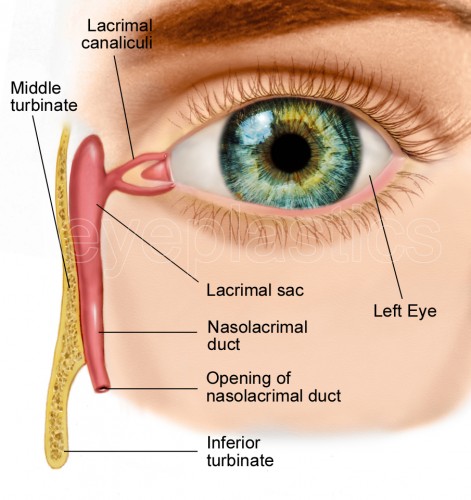
Canalicular tear repair refers to a surgical procedure designed to address injuries or damage to the canaliculi (small ducts) of the lacrimal system, which is responsible for tear drainage from the eyes. The lacrimal system includes the tear ducts that carry tears from the eyes into the nose. A canalicular tear can occur due to trauma, injury, or congenital abnormalities, disrupting the tear drainage process and leading to excessive tearing (epiphora) or even more severe complications if left untreated.
The lacrimal canaliculi are delicate structures located in the inner corner of the eye, and tears flow through them to the nasolacrimal duct, ultimately draining into the nasal cavity. Canalicular tears can occur from facial trauma, especially fractures or sharp objects, or following surgical procedures that affect the delicate lacrimal system. If left untreated, these tears can lead to chronic eye infections, tearing, or even permanent damage to the tear drainage system.
The primary goal of canalicular tear repair is to restore the normal function of the tear ducts, relieve symptoms, and prevent long-term complications. Depending on the severity of the tear, the procedure may be performed using various surgical methods, including canaliculodacryocystorhinostomy (CDCR), or simple suturing if the tear is more localized.
Canalicular tears are primarily caused by trauma or injury to the lacrimal system, although other underlying factors may contribute. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with canalicular tears helps in the early identification of individuals who may need repair procedures.
1. Trauma and Injury
-
Facial Trauma: One of the most common causes of canalicular tears is facial trauma, which can occur due to accidents, sports injuries, or falls. Trauma to the eye socket or cheekbones can lead to fractures that disrupt the lacrimal system and cause damage to the canaliculi.
-
Sharp Objects: Injuries involving sharp objects, such as knives, branches, or other foreign bodies, can puncture or tear the delicate canaliculi, leading to significant damage.
-
Post-Surgical Complications: Sometimes, surgical procedures around the eyes, particularly blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery) or facial fracture repairs, may inadvertently damage the canaliculi, leading to a tear or obstruction.
2. Congenital Abnormalities
Some individuals are born with congenital defects in the lacrimal system, which predispose them to tear duct malfunctions. These abnormalities may lead to incomplete or improperly formed canaliculi, making them more susceptible to tears or blockages, even without significant trauma.
3. Age and Gender
While canalicular tear repair can affect anyone, older adults are at greater risk due to the natural decline in tissue elasticity and the increased likelihood of trauma. Women may also be at higher risk because of cosmetic surgeries (such as blepharoplasty) which are more common among females.
4. Chronic Infections
Recurrent infections of the lacrimal system, such as dacryocystitis (inflammation of the tear sac), may weaken the tissue structure, making the canaliculi more prone to tearing or rupturing during external trauma.
5. Tumors or Growths
Though less common, benign or malignant tumors affecting the lacrimal system can lead to structural changes or blockages that predispose the canaliculi to tears. If untreated, these growths can exert pressure on the delicate duct system.
The symptoms of a canalicular tear depend on the severity of the injury and the area of the lacrimal system that is affected. When there is a canalicular tear, the patient may experience several discomforting signs, including:
1. Epiphora (Excessive Tearing)
-
Epiphora is one of the most common symptoms of canalicular tears. When the tear ducts are damaged, they may fail to drain tears properly, leading to excessive tearing. Patients may notice that their eyes water frequently or uncontrollably, particularly when they are exposed to bright light, wind, or strong emotions.
2. Pain and Discomfort
-
Pain around the inner corner of the eye, especially after trauma, is common. The pain may be sharp or aching and may worsen with movement of the eye. Swelling around the tear duct area is also a typical sign of injury to the lacrimal system.
3. Infections
-
Canalicular tears often result in the formation of infections in the tear drainage system, leading to symptoms like redness, swelling, pus discharge, and pain. These infections occur because stagnant tears cannot drain properly, leading to the accumulation of bacteria.
4. Blocked Tear Ducts
-
If the tear duct is partially blocked due to trauma, you may notice a partial drainage issue. This could result in watery eyes, blurred vision, and discomfort. Chronic blockage can lead to the accumulation of mucus or pus, causing further complications.
5. Visible Tear Duct Damage
-
In some cases, the injury or tear to the lacrimal system may be visible. The tear duct may appear swollen, bruised, or discolored at the inner corner of the eye. There may also be external scars visible after trauma.
6. Vision Issues
-
If the tear ducts are affected in conjunction with nearby tissues or structures, patients may also experience vision problems due to the physical proximity of the canaliculi to the cornea and optic nerve. However, vision issues are not always directly related to canalicular tears.
Diagnosing a canalicular tear typically requires a thorough ocular examination and a combination of diagnostic imaging techniques. The ophthalmologist will assess the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and potential causes for the tear.
1. Comprehensive Eye Examination
-
During the eye exam, the doctor will visually inspect the tear duct area to identify any signs of swelling, bruising, or visible damage to the canaliculi. They may also press gently on the tear sac to check for signs of pus or excessive tearing.
2. Fluorescein Dye Test
-
A fluorescein dye test involves placing a small amount of dye into the eye to assess the drainage of the tear duct. The presence of dye in the nose confirms that the lacrimal system is functioning properly. If the dye does not drain, it suggests a blockage or tear in the system.
3. Canaliculography
-
Canaliculography is a specialized imaging technique that involves injecting dye into the tear duct system and taking X-ray images. This method helps visualize the precise location and extent of the tear or blockage, allowing the surgeon to plan the appropriate repair procedure.
4. CT or MRI Scans
-
In cases of significant trauma, CT scans or MRI imaging may be employed to assess the degree of damage to the tear ducts and surrounding tissues, especially if the injury involves fractures or other complex eye structures.
The primary goal of canalicular tear repair is to restore proper tear drainage, prevent infections, and preserve the integrity of the lacrimal system. The treatment approach depends on the severity of the tear and the presence of any other complications.
1. Suture Repair
-
For localized or minor canalicular tears, suture repair can be performed. The surgeon may use specialized stitches to reattach the canaliculi, ensuring that the tear duct is restored to its normal position. This is typically done under local anesthesia and can be performed in an outpatient setting.
2. Canaliculodacryocystorhinostomy (CDCR)
-
In more severe cases, particularly when there is significant damage to the tear duct or surrounding tissues, canaliculodacryocystorhinostomy (CDCR) may be necessary. This procedure involves creating a new passage between the tear sac and the nasal cavity, bypassing the damaged canaliculi. A silicone tube may be placed temporarily to ensure proper drainage during healing.
3. Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)
-
DCR is another surgical procedure used to bypass blocked or damaged tear ducts by creating a new drainage route from the lacrimal sac to the nasal cavity. This is a more complex procedure and may be necessary for patients with severe damage.
4. Silicone Tube Placement
-
A silicone tube may be temporarily inserted into the canaliculi to keep the tear ducts open and facilitate proper drainage during the healing process. This tube is usually removed after several months, depending on the extent of the repair.
5. Endoscopic Repair
-
In certain cases, endoscopic surgery may be performed to repair the canaliculi without making large incisions. This minimally invasive approach can be effective for certain types of tears, especially when detected early.
While some canalicular tears are caused by unavoidable trauma, the following preventive measures and management strategies can help minimize the risks of future injuries or complications:
1. Avoiding Trauma
-
To reduce the risk of canalicular tears, it is important to avoid facial injuries and trauma to the eye area. Protective eyewear should be worn during contact sports or activities that involve flying debris or sharp objects.
2. Prompt Medical Attention
-
Immediate medical attention following any eye injury is crucial. Timely treatment can prevent complications like infections, further tearing, or blockage.
3. Regular Follow-ups
-
Patients who undergo canalicular tear repair should have regular follow-up visits with their ophthalmologist to ensure the repair is healing correctly and that the tear drainage system is functioning properly.
4. Post-Surgical Care
-
Post-surgical care often involves avoiding rubbing the eyes, using prescribed antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection, and following the surgeon’s instructions on avoiding physical activities that might disturb the repair.
Though canalicular tear repair is generally effective, it may carry risks and potential complications, including:
1. Infection
-
As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection, particularly in the tear duct area. Antibiotic eye drops are typically prescribed to reduce this risk.
2. Scar Tissue Formation
-
Scar tissue can form in the area of the tear duct, which may lead to further blockages or re-tearing of the canaliculi. This is a common complication that may require additional surgical intervention.
3. Tube Displacement
-
If a silicone tube is used, there is a risk that it may move out of place, requiring repositioning or removal.
4. Recurrence of Symptoms
-
In some cases, the tear duct may become blocked again, resulting in a recurrence of epiphora or infection. This may require further surgery or treatment.
After undergoing canalicular tear repair, patients can generally expect to recover fully, although they may need to make certain adjustments in their daily life. This can include managing post-surgical care, adjusting to temporary vision changes, and ensuring that the tear drainage system remains functional.
1. Post-Operative Rehabilitation
-
Patients may need to engage in eye rehabilitation exercises to help restore normal tear drainage and reduce discomfort. This may include massage or warm compresses to help the ducts heal properly.
2. Emotional Support
-
Trauma to the face or eye area can be distressing, especially if it leads to long-term vision changes. Emotional support and counseling can help patients cope with any anxiety or stress related to their recovery.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
-
Patients may need to make lifestyle changes, such as avoiding harsh weather conditions or protecting the eyes from dust and debris. Wearing sunglasses or protective eyewear can help shield the tear ducts from further irritation.
1. What is a canalicular tear?
A canalicular tear is an injury to the tear ducts, specifically the canaliculi, which are small tubes responsible for draining tears from the eye into the nasal cavity. Canalicular tears can be caused by trauma to the face or eye, such as a direct blow, accidents, or surgery. These tears can disrupt the normal flow of tears, leading to excessive tearing or other complications like infection.
2. What is canalicular tear repair?
Canalicular tear repair is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring the function of the tear ducts after a canalicular tear. The goal of the surgery is to re-establish the normal drainage of tears from the eye and prevent chronic tearing or infection. The procedure may involve stitching the torn canaliculus back together, or in more complex cases, using a small tube or stent to hold the tear duct in place during healing.
3. What causes a canalicular tear?
Canalicular tears are most commonly caused by trauma or injury to the eye or surrounding area, such as:
-
A direct blow to the eye, often from sports, accidents, or falls.
-
Facial fractures that affect the eye socket.
-
Surgical complications during eye or facial surgery.
-
In rare cases, a canalicular tear can be caused by chronic irritation or conditions that weaken the tear duct walls.
4. What are the symptoms of a canalicular tear?
Symptoms of a canalicular tear may include:
-
Excessive tearing (epiphora): The inability of tears to drain properly leads to watery eyes.
-
Infection or discharge: Blocked or damaged tear ducts may lead to bacterial infections and yellow or green discharge.
-
Pain or tenderness: Swelling or sensitivity around the eye and tear duct area.
-
Puffy eyes: Swelling can occur due to blocked tears that accumulate around the eye.
If left untreated, these symptoms may worsen, leading to chronic discomfort and complications.
5. How is a canalicular tear diagnosed?
Diagnosis of a canalicular tear typically involves:
-
Physical examination: The doctor will inspect the eye and surrounding area to check for signs of trauma, swelling, or infection.
-
Fluorescein dye test: A special dye is applied to the eye to assess the tear flow and identify any blockages or tear duct damage.
-
Nasal endoscopy: A small camera is sometimes used to view the tear duct system and assess the extent of the injury.
-
Imaging tests: In some cases, a CT scan or X-ray of the facial bones may be ordered if the tear is suspected to be associated with facial fractures.
6. What are the treatment options for a canalicular tear?
Treatment for canalicular tears can range from conservative approaches to surgery:
-
Conservative treatment: In some cases, if the tear is minor, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection, and warm compresses can help with swelling.
-
Surgical repair: The most common treatment for significant canalicular tears, where the tear duct is repaired using sutures or sometimes a stent or silicone tube to keep the canaliculus open while it heals.
-
Stent placement: A small tube or stent is often inserted into the tear duct to hold the canaliculus open during healing. This can stay in place for several months.
-
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR): In severe cases, if the tear duct is completely blocked, a surgical procedure to bypass the tear duct may be needed.
7. What is the recovery process for canalicular tear repair?
Recovery after canalicular tear repair varies depending on the severity of the injury and the type of surgery performed. Generally:
-
Post-operative care: The patient may be given antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection, and may need to apply warm compresses to the area.
-
Follow-up visits: Regular check-ups are essential to ensure proper healing and to monitor for complications.
-
Stent removal: If a stent was placed during surgery, it may need to be removed after several weeks to a few months, depending on the healing progress.
-
Activity restrictions: The patient is usually advised to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities, and rubbing the eyes during the healing process.
8. What are the risks of canalicular tear repair surgery?
As with any surgery, canalicular tear repair carries some risks, including:
-
Infection: A risk of infection at the surgical site.
-
Scarring: There may be scarring within the tear duct or around the eye.
-
Tear duct obstruction: In some cases, the duct may become blocked again after surgery, requiring further treatment.
-
Poor healing or failure of the repair: In some instances, the tear duct may not heal properly, requiring additional surgeries or interventions.
-
Nerve damage: Rarely, the surgery may affect surrounding nerves, potentially leading to loss of sensation or muscle function in the area.
9. How long does the canalicular tear repair surgery take?
The canalicular tear repair surgery typically takes between 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the complexity of the tear and the type of repair needed. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia with or without sedation. In some cases, general anesthesia may be required if the tear is extensive or if the patient is a child.
10. Can canalicular tear repair be done on both eyes?
Yes, canalicular tear repair can be performed on both eyes if necessary. In cases where both tear ducts are damaged, the surgeon may repair each duct during separate surgeries or in a single procedure, depending on the extent of the injury and the patient's health. The decision is based on the severity of the injury and the risk of complications.
The other Ophthalmology Procedures are
Few Major Hospitals for Canalicular Tear Repair are
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.