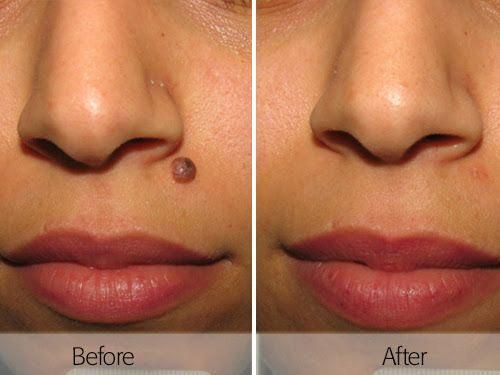
Moles, medically termed as nevi, are benign skin growths formed by clusters of melanocytes—the pigment-producing cells of the skin. They appear in various sizes, shapes, colors, and locations and are a common dermatological finding in people of all ages. While the majority of moles are harmless, many individuals seek mole removal for cosmetic reasons, physical discomfort, or concerns about malignant transformation.
Removal of moles is a widely performed procedure that ranges from simple outpatient excisions to more complex surgical interventions. Advances in dermatology and surgical techniques have made mole removal safer, minimally invasive, and cosmetically favorable, while also serving as a crucial step in diagnosing and preventing melanoma and other skin cancers.
This comprehensive article explores the causes and risk factors prompting mole removal, symptoms and signs indicating the need for evaluation, diagnostic methodologies, various treatment options, preventive measures, potential complications, and advice for life following mole removal.
Why Do Moles Develop?
Moles form due to localized proliferation of melanocytes. Several factors contribute to their development and behavior:
-
Genetic Predisposition: Family history significantly influences mole count and type, including atypical moles.
-
Ultraviolet (UV) Exposure: Sunlight and artificial tanning lead to increased mole formation and mutations in melanocytes.
-
Hormonal Influences: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or hormone therapy can alter existing moles or trigger new ones.
-
Skin Type: Individuals with lighter skin types tend to develop more moles.
-
Immune System Factors: Immunosuppression may influence mole growth and transformation.
When Is Mole Removal Indicated?
-
Cosmetic Reasons: Moles in visible areas like the face or hands causing distress or dissatisfaction.
-
Functional Problems: Moles that are frequently irritated by clothing or jewelry.
-
Suspicious Changes: Rapid enlargement, irregular borders, color heterogeneity, ulceration, bleeding, or new onset after age 30.
-
History of Skin Cancer: Presence of atypical or dysplastic nevi requiring removal for monitoring or prevention.
Risk Factors for Malignant Transformation
-
Large number of moles, especially over 50.
-
Presence of atypical or dysplastic nevi.
-
History of intense intermittent sun exposure or sunburns.
-
Immunosuppression or prior melanoma diagnosis.
Recognizing Suspicious Moles
The ABCDE criteria provide a framework to identify concerning features:
-
A – Asymmetry: One half unlike the other.
-
B – Border irregularity: Scalloped, ragged, or poorly defined edges.
-
C – Color variation: Multiple colors or uneven pigmentation.
-
D – Diameter: Larger than 6 mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
-
E – Evolving: Changes in size, shape, color, or symptoms like itching or bleeding.
Additional Warning Signs
-
Persistent itching, tenderness, or pain localized to the mole.
-
Ulceration or bleeding without trauma.
-
New growth on previously stable moles.
-
Moles appearing suddenly in adulthood.
When to Seek Medical Evaluation
Any mole exhibiting suspicious characteristics or new symptoms warrants prompt evaluation by a dermatologist or qualified healthcare provider.
Clinical Evaluation
-
History Taking: Document onset, duration, changes, family and personal history of skin cancer, sun exposure habits.
-
Physical Examination: Thorough skin exam assessing the size, color, shape, and texture of moles.
-
Dermoscopy: A non-invasive magnification technique revealing specific pigment patterns aiding differentiation between benign and malignant lesions.
Biopsy Techniques
-
Shave Biopsy: Removal of raised moles for superficial sampling.
-
Punch Biopsy: Circular blade used to obtain full-thickness skin samples.
-
Excisional Biopsy: Complete removal of the lesion with clear margins; preferred if malignancy is suspected.
Histopathology
-
Tissue analysis under the microscope confirms diagnosis and guides treatment.
-
Identifies melanoma, dysplastic nevi, or benign lesions.
Imaging (Rarely Needed)
-
High-risk or deep lesions may require imaging (ultrasound or MRI) for assessment.
Surgical Removal
-
Excision with Suturing: Complete removal including some surrounding healthy skin; results in a linear scar.
-
Shave Removal: Ideal for raised, benign moles; minimal scarring, no stitches required.
-
Punch Removal: Used for small lesions; healing by secondary intention or closure.
-
Laser Removal: Effective for flat, pigmented lesions; minimal scarring but no tissue for biopsy.
-
Cryotherapy: Liquid nitrogen freezing; typically for benign superficial lesions.
-
Electrosurgery: Burning off the mole tissue; combined with curettage in some cases.
Considerations in Choosing Technique
-
Size, depth, and location of the mole.
-
Suspicion of malignancy (requires excisional biopsy).
-
Cosmetic concerns.
-
Patient medical history.
Post-Removal Care
-
Keep wound clean and dry.
-
Apply antibiotic ointments as advised.
-
Avoid sun exposure and use sunscreen.
-
Monitor healing and report any signs of infection.
Preventive Measures
-
Sun Protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen SPF 30 or higher.
-
Avoidance of Tanning Beds: Artificial UV sources increase mole formation and skin cancer risk.
-
Protective Clothing: Hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves.
-
Skin Self-Examinations: Monthly checks for new or changing moles.
-
Regular Dermatologist Visits: Particularly for individuals with multiple or atypical moles.
Managing Existing Moles
-
Keep moles under observation if benign and asymptomatic.
-
Prompt removal if suspicious changes arise.
-
Educate patients on warning signs.
Common Side Effects
-
Redness, swelling, mild pain, or itching.
-
Minor bleeding or crusting.
-
Temporary skin discoloration.
-
Scarring – varies with technique and individual healing.
Potential Complications
-
Infection: Requires antibiotics.
-
Hypertrophic or Keloid Scars: Raised, thickened scars especially in prone individuals.
-
Recurrence: Rare regrowth if mole tissue incompletely removed.
-
Pigment Changes: Hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation.
-
Allergic Reactions: To local anesthetics or topical agents.
Minimizing Risks
-
Proper surgical technique by experienced providers.
-
Patient adherence to postoperative instructions.
-
Early intervention on complications.
Healing and Recovery
-
Most minor excisions heal within 1-2 weeks.
-
Larger excisions may require longer healing and scar maturation (up to 6-12 months).
-
Avoid sun exposure during healing to prevent pigmentation changes.
Psychological Impact
-
Relief from cosmetic or anxiety-provoking lesions.
-
Peace of mind following cancer exclusion.
-
Empowerment through skin health awareness.
Long-Term Skin Care
-
Continue sun protection lifelong.
-
Regular dermatologist evaluations.
-
Prompt evaluation of new or changing lesions.
1. What are moles, and why do people want them removed?
Moles are common skin growths made up of clusters of pigmented cells. People often seek removal for cosmetic reasons, discomfort, irritation, or if there’s concern about potential malignancy.
2. What methods are used to remove moles?
Common methods include surgical excision, shave removal, laser removal, and cryotherapy (freezing). The method depends on mole size, type, location, and suspicion of cancer.
3. Is mole removal painful?
Local anesthesia is used during the procedure, so pain during removal is minimal. Some discomfort or soreness may occur during recovery.
4. How long does it take to heal after mole removal?
Healing time varies with the removal method but typically takes 1 to 2 weeks. The area may scab and then heal, sometimes leaving a small scar.
5. Are mole removal procedures safe?
Yes, mole removal is generally safe when performed by a qualified healthcare professional. The removed mole is often sent for biopsy if there is any suspicion of cancer.
6. Will mole removal leave a scar?
Some scarring is possible, especially with surgical excision. The extent depends on mole size, removal method, and individual healing. Skilled techniques minimize scarring.
7. Can all moles be removed with laser treatment?
Laser treatment is effective for some benign moles but not recommended if there is any suspicion of cancer since it doesn’t provide tissue for biopsy.
8. Is mole removal covered by insurance?
If the mole is suspected to be cancerous or medically concerning, insurance may cover removal. Cosmetic mole removal is usually not covered.
9. Can moles grow back after removal?
Moles removed completely usually do not grow back. However, incomplete removal or skin regeneration can sometimes cause regrowth.
10. When should I see a doctor about a mole?
See a doctor if a mole changes in size, shape, color, bleeds, itches, or looks different from others (ABCDE rule). Early evaluation is key for melanoma detection.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Removal of Moles are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



