-
While varicose veins are usually not life-threatening, untreated or severe cases can lead to complications that can significantly affect a person’s health.
Potential Complications:
-
Skin Ulcers:
-
Venous ulcers can develop near the ankles as a result of poor circulation and chronic inflammation in the veins. These ulcers are painful and can be difficult to heal.
-
-
Blood Clots (Thrombophlebitis):
-
Varicose veins can increase the risk of blood clots, which can cause thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the vein). In more severe cases, clots can travel to the lungs, leading to a pulmonary embolism, which is life-threatening.
-
-
Bleeding:
-
Large varicose veins are prone to rupturing and bleeding, especially when bumped or injured. Even minor trauma can lead to significant bleeding from the affected vein.
-
-
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI):
-
Chronic venous insufficiency occurs when the veins are no longer able to return blood to the heart effectively. This condition causes symptoms such as swelling, leg fatigue, and skin changes. If left untreated, CVI can lead to leg ulcers and other complications.
-
Managing varicose veins involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, treatments, and regular monitoring. While the condition is typically not dangerous, it can lead to significant discomfort if left untreated.
Managing Varicose Veins:
-
Lifestyle Adjustments:
-
Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and elevating your legs can significantly reduce symptoms and improve circulation.
-
-
Follow-up Care:
-
For those who have undergone treatment, follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the condition of the veins and to ensure that symptoms are well-managed.
-
-
Coping with Emotional Impact:
-
The appearance of varicose veins can affect self-esteem, especially if the veins are large or visible. Support groups and counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of living with varicose veins.
-
1. What are varicose veins?
Varicose veins are enlarged, swollen, and twisted veins that often appear on the legs and feet. They occur when the valves in the veins, which help blood flow toward the heart, become weakened or damaged, leading to blood pooling and causing the veins to become visible and distended.
2. What causes varicose veins?
Varicose veins are caused by a combination of factors that lead to increased pressure in the veins, including:
-
Genetics: A family history of varicose veins increases the risk.
-
Age: As you get older, the veins may lose elasticity, causing them to stretch and weaken.
-
Pregnancy: Increased blood volume and hormonal changes can contribute to varicose veins.
-
Prolonged standing or sitting: Jobs that require long periods of standing or sitting can put pressure on the veins.
-
Obesity: Excess weight can put added pressure on the veins.
3. What are the symptoms of varicose veins?
The symptoms of varicose veins can include:
-
Swollen, twisted, or bulging veins, often visible under the skin.
-
Aching, throbbing, or a heavy feeling in the legs.
-
Itching or skin changes near the affected veins.
-
Cramping or restlessness in the legs, especially at night.
-
In severe cases, ulcers or skin sores may develop near the varicose veins.
4. Are varicose veins dangerous?
In most cases, varicose veins are more of a cosmetic concern and are not dangerous. However, in some instances, they can lead to complications, such as:
-
Blood clots: Varicose veins can increase the risk of developing blood clots (deep vein thrombosis).
-
Ulcers: Painful skin sores may develop around the varicose veins.
-
Bleeding: Varicose veins close to the skin's surface can rupture and bleed, especially after injury.
5. How are varicose veins diagnosed?
Varicose veins are typically diagnosed through a physical examination. In some cases, your doctor may recommend a duplex ultrasound, which is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to check blood flow and detect any abnormalities in the veins, such as blood clots or valve failure.
6. What are the treatment options for varicose veins?
There are several treatment options for varicose veins, depending on the severity and symptoms:
-
Compression stockings: These stockings help improve circulation and reduce swelling.
-
Lifestyle changes: Elevating the legs, regular exercise, and weight management can help reduce symptoms.
-
Sclerotherapy: A treatment where a solution is injected into the veins, causing them to collapse and fade away.
-
Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT): A laser is used to seal the affected veins.
-
Vein stripping: A surgical procedure to remove or tie off the damaged veins.
7. What is sclerotherapy?
Sclerotherapy is a common treatment for varicose veins in which a special solution is injected into the affected veins. This solution irritates the vein walls, causing them to collapse and eventually fade. It is typically used for smaller varicose veins and spider veins and can be done in a doctor's office with little downtime.
8. Can varicose veins be prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent varicose veins, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk:
-
Stay active: Regular exercise helps improve circulation and strengthen vein walls.
-
Maintain a healthy weight: Reducing excess weight can lessen pressure on the veins.
-
Avoid prolonged periods of standing or sitting: Take breaks and move around to improve blood flow.
-
Wear compression stockings: These help prevent swelling and support the veins.
9. What is the recovery time after varicose vein treatment?
Recovery time after varicose vein treatment depends on the method used. For minimally invasive treatments like sclerotherapy or endovenous laser treatment, most people can return to normal activities within a few days to a week. For more invasive procedures like vein stripping, recovery may take a few weeks, and you may need to avoid heavy exercise or lifting during this time.
10. Are varicose veins common?
Yes, varicose veins are very common, especially among adults. It is estimated that about 1 in 4 adults will develop varicose veins during their lifetime. They are more common in women than men, particularly during or after pregnancy, and the risk increases with age.
The other general surgical procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Varicose vein therapy are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Varicose Veins | Hospitals For Varicose Veins Treatment | Doctors Varicose Veins Treatment | Surgery Varicose Veins | Cost Of Varicose Veins Treatment | Treatment For Varicose Veins | Destinations For Varicose Veins Treatment | Risks Varicose Veins Treatment | Varicose Vein Treatments In India | Varicose Veins Recovery | Varicose Veins Information | Varicose Veins Treatment Thailand | Varicose Veins Treatments Malaysia | Varicose Veins Treatments Abroad | Varicose Vein Treatment Overseas | Varicose Veins Low Cost Treatment | Varicose Vein Treatment In Singapore | Enlarged Veins | Surgical Vein Stripping | Sclerotherapy | Endovenous Ablation Therapy | Ulcers | Phlebitis | Embolism | Deep Venous Thrombosis
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



