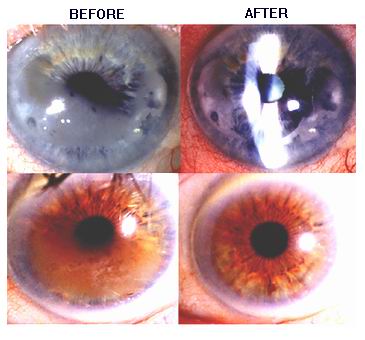
Phototherapeutic Keratectomy (PTK) is a laser eye surgery designed to treat corneal diseases and conditions that affect the outer layers of the cornea, leading to visual impairment. PTK uses an excimer laser to remove diseased tissue from the epithelium and anterior stroma of the cornea, allowing the eye to heal and restore clarity to the vision. This procedure is primarily used to treat corneal scarring, dystrophies, and other surface irregularities that cannot be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
Unlike Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis (LASIK), which is used for refractive vision correction, PTK focuses on addressing the outer surface of the cornea. It works by carefully reshaping the corneal tissue to remove irregularities caused by scarring, dystrophies, or other disorders, improving vision and reducing discomfort.
PTK is a highly effective treatment for individuals suffering from corneal conditions that have not responded to traditional treatments. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is minimally invasive, typically requiring no stitches. With its precision and advanced laser technology, PTK provides a safe and reliable option for those struggling with corneal abnormalities.
Phototherapeutic keratectomy is most commonly used to treat various corneal diseases and dystrophies that affect the cornea’s transparency and shape. The following are common causes and risk factors that may lead to the need for PTK:
1. Corneal Scarring
Corneal scarring can result from various sources of trauma, such as eye injuries, abrasions, or infections (such as herpes simplex virus keratitis). These scars can cause visual distortion and decreased vision that may not respond to traditional corrective methods, making PTK an ideal solution.
2. Corneal Dystrophies
Corneal dystrophies are a group of inherited eye disorders that affect the cornea. Some common dystrophies treated with PTK include:
-
Map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy: A condition that causes the cornea to develop irregular shapes and layers, leading to visual disturbances and discomfort.
-
Anterior basement membrane dystrophy: A condition characterized by abnormal growth of the basement membrane in the cornea, which can lead to painful recurrent erosions.
-
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy: Causes epithelial irregularities and leads to recurrent corneal erosions, which are painful and may result in scarring.
3. Pterygium and Pinguecula
Pterygium is a growth of fleshy tissue that can extend from the conjunctiva onto the cornea. In some cases, this growth can cause irritation, scarring, and vision issues. Pinguecula refers to a yellowish, raised area on the conjunctiva, often caused by UV light exposure, which can affect the corneal surface and lead to visual disturbances.
4. Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a progressive condition where the cornea thins and becomes cone-shaped. This leads to astigmatism and blurred vision. While PTK is not a primary treatment for keratoconus, it may be used to smooth the cornea’s surface and improve visual clarity in mild cases.
5. Recurrent Corneal Erosion (RCE)
Recurrent corneal erosion is a condition where the corneal epithelium fails to adhere properly to the underlying tissue. This causes painful episodes of eye irritation, redness, and sensitivity to light. PTK can be used to remove the damaged layers of the cornea, promoting healing and preventing further erosions.
6. Contact Lens Overuse
Excessive use of contact lenses, especially if not cleaned properly, can lead to corneal abrasions, infections, or scarring. People who wear contact lenses for extended periods of time may develop surface irregularities that can be treated with PTK.
7. UV Exposure
Chronic exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can contribute to the development of pterygium, pinguecula, and other conditions that lead to corneal abnormalities. UV-blocking sunglasses can help protect the eyes from UV damage.
The symptoms that indicate the need for PTK are generally related to visual impairment and discomfort caused by corneal irregularities. Common symptoms include:
1. Blurry or Distorted Vision
One of the primary symptoms that lead individuals to seek PTK is blurry or distorted vision. Whether caused by scarring, dystrophies, or refractive errors, PTK can restore clarity to the cornea and improve visual quality.
2. Eye Pain or Discomfort
Conditions like recurrent corneal erosion, pterygium, and map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy can cause significant discomfort. Patients may experience a sensation of something stuck in the eye, light sensitivity, and general eye irritation. PTK can help alleviate these symptoms by removing abnormal tissue and promoting healing.
3. Sensitivity to Light (Photophobia)
Increased sensitivity to light, particularly in individuals with corneal surface irregularities or dystrophies, is a common symptom. PTK can help reduce this sensitivity by smoothing out the corneal surface and reducing the optical distortions that cause glare.
4. Foreign Body Sensation
A feeling of having a foreign body in the eye, which is common in patients with corneal abrasions or epithelial disorders, can be significantly reduced with PTK by removing damaged or abnormal layers of the cornea.
5. Recurrent Corneal Erosions
Individuals with recurrent corneal erosions often experience painful episodes in the morning or after prolonged eye irritation. PTK is often recommended for individuals who suffer from frequent erosions that do not respond to other treatments.
6. Difficulty Wearing Contact Lenses
People with corneal scarring or irregular corneal shapes may find it difficult to wear contact lenses comfortably. PTK can improve the surface of the cornea, making it easier to wear contact lenses and improve vision.
The diagnosis and decision to proceed with PTK surgery typically involve several steps to evaluate the corneal condition. These may include:
1. Comprehensive Eye Examination
A thorough eye examination is performed to evaluate the health of the cornea and assess the degree of visual impairment. The ophthalmologist will test visual acuity, evaluate the pupil response, and assess the overall structure of the eye.
2. Slit Lamp Examination
A slit lamp is used to examine the cornea under high magnification. This allows the ophthalmologist to evaluate the corneal surface, check for scarring, and identify any irregularities that may indicate the need for PTK.
3. Corneal Topography
Corneal topography is a specialized test that maps the surface of the cornea, providing a detailed map of its shape and curvature. This test is essential for identifying irregularities, such as those caused by keratoconus, corneal scars, or dystrophies.
4. Pachymetry
Pachymetry is used to measure the thickness of the cornea, which is important for determining if the cornea is healthy enough for the surgery and whether sufficient tissue remains after PTK.
5. Fluorescein Staining
Fluorescein dye is applied to the eye to highlight areas of corneal damage or epithelial irregularities. This helps the ophthalmologist identify areas of the cornea that require treatment and ensure that the PTK procedure targets the correct tissue.
The primary treatment for conditions like corneal scarring, dystrophies, and recurrent corneal erosion is Phototherapeutic Keratectomy. The procedure involves the following steps:
1. Laser Treatment
During PTK, the excimer laser is used to precisely remove the diseased or irregular corneal tissue. The laser’s energy breaks down and vaporizes the damaged tissue, improving the cornea’s surface and restoring visual clarity.
2. Customization of Treatment
The laser can be customized to target specific areas of the cornea that need treatment. For conditions like keratoconus or epithelial dystrophies, the procedure may involve smoothing out the corneal surface and removing scarring.
3. Intraoperative Care
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia (usually topical eye drops) to numb the eye. The ophthalmologist uses the excimer laser to treat the corneal surface with great precision. The surgery is relatively quick, with minimal discomfort during the procedure.
While PTK is not typically a preventive procedure, managing risk factors and regular eye health assessments can help reduce the need for the surgery:
1. Regular Eye Exams
Routine eye exams can help detect early signs of corneal scarring, dystrophies, or other abnormalities that may lead to the need for PTK. Early detection allows for timely intervention.
2. Protection from UV Light
Wearing UV-blocking sunglasses can help reduce exposure to harmful UV radiation, preventing conditions like pterygium and pinguecula, which can affect the corneal surface.
3. Proper Contact Lens Care
For individuals who wear contact lenses, ensuring proper lens hygiene and taking regular breaks from wearing them can help prevent abrasions and infections that may lead to corneal damage.
4. Managing Corneal Conditions
People with recurrent corneal erosions or epithelial dystrophies should follow their doctor’s advice to manage symptoms and prevent the need for surgical intervention.
Like any surgical procedure, PTK carries some risks. The potential complications include:
1. Infection
While rare, infection following PTK can occur. Strict adherence to post-operative care and antibiotic eye drops can minimize this risk.
2. Corneal Haze
A temporary condition known as corneal haze may occur after PTK, particularly in the initial stages of recovery. This condition is typically self-resolving but may require further treatment in severe cases.
3. Recurrent Erosion
In some cases, recurrent corneal erosions can return after PTK, requiring additional treatments or surgery.
4. Incomplete Healing
If the cornea fails to heal properly after surgery, further interventions may be needed. Follow-up care is essential to ensure proper healing and visual recovery.
After PTK, most patients experience significant improvement in vision and relief from symptoms like pain or discomfort. However, continued care is essential for the best results:
1. Post-Operative Care
-
Use prescribed antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
-
Wear protective eyewear as recommended by the ophthalmologist.
-
Avoid rubbing the eyes to allow the cornea to heal properly.
2. Regular Follow-Up Appointments
-
Attend scheduled follow-up visits to monitor healing progress and check for potential complications such as infection or haze.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
-
Avoid UV exposure by wearing sunglasses, particularly in sunny conditions, to protect the cornea.
-
Rest your eyes after the procedure to reduce strain and allow for proper healing.
1. What is phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK)?
Phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) is a type of laser eye surgery used to treat various corneal conditions. It involves the use of an excimer laser to remove damaged or diseased tissue from the cornea’s surface. PTK is typically used to treat conditions such as corneal scars, corneal dystrophies, and certain types of epithelial irregularities. The goal of PTK is to improve vision by smoothing the corneal surface and promoting healing.
2. How does phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) work?
PTK works by using an excimer laser to precisely remove the outer layers of the cornea. The procedure is performed as follows:
-
Anesthesia: The eye is numbed with topical eye drops.
-
Laser treatment: The excimer laser is used to vaporize and smooth out the damaged or scarred areas of the cornea.
-
Healing: The cornea regenerates, and new, healthy tissue forms, leading to improved vision.
Unlike LASIK, which reshapes the entire cornea, PTK only affects the surface layers, making it a less invasive procedure.
3. What conditions can be treated with PTK?
PTK is effective for treating a variety of corneal conditions, including:
-
Corneal scars: Scarring from previous injuries, infections, or surgeries can be treated to improve vision.
-
Corneal dystrophies: These are inherited disorders where abnormal deposits or tissue growth in the cornea affect vision.
-
Recurrent corneal erosion: This occurs when the surface layers of the cornea fail to adhere properly, causing pain and blurry vision.
-
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy: A condition in which the layers of the cornea become irregular, causing visual impairment.
4. Is phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) painful?
PTK is generally not painful because local anesthesia (eye drops) is used to numb the eye during the procedure. Most patients experience little to no discomfort during the surgery itself. After the procedure, mild discomfort or a foreign body sensation may occur as the eye heals, but this is usually temporary and can be managed with prescribed medications. Pain usually resolves within a few days.
5. What is the recovery process like after PTK?
Recovery from PTK surgery is typically quick, but it varies for each patient:
-
First 24-48 hours: Mild discomfort, blurry vision, and sensitivity to light are common. Patients may be prescribed pain relief and anti-inflammatory eye drops.
-
First week: Vision may be cloudy or fluctuating as the cornea heals. Protective contact lenses may be worn to aid the healing process.
-
1-3 weeks: Most patients notice significant improvement in vision as the cornea heals. Follow-up visits with the ophthalmologist are necessary to monitor healing and check for complications.
-
Full recovery: Full visual stabilization can take up to 1-3 months, depending on the individual case.
6. Are there any risks or complications associated with PTK?
While PTK is generally safe, as with any surgical procedure, there are some potential risks and complications:
-
Infection: Although rare, infection can occur and may delay healing.
-
Corneal haze: Some patients may experience a hazy or cloudy vision as the cornea heals, but this often resolves over time.
-
Undercorrection or overcorrection: In some cases, the desired outcome may not be fully achieved, and further treatment may be necessary.
-
Recurrent corneal erosion: If not treated properly, the condition may recur, leading to further discomfort and vision problems.
Most complications are minor and can be managed with proper post-operative care.
7. How long does it take to see results after PTK?
While visual improvements are often noticeable within a few days to weeks, full recovery and stabilization of vision may take up to 3 months. Some patients may notice rapid improvements, while others may experience gradual vision enhancement. Regular follow-up visits with the ophthalmologist will help track progress and address any concerns during the recovery process.
8. Can PTK be performed on both eyes at the same time?
Yes, PTK can be performed on both eyes during the same visit, depending on the patient’s overall eye health and the specific condition being treated. Some patients opt for one eye at a time to allow for easier recovery, but treating both eyes simultaneously is often done for convenience, particularly if the condition is similar in both eyes. The decision will depend on individual circumstances and the recommendation of the surgeon.
9. Who is a good candidate for phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK)?
Good candidates for PTK are individuals who have certain corneal conditions that affect the surface layers of the cornea, including:
-
Those with corneal scars or dystrophies that impair vision.
-
Individuals who suffer from recurrent corneal erosion or epithelial basement membrane dystrophy.
-
Patients who have healthy corneal tissue beneath the damaged surface.
It is important that candidates have no significant underlying eye diseases, such as glaucoma or active infections. A thorough eye exam by an ophthalmologist will determine if PTK is suitable for the individual.
10. Is PTK covered by insurance?
In many cases, PTK is considered medically necessary and may be covered by insurance, especially if it is being used to treat conditions like corneal scarring or recurrent corneal erosion that significantly affect vision. However, coverage can vary depending on the insurance provider, the patient's plan, and whether the procedure is deemed medically necessary. It’s important to check with your insurance provider to understand the specifics of your coverage.
The other Ophthalmology Procedures are
Few Major Hospitals for Photo-therapeutic Keratectomy are
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.