Birthmarks are common skin conditions that are typically present at birth or appear shortly afterward. These marks can vary greatly in terms of color, size, shape, and location. While most birthmarks are harmless and do not require treatment, some individuals may choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons, discomfort, or due to health concerns.
Birthmarks come in a variety of types and are generally categorized into pigmented birthmarks and vascular birthmarks. Pigmented birthmarks, such as moles or café-au-lait spots, occur due to an excess of melanin (the pigment responsible for skin color), while vascular birthmarks, such as hemangiomas or port-wine stains, result from abnormalities in blood vessels.
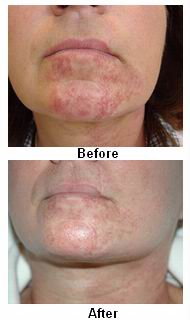
Birthmark removal involves eliminating or reducing the appearance of a birthmark, usually for cosmetic purposes. However, some birthmarks, especially those that are large, growing, or located in areas that may cause functional issues, might be removed for medical reasons. The decision to remove a birthmark depends on its type, size, location, and the impact it has on an individual’s health or self-esteem.
The exact causes of birthmarks are not always clear, but they are typically the result of either abnormal growth of skin cells (for pigmented birthmarks) or abnormal development of blood vessels (for vascular birthmarks). The following causes and risk factors are associated with the development of birthmarks:
1. Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the development of many types of birthmarks. Certain birthmarks, such as moles and café-au-lait spots, may run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition. Vascular birthmarks, such as hemangiomas, may also have a hereditary component, as they are often more common in certain genetic backgrounds.
2. Abnormal Pigmentation
Pigmented birthmarks like moles, café-au-lait spots, and freckles are caused by an excess production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. These marks result from the overgrowth of melanocytes, the skin cells that produce melanin. The exact cause of this overgrowth is unclear, but it may be influenced by genetic and environmental factors, such as sun exposure.
3. Abnormal Blood Vessel Development
Vascular birthmarks like hemangiomas, port-wine stains, and strawberry marks are caused by the abnormal growth of blood vessels in the skin. The reasons for this are not entirely understood, but it is believed to be related to genetic factors or certain vascular malformations that occur during development.
4. Hormonal Factors
Hormonal changes during pregnancy or infancy can influence the development of birthmarks. For example, hemangiomas are more common in female infants, suggesting a role of female hormones in their development. Hormonal fluctuations can also exacerbate the visibility of certain pigmented birthmarks, particularly during periods of hormonal change, like puberty or pregnancy.
5. Prematurity
Preterm infants are more likely to develop hemangiomas or other vascular birthmarks. Premature birth may interfere with the normal growth and formation of blood vessels, which can lead to the development of these marks.
6. Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure can exacerbate or darken pigmented birthmarks, especially those that are already visible. Over time, prolonged sun exposure can cause moles and other pigmented lesions to grow darker or more prominent, particularly in individuals who are prone to freckles or moles.
Birthmarks are usually recognizable based on their visual appearance, which can vary depending on the type of birthmark. While most birthmarks do not cause symptoms or health problems, some individuals may experience symptoms related to their size, location, or type.
1. Raised or Flat Texture
-
Raised Birthmarks: Vascular birthmarks like hemangiomas are typically raised above the surface of the skin and may be soft and spongy to the touch. These can be red, purple, or blue and may cause irritation or discomfort if they are located in areas prone to friction, such as the neck or armpits.
-
Flat Birthmarks: Pigmented birthmarks such as moles, freckles, and café-au-lait spots are often flat or slightly elevated, with a defined color that varies from tan, brown, or black to pink or red.
2. Color and Appearance Changes
Certain color changes in birthmarks may warrant medical attention:
-
Darkening or irregular pigmentation in a pigmented birthmark can be a sign of skin cancer.
-
Rapid changes in size or shape of a birthmark may indicate potential problems.
-
Redness or purple hues in vascular birthmarks may become more prominent or change color over time, which could be a sign of increased blood flow or the need for removal.
3. Bleeding, Ulceration, or Infection
Any birthmark that starts to bleed, ooze, or become ulcerated requires immediate medical attention. This could indicate infection, skin damage, or a change in the birthmark's nature, such as a transition into a more serious condition like skin cancer. Birthmarks located in areas prone to friction or trauma are particularly vulnerable to these issues.
4. Functional or Aesthetic Concerns
Certain birthmarks may interfere with vision (when located near the eyes), breathing (in the case of large hemangiomas), or movement. These marks might require removal if they cause functional difficulties or if they significantly affect a person's self-esteem or emotional well-being.
Diagnosis of a birthmark typically begins with a visual examination by a healthcare provider, often a dermatologist. Most birthmarks can be diagnosed based on their appearance, but in some cases, additional tests may be required to determine whether the mark is benign or has become problematic.
1. Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is conducted to assess the birthmark’s characteristics, including its size, shape, color, texture, and location. The provider will also take a detailed medical history to check for any family history of skin cancer, vascular diseases, or other related conditions.
2. Skin Biopsy
If the birthmark appears suspicious or has changed in appearance, a skin biopsy may be performed to determine whether it is benign or malignant. During a biopsy, a small sample of the tissue from the birthmark is removed and examined under a microscope by a pathologist.
3. Imaging Tests
In cases of deeper birthmarks or vascular abnormalities, imaging tests like ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be used to assess the size, depth, and blood supply of the birthmark, especially if it affects internal organs or structures.
Several treatment options exist for removing birthmarks, depending on the type, size, location, and the patient’s preferences. Treatment choices may range from non-invasive procedures to surgical removal.
1. Laser Therapy
Laser treatments are one of the most effective methods for removing vascular birthmarks, such as port-wine stains, hemangiomas, and strawberry marks. Pulsed dye lasers are commonly used to target and destroy abnormal blood vessels without damaging the surrounding skin. The treatment causes the blood vessels to collapse and fade away over time.
-
Pros: Non-invasive, minimal downtime, and effective for smaller vascular birthmarks.
-
Cons: May require multiple sessions, and not suitable for all types of birthmarks.
2. Surgical Removal
For larger or raised birthmarks like congenital nevi, moles, or hemangiomas, surgical excision may be necessary. This procedure involves cutting out the birthmark and stitching the skin back together. Surgical removal is often recommended when a birthmark is large, growing, or causing functional issues.
-
Pros: Effective for large or deep birthmarks.
-
Cons: Involves a scar, and recovery time can vary depending on the procedure’s complexity.
3. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the birthmark with liquid nitrogen. This is an effective method for smaller moles or cysts and can also be used to treat some pigmented birthmarks.
-
Pros: Quick procedure with minimal scarring.
-
Cons: Multiple treatments may be necessary, and there is a risk of skin discoloration or scarring.
4. Topical Treatments
For small, flat pigmented birthmarks, topical treatments like hydroquinone (a skin-lightening agent) or steroid creams may be recommended. These are generally less invasive and work by gradually lightening or flattening the birthmark.
-
Pros: Non-invasive, can be done at home.
-
Cons: Takes time to see results, and effectiveness varies.
While it’s not possible to prevent birthmarks from developing, there are steps you can take to manage existing birthmarks and reduce the risk of complications:
1. Sun Protection
Excessive sun exposure can make pigmented birthmarks darker and more prominent. Always use sunscreen with a high SPF to protect birthmarks, particularly moles or freckles, from UV damage. Wearing protective clothing and avoiding tanning beds are also effective in preventing skin changes.
2. Regular Skin Checks
Routine self-examination and regular skin checks by a healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring the development or changes in existing birthmarks. Early detection of any unusual changes in a birthmark can help prevent complications.
3. Healthy Skin Care
Moisturizing the skin regularly and avoiding harsh chemicals can prevent skin irritation and minimize the appearance of birthmarks. Good skincare habits can also help in the healing process following birthmark removal.
While the procedures for birthmark removal are generally safe, there are potential complications:
1. Scarring
One of the most common side effects of birthmark removal, particularly surgical excision, is scarring. Depending on the size and location of the birthmark, a scar may remain after removal. However, scars often fade over time.
2. Infection
As with any procedure that involves breaking the skin, there is a risk of infection. To reduce this risk, proper post-procedure care, including keeping the area clean and dry, is essential.
3. Hyperpigmentation or Hypopigmentation
After removal, the skin may become either darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation) than the surrounding skin. This is especially common in people with darker skin tones.
After the removal of a birthmark, individuals may need to make certain lifestyle adjustments depending on the procedure used and the location of the birthmark. Here are some considerations for living with a birthmark removal:
1. Post-Procedure Care
-
Wound Care: Follow your doctor’s instructions for cleaning and caring for the removal site. Use any prescribed ointments or creams to promote healing.
-
Sun Protection: After removal, the area may be sensitive to sunlight. Continue using sunscreen on the treated area to prevent sunburn and further skin damage.
2. Emotional Well-Being
For many people, birthmark removal can significantly improve self-esteem and confidence, especially if the birthmark caused emotional distress. It is important to follow up with your healthcare provider to ensure proper healing and to address any emotional concerns related to the procedure.
3. Regular Follow-Up Visits
Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to ensure proper healing and assess the results of the treatment. If a birthmark was removed due to health concerns, your doctor may recommend ongoing monitoring.
1. What is birthmark removal?
Birthmark removal is a cosmetic or medical procedure designed to remove or reduce the appearance of birthmarks, which are colored marks or lesions that appear on the skin at birth or shortly after. These birthmarks can be caused by an overgrowth of blood vessels, pigment cells, or other skin tissues. Birthmark removal can be done through various methods, including laser therapy, surgical excision, cryotherapy (freezing), or chemical peeling.
2. Why would someone want to remove a birthmark?
People choose to remove birthmarks for several reasons, including:
-
Cosmetic reasons: Birthmarks can sometimes be a source of embarrassment, especially if they are large, located in visible areas, or if they cause self-consciousness.
-
Medical reasons: In some cases, birthmarks can be associated with medical conditions. For example, a rapidly changing birthmark could indicate potential skin cancer, such as melanoma, requiring medical intervention.
-
Discomfort: Certain types of birthmarks, such as those that protrude or are located in areas prone to friction, may cause discomfort or irritation.
3. What are the types of birthmarks that can be removed?
There are two main types of birthmarks that can be removed:
-
Pigmented birthmarks: These include moles, café-au-lait spots, and other pigmented marks that are darker than the surrounding skin.
-
Vascular birthmarks: These include port-wine stains, hemangiomas, and strawberry marks, which are caused by an overgrowth of blood vessels and appear red or purple.
Both types of birthmarks can often be treated effectively with the appropriate removal method.
4. How is a birthmark removal procedure performed?
The method of birthmark removal depends on the type, size, and location of the birthmark. Common techniques include:
-
Laser treatment: Lasers can target and break down the pigment or blood vessels in the birthmark. This is a non-invasive procedure with minimal recovery time.
-
Surgical excision: For larger or raised birthmarks, a surgeon may remove the birthmark by cutting it out, followed by stitches. This is typically done under local anesthesia.
-
Cryotherapy: Liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and remove the birthmark.
-
Chemical peeling: A chemical solution is applied to the skin to remove the top layers, which can lighten or remove pigmented birthmarks.
Each procedure will be discussed and recommended by a doctor based on the patient's specific case.
5. Is birthmark removal painful?
The level of discomfort during birthmark removal depends on the procedure used. For most non-invasive methods like laser treatment, there is minimal pain, but some patients may experience mild discomfort or a tingling sensation during the procedure. Surgical excision may involve local anesthesia to numb the area, and post-surgery pain is usually manageable with over-the-counter pain medications. Cryotherapy or chemical peeling may cause slight discomfort or stinging during the treatment but typically does not require strong pain relief afterward.
6. How long does it take to recover from birthmark removal?
The recovery time for birthmark removal depends on the method used:
-
Laser treatment: Recovery time is usually minimal, with most patients returning to normal activities within a few days. There may be some redness or swelling around the treated area, but this typically resolves quickly.
-
Surgical excision: Recovery from surgery may take 1 to 2 weeks, with stitches being removed after the area has healed. Some swelling or bruising may occur, and there may be a scar that fades over time.
-
Cryotherapy: Healing usually takes 1 to 2 weeks, and the skin may scab over before the birthmark falls off.
-
Chemical peeling: This process may require several days for the skin to heal completely, and patients may experience some peeling or redness during the recovery period.
7. Will there be scarring after birthmark removal?
There is a possibility of scarring, especially with surgical excision, as the skin is cut and stitched. However, most scars from birthmark removal tend to fade over time, especially if proper aftercare is followed. Laser treatment generally causes minimal scarring, and most patients experience very little or no visible scarring after the procedure. The extent of scarring will depend on the size of the birthmark, the removal technique, and how well the skin heals.
8. Are there any risks associated with birthmark removal?
As with any medical procedure, there are risks associated with birthmark removal, including:
-
Infection: Though rare, an infection could occur, especially after surgical excision or cryotherapy.
-
Scarring: There is a risk of scarring, particularly if the skin does not heal properly.
-
Changes in skin color: The treated area may become lighter or darker than the surrounding skin, a condition known as hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation.
-
Recurrence: In some cases, a birthmark may grow back, particularly if it was not completely removed.
To minimize these risks, it’s important to follow aftercare instructions provided by your doctor.
9. How do I know if my birthmark needs to be removed?
If your birthmark is causing cosmetic concerns or discomfort, it may be worth considering removal. However, it is also important to have any birthmark that changes in size, shape, or color evaluated by a healthcare professional. Birthmarks that show signs of rapid growth, irregular borders, or unusual color changes could indicate a more serious condition, such as skin cancer. In these cases, removal may be necessary for medical reasons, and a biopsy may be performed to rule out malignancy.
10. Are there any alternatives to birthmark removal?
If you are not ready to remove a birthmark, there are some alternative treatments to reduce its appearance or manage it:
-
Makeup or concealing products: Cosmetic products like concealers or foundation can help mask birthmarks temporarily.
-
Laser therapy: For some types of birthmarks, especially pigmented ones, laser therapy can help lighten or reduce their visibility without full removal.
-
Observation: If the birthmark is not causing any problems, your doctor may recommend simply monitoring it for any changes over time.
It’s important to consult with a doctor to determine the most appropriate treatment for your individual case.
The other Skin Procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Birth-Marks Removal are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


