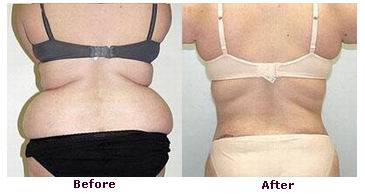
Abdominoplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at removing excess skin and fat from the abdominal area and tightening the abdominal muscles. It is particularly beneficial for people who have lost significant weight or women who have gone through pregnancy. In these cases, the skin and muscles often lose elasticity and become stretched, which can result in a sagging or protruding belly.
This procedure can significantly enhance physical appearance, improve posture, and in some cases, provide relief from discomfort or irritation caused by excess abdominal skin.
Why Choose Abdominoplasty?
-
Cosmetic Enhancement: One of the main reasons people choose abdominoplasty is to enhance their physical appearance. After weight loss or pregnancy, the skin often loses its ability to shrink back, and a tummy tuck can help smooth and tighten the abdomen, providing a firmer contour.
-
Restore Muscle Tone: Pregnancy and weight fluctuations can lead to muscle separation (diastasis recti), which weakens the abdominal wall. Abdominoplasty not only removes excess skin and fat but also tightens the underlying muscles, improving abdominal tone.
-
Posture and Back Support: As the abdominal muscles are tightened, many people notice improved posture and less back pain, as a strong abdominal wall supports the spine more effectively.
While abdominoplasty is often sought for aesthetic reasons, several causes and risk factors contribute to the need for this surgery. These factors are typically related to pregnancy, significant weight loss, aging, and genetics.
Causes for Considering Abdominoplasty
-
Pregnancy:
-
Pregnancy can cause significant changes to the abdominal area. The skin stretches to accommodate the growing fetus, and the abdominal muscles can become separated. After childbirth, some individuals find it difficult to regain pre-pregnancy abdominal shape, especially if the skin has lost its elasticity.
-
Abdominoplasty can help remove excess skin, tighten the muscles, and restore the abdominal contour that may be lost during pregnancy.
-
-
Significant Weight Loss:
-
Bariatric surgery or other methods of weight loss can lead to excess skin hanging around the abdomen. For people who have lost a large amount of weight, abdominoplasty can remove the sagging skin and help the person achieve a more proportionate body shape.
-
After extreme weight loss, the skin may not have the elasticity to tighten on its own, leading to permanent skin folds or sagging, which can be corrected through surgery.
-
-
Aging:
-
As we age, the skin loses its elasticity and the muscles weaken, which can cause the abdomen to sag. This natural aging process can lead to a protruding belly, making abdominoplasty a viable option to reverse these effects.
-
-
Genetics:
-
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to have weaker abdominal muscles or skin that is more prone to sagging. This means that even without significant weight gain or pregnancy, some people might develop loose skin or muscle weakness in the abdominal region.
-
Risk Factors for Abdominoplasty
-
Obesity:
-
People who are overweight or obese have a higher chance of developing sagging skin and weakened muscles in the abdominal region. While weight loss should be achieved before surgery, morbid obesity may increase risks of complications during surgery.
-
-
Previous Surgeries:
-
Individuals who have had abdominal surgeries in the past, such as C-sections, appendectomies, or other abdominal procedures, may have scarring or weakened muscles in the abdominal area, making them more likely to benefit from a tummy tuck.
-
-
Poor Skin Elasticity:
-
People with poor skin elasticity—whether due to genetics, pregnancy, or aging—are more likely to have sagging skin that doesn’t tighten well on its own.
-
-
Health Conditions:
-
Certain conditions, like diabetes or heart disease, may increase the risks during surgery and require closer monitoring. Pre-existing health conditions must be evaluated by the surgeon before proceeding.
-
Abdominoplasty is typically sought when individuals experience significant symptoms or signs due to sagging skin, muscle separation, or excess fat in the abdominal region. Commonly, these symptoms indicate the need for surgery:
Signs That May Indicate the Need for Abdominoplasty
-
Excess Skin:
-
One of the most common signs of needing a tummy tuck is the presence of loose or hanging skin on the abdomen that doesn’t respond to diet or exercise.
-
-
Stretched or Weakened Muscles:
-
Muscle separation (diastasis recti) after pregnancy or weight loss can cause the abdominal muscles to stretch or weaken, leading to a protruding abdomen. This muscle weakness can cause discomfort, and in some cases, difficulty with physical activities like bending or lifting.
-
-
Persistent Abdominal Fat:
-
Some individuals may have stubborn fat deposits in the abdominal area that do not respond well to exercise or diet, despite overall weight loss.
-
-
Difficulty Wearing Certain Clothing:
-
Individuals may feel self-conscious about the appearance of their abdomen, particularly if they have excess skin that makes it difficult to wear certain clothes or swimwear comfortably.
-
-
Back Pain and Postural Issues:
-
For some people, excess abdominal skin and weak abdominal muscles can cause back pain and postural problems. The excess weight from sagging skin may contribute to discomfort or difficulty in maintaining proper posture.
-
-
Skin Rashes or Irritation:
-
Excess skin folds can cause skin irritation, rashes, or fungal infections, especially in hot, humid weather, making abdominoplasty an effective solution for this issue.
-
The decision to undergo abdominoplasty is typically made after a thorough consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon will assess the patient's goals, physical condition, and any medical history to determine if the surgery is appropriate.
Diagnostic and Pre-Surgical Steps
-
Physical Examination:
-
The surgeon will examine the abdominal area, assessing the amount of excess skin, fat, and muscle tone. This helps to determine the extent of the surgery required.
-
-
Health Evaluation:
-
The surgeon will assess the patient's overall health by reviewing their medical history. Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or obesity can impact the healing process and require additional attention.
-
-
Weight Stability:
-
Candidates should have achieved a stable weight for at least six months prior to surgery. Significant weight fluctuations can affect the outcome of the procedure.
-
-
Discussion of Goals:
-
The surgeon will ask about your aesthetic goals and expectations, ensuring they are realistic and achievable. It’s essential to have a clear understanding of the results you desire.
-
The main treatment for individuals with excess abdominal skin and weakened muscles is abdominoplasty surgery. However, the specific approach to the surgery will vary depending on the extent of the problem.
Surgical Treatment Options
-
Full Abdominoplasty (Traditional Tummy Tuck):
-
The most common form of abdominoplasty involves a larger horizontal incision made across the lower abdomen. The surgeon will remove excess skin and fat, tighten the abdominal muscles, and reposition the skin for a smoother, firmer appearance.
-
-
Mini Abdominoplasty:
-
A mini tummy tuck is less invasive and involves a smaller incision. It is suitable for individuals with only a small amount of excess skin in the lower abdomen.
-
-
Extended Abdominoplasty:
-
For those who have experienced significant weight loss, an extended tummy tuck may be necessary. This involves a larger incision and may address not only the abdomen but also the flanks and sides of the body.
-
-
Liposuction:
-
Liposuction may be performed in conjunction with abdominoplasty to remove stubborn fat deposits, creating a more sculpted abdominal area. It is often used in individuals who still have localized fat, even after weight loss.
-
-
Lipoabdominoplasty:
-
Lipoabdominoplasty is a combination of liposuction and abdominoplasty, allowing for better contouring of the abdomen while also removing excess fat.
-
While it is not possible to prevent the need for abdominoplasty in cases where significant weight loss, pregnancy, or aging has occurred, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent further abdominal issues and support the results of surgery.
Pre-Operative Management
-
Stable Weight:
-
Maintaining a stable weight for several months before surgery is crucial to achieving the best results. Large fluctuations in weight can compromise the surgical outcome.
-
-
Healthy Diet and Exercise:
-
A balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce excess fat in the abdomen, improve skin elasticity, and strengthen muscles.
-
-
Quit Smoking:
-
Smoking reduces blood flow and impairs healing, so it is essential to quit smoking several weeks before and after surgery.
-
-
Avoid Alcohol:
-
Alcohol can interfere with healing and increase the risk of complications. It should be avoided before and after surgery.
-
Post-Operative Management
-
Compression Garment:
-
A compression garment is typically worn after surgery to help reduce swelling, support the abdominal area, and improve the contour.
-
-
Wound Care:
-
Proper wound care is essential to avoid infection and promote healing. Follow your surgeon's instructions on cleaning and dressing the surgical site.
-
-
Rest and Recovery:
-
Avoid strenuous activities for several weeks following surgery. Resting and allowing the body to heal are critical during this phase.
-
While abdominoplasty is generally a safe procedure, there are risks involved, like any major surgery. Complications can arise, especially if proper post-operative care is not followed.
Potential Complications
-
Infection:
-
As with any surgery, infection is a potential risk. Following proper hygiene and care instructions is essential to minimize this risk.
-
-
Seroma or Hematoma:
-
A seroma is a collection of fluid, while a hematoma is a collection of blood under the skin. Both can occur after surgery and may require drainage.
-
-
Scarring:
-
The incision will leave a scar, though the surgeon will place it in a discreet location to minimize its visibility. Scarring can vary depending on the extent of the surgery.
-
-
Blood Clots:
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) can occur after surgery. Preventive measures, such as early mobilization and compression garments, can help reduce this risk.
-
-
Poor Wound Healing:
-
Some individuals may experience poor wound healing, particularly if they have underlying health conditions or don’t follow post-surgical care instructions.
-
After undergoing abdominoplasty, most individuals experience a significant improvement in their appearance and self-esteem. However, continued care and lifestyle modifications are essential to maintain the results.
Post-Surgery Lifestyle
-
Exercise and Physical Activity:
-
Light physical activity can be resumed after a few weeks. However, strenuous exercise should be avoided for at least six weeks to allow the body to heal properly.
-
-
Dietary Modifications:
-
A healthy diet is essential to maintaining the results of your surgery. Consuming nutrient-dense foods and staying hydrated supports the healing process and helps maintain weight.
-
-
Regular Follow-Ups:
-
Follow-up appointments with your surgeon are necessary to monitor the healing process, address any concerns, and ensure that complications are addressed promptly.
-
1. What is abdominoplasty (tummy tuck)?
Abdominoplasty, commonly known as a tummy tuck, is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to remove excess skin and fat from the abdomen while tightening the muscles of the abdominal wall. This procedure is often sought by individuals who have excess abdominal skin or weakened muscles due to pregnancy, significant weight loss, or aging.
2. Why would I need an abdominoplasty?
Abdominoplasty is typically considered for individuals who:
-
Have loose or sagging skin after significant weight loss or pregnancy.
-
Experience separation of abdominal muscles (diastasis recti) following pregnancy or weight fluctuations.
-
Want to achieve a flatter, more toned abdomen.
-
Struggle with excess skin folds or stretch marks in the abdominal area.
3. How is an abdominoplasty performed?
The procedure involves several steps:
-
The surgeon makes an incision, usually just above the pubic area, from hip to hip.
-
Excess fat and skin are removed, and the abdominal muscles are tightened to restore the contour of the abdomen.
-
In some cases, a small incision around the belly button is required for repositioning.
-
The incision is closed with sutures, and drains may be placed temporarily to remove excess fluid.
4. What are the different types of abdominoplasty?
There are several variations of abdominoplasty:
-
Full abdominoplasty: Involves a large incision from hip to hip and addresses the entire abdomen, including the upper and lower sections.
-
Mini abdominoplasty: A smaller incision is made, usually in the lower abdomen, and is ideal for individuals with minimal excess skin.
-
Extended abdominoplasty: A more extensive procedure that also addresses the flanks (love handles) and may be necessary for those with significant weight loss.
-
Circumferential abdominoplasty: Also known as a lower body lift, this procedure targets the abdomen, buttocks, and thighs.
5. Is abdominoplasty painful?
While abdominoplasty is a major surgery, it is typically performed under general anesthesia, so there is no pain during the procedure. After surgery, patients can experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort for several days to weeks. Pain management strategies, including prescription medications, are provided to keep discomfort under control. Most patients report feeling some soreness in the abdomen during recovery.
6. How long is the recovery time after abdominoplasty?
The initial recovery period typically lasts around 2 to 3 weeks, during which you may need to take time off from work and avoid strenuous activities. Swelling and bruising can last for several weeks, and full recovery can take 3 to 6 months, depending on the extent of the surgery. Most patients can return to light activities after 4 to 6 weeks and gradually resume more strenuous exercises after 2 to 3 months.
7. What are the risks and complications of abdominoplasty?
Like all surgeries, abdominoplasty carries some risks, including:
-
Infection at the incision site.
-
Bleeding during or after surgery.
-
Scarring, which may be permanent but can usually be hidden by clothing or a bikini.
-
Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT), especially if post-surgery mobility is limited.
-
Poor wound healing or skin necrosis in rare cases.
-
Changes in sensation around the incision site.
These risks can be minimized by choosing an experienced surgeon and following pre- and post-operative care instructions.
8. How long do the results of an abdominoplasty last?
The results of an abdominoplasty are generally long-lasting, particularly if patients maintain a healthy weight. However, significant weight gain, pregnancy, or the natural aging process can impact the appearance of the abdomen over time. To preserve the results, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle with proper diet and exercise.
9. Will abdominoplasty get rid of stretch marks?
Abdominoplasty can improve the appearance of stretch marks, especially those located on the lower abdomen, as excess skin is removed. However, stretch marks above the belly button may not be significantly improved unless they are directly affected by the surgery. The surgery does not completely eliminate all stretch marks, but it can make them less noticeable.
10. Is abdominoplasty covered by insurance?
Abdominoplasty is typically considered a cosmetic procedure, and as such, it is not covered by insurance. However, if the procedure is deemed medically necessary (for example, if the excess skin causes functional issues like rashes or infections), some insurance providers may offer partial coverage. It’s important to check with your insurance provider to determine if you qualify for coverage.
The other general procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Abdominoplasty are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Abdominoplasty | Hospitals Abdominoplasty | Doctors Abdominoplasty | Surgery Abdominoplasty | Cost Of Abdominoplasty | Treatment For Abdominoplasty | Destinations For Abdominoplasty | Risks Abdominoplasty | Abdominoplasty India | Abdominoplasty Recovery | Abdominoplasty Information | Abdominoplasty Thailand | Abdominoplasty Malaysia | Abdominoplasty Abroad | Abdominoplasty Overseas | Abdominoplasty Low Cost | Abdominoplasty Singapore | Apronectomy | Tummy Tuck | Partial Tummy Tuck | Full Tummy Tuck
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



