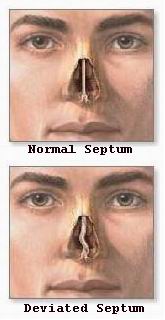
The nasal septum is the crucial internal structure that divides the nasal cavity into two nostrils, providing support to the nose and regulating airflow. Septal deviation occurs when this partition is displaced or crooked, causing nasal obstruction, impaired breathing, recurrent sinus infections, and sometimes cosmetic asymmetry. Reshaping septal deviation—commonly performed through septoplasty—is a surgical solution to realign and correct this deviation, restoring both function and appearance.
Septal deviation affects a significant percentage of the population, ranging from mild to severe deformities. While some individuals remain asymptomatic, others experience significant breathing difficulties, nasal congestion, and decreased quality of life. Advances in surgical techniques and preoperative evaluation allow for tailored interventions that improve outcomes and reduce complications.
This comprehensive guide discusses causes and risk factors associated with septal deviation, symptoms and signs that indicate the need for correction, diagnostic evaluation, detailed treatment options, prevention and postoperative management, possible complications, and guidance on life after correction.
Causes of Septal Deviation
-
Congenital Deviations: Some individuals are born with a crooked
septum due to developmental anomalies.
-
Nasal Trauma: Trauma is the most common cause of significant
deviation, occurring from accidents, sports injuries, or violence.
-
Developmental Growth Factors: Uneven growth of nasal bones and
cartilage during adolescence.
-
Previous Nasal Surgery: Complications or scarring from prior
procedures.
-
Inflammatory Conditions: Chronic rhinitis or infections can
exacerbate mucosal swelling, masking or worsening underlying deviations.
Risk Factors
-
History of Nasal Injury: Strongly correlates with septal
deformities.
-
Age: Deviation may worsen with age due to structural changes.
-
Environmental Exposures: Allergens and irritants promoting chronic
inflammation.
-
Systemic Diseases: Connective tissue disorders that affect cartilage
integrity.
Congenital Deviations: Some individuals are born with a crooked septum due to developmental anomalies.
Nasal Trauma: Trauma is the most common cause of significant deviation, occurring from accidents, sports injuries, or violence.
Developmental Growth Factors: Uneven growth of nasal bones and cartilage during adolescence.
Previous Nasal Surgery: Complications or scarring from prior procedures.
Inflammatory Conditions: Chronic rhinitis or infections can exacerbate mucosal swelling, masking or worsening underlying deviations.
-
History of Nasal Injury: Strongly correlates with septal deformities.
-
Age: Deviation may worsen with age due to structural changes.
-
Environmental Exposures: Allergens and irritants promoting chronic inflammation.
-
Systemic Diseases: Connective tissue disorders that affect cartilage integrity.
-
Nasal Obstruction: Persistent blockage, typically unilateral but can be bilateral.
-
Nasal Congestion: Frequently misdiagnosed as allergic rhinitis or sinusitis.
-
Recurrent Sinus Infections: Due to impaired sinus drainage.
-
Epistaxis (Nosebleeds): From mucosal dryness or crusting.
-
Facial Pain and Headache: Related to sinus pressure and poor ventilation.
-
Sleep Disorders: Snoring or obstructive sleep apnea linked to airway obstruction.
-
Noisy Breathing: Especially in children.
-
Examination Findings: Visual inspection and endoscopy reveal septal deviation, mucosal inflammation, and hypertrophied turbinates.
Patient History and Physical Exam
-
Inquiry about nasal obstruction severity, duration, trauma history, allergies, and
previous nasal surgeries.
-
Inspection of external nose and palpation.
-
Anterior rhinoscopy and nasal endoscopy to assess septal anatomy and nasal mucosa.
Imaging Studies
-
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Essential for preoperative planning
in complex or revision cases; evaluates septal deviation, sinus disease, and
anatomical variants.
Functional Tests
-
Rhinomanometry: Measures nasal airway resistance.
-
Acoustic Rhinometry: Assesses cross-sectional area and nasal cavity
volume.
-
Sleep Studies: If sleep apnea suspected.
Inquiry about nasal obstruction severity, duration, trauma history, allergies, and previous nasal surgeries.
Inspection of external nose and palpation.
Anterior rhinoscopy and nasal endoscopy to assess septal anatomy and nasal mucosa.
-
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Essential for preoperative planning in complex or revision cases; evaluates septal deviation, sinus disease, and anatomical variants.
Functional Tests
-
Rhinomanometry: Measures nasal airway resistance.
-
Acoustic Rhinometry: Assesses cross-sectional area and nasal cavity
volume.
-
Sleep Studies: If sleep apnea suspected.
Rhinomanometry: Measures nasal airway resistance.
Acoustic Rhinometry: Assesses cross-sectional area and nasal cavity volume.
Sleep Studies: If sleep apnea suspected.
Non-Surgical Management
-
Nasal steroids and antihistamines for associated inflammation.
-
Nasal saline irrigation to reduce crusting and dryness.
-
Allergy control and avoidance of irritants.
Surgical Management – Septoplasty
-
Standard Septoplasty: Involves lifting mucosal flaps, removing or
repositioning deviated cartilage and bone, and suturing mucosa back.
-
Endoscopic Septoplasty: Minimally invasive, uses nasal endoscope for
better visualization, less trauma, and precise correction.
-
Turbinate Reduction: Often combined with septoplasty to improve
airway.
-
Spreader Grafts: Used in complex cases to prevent internal nasal
valve collapse.
-
Anesthesia: Typically performed under local with sedation or general
anesthesia.
Postoperative Care
-
Nasal packing or splints may be placed to support septum.
-
Analgesics and antibiotics as needed.
-
Avoid nose blowing, strenuous activity, and trauma for 2-3 weeks.
-
Regular follow-up to monitor healing.
Nasal steroids and antihistamines for associated inflammation.
Nasal saline irrigation to reduce crusting and dryness.
Allergy control and avoidance of irritants.
-
Standard Septoplasty: Involves lifting mucosal flaps, removing or repositioning deviated cartilage and bone, and suturing mucosa back.
-
Endoscopic Septoplasty: Minimally invasive, uses nasal endoscope for better visualization, less trauma, and precise correction.
-
Turbinate Reduction: Often combined with septoplasty to improve airway.
-
Spreader Grafts: Used in complex cases to prevent internal nasal valve collapse.
-
Anesthesia: Typically performed under local with sedation or general anesthesia.
Postoperative Care
-
Nasal packing or splints may be placed to support septum.
-
Analgesics and antibiotics as needed.
-
Avoid nose blowing, strenuous activity, and trauma for 2-3 weeks.
-
Regular follow-up to monitor healing.
Nasal packing or splints may be placed to support septum.
Analgesics and antibiotics as needed.
Avoid nose blowing, strenuous activity, and trauma for 2-3 weeks.
Regular follow-up to monitor healing.
Prevention
-
Use protective gear during sports or activities.
-
Prompt management of nasal trauma.
-
Early treatment of nasal allergies and infections.
-
Avoidance of irritants like smoke and pollutants.
Preoperative Management
-
Complete medical evaluation.
-
Optimize control of allergies and infections.
-
Patient education about procedure and expectations.
Postoperative Management
-
Adherence to wound care protocols.
-
Use humidification to prevent dryness.
-
Gradual return to physical activities.
-
Manage complications promptly.
Use protective gear during sports or activities.
Prompt management of nasal trauma.
Early treatment of nasal allergies and infections.
Avoidance of irritants like smoke and pollutants.
-
Complete medical evaluation.
-
Optimize control of allergies and infections.
-
Patient education about procedure and expectations.
Postoperative Management
-
Adherence to wound care protocols.
-
Use humidification to prevent dryness.
-
Gradual return to physical activities.
-
Manage complications promptly.
Adherence to wound care protocols.
Use humidification to prevent dryness.
Gradual return to physical activities.
Manage complications promptly.
Common Side Effects
-
Mild pain and nasal congestion post-surgery.
-
Temporary numbness of upper teeth or nasal tip.
-
Mild bleeding or crusting.
Possible Complications
-
Septal Hematoma: May require urgent drainage.
-
Infection: Rare but serious if occurs.
-
Septal Perforation: Persistent hole causing crusting and whistling.
-
Adhesions: Scar bands that block nasal passage.
-
Incomplete Correction: Residual obstruction or deviation.
-
External Nose Deformity: Rare saddle nose or tip collapse.
-
Anesthesia Risks
Prevention of Complications
-
Meticulous surgical technique.
-
Adequate postoperative monitoring.
-
Patient compliance with instructions.
Mild pain and nasal congestion post-surgery.
Temporary numbness of upper teeth or nasal tip.
Mild bleeding or crusting.
-
Septal Hematoma: May require urgent drainage.
-
Infection: Rare but serious if occurs.
-
Septal Perforation: Persistent hole causing crusting and whistling.
-
Adhesions: Scar bands that block nasal passage.
-
Incomplete Correction: Residual obstruction or deviation.
-
External Nose Deformity: Rare saddle nose or tip collapse.
-
Anesthesia Risks
Prevention of Complications
-
Meticulous surgical technique.
-
Adequate postoperative monitoring.
-
Patient compliance with instructions.
Meticulous surgical technique.
Adequate postoperative monitoring.
Patient compliance with instructions.
Recovery and Outcomes
-
Initial swelling and congestion resolve in 1-2 weeks.
-
Most patients notice significant improvement in breathing within weeks.
-
Full healing and remodeling may take up to 6 months.
-
Some residual numbness or altered sensation may persist temporarily.
Quality of Life Improvements
-
Enhanced nasal airflow improves sleep and exercise tolerance.
-
Reduction in sinus infections and nosebleeds.
-
Improved sense of smell in some cases.
Long-Term Care
-
Avoid nasal trauma.
-
Manage allergies proactively.
-
Annual ENT evaluations recommended.
Initial swelling and congestion resolve in 1-2 weeks.
Most patients notice significant improvement in breathing within weeks.
Full healing and remodeling may take up to 6 months.
Some residual numbness or altered sensation may persist temporarily.
-
Enhanced nasal airflow improves sleep and exercise tolerance.
-
Reduction in sinus infections and nosebleeds.
-
Improved sense of smell in some cases.
Long-Term Care
-
Avoid nasal trauma.
-
Manage allergies proactively.
-
Annual ENT evaluations recommended.
Avoid nasal trauma.
Manage allergies proactively.
Annual ENT evaluations recommended.
1. What is septal deviation correction?
Septal deviation correction, also known as septoplasty, is a surgical procedure that
straightens a deviated nasal septum to improve airflow and correct nasal obstruction.
2. What causes septal deviation?
Septal deviation can be congenital (present at birth) or result from trauma, injury, or
aging, causing the nasal septum to shift from the center.
3. Who is a good candidate for septal deviation correction?
Candidates are individuals experiencing nasal blockage, difficulty breathing, chronic sinus
infections, or snoring due to a deviated septum.
4. How is the septal deviation correction procedure performed?
The surgeon makes incisions inside the nose to access the septum, removes or repositions the
deviated cartilage and bone, then repositions the septum to the midline.
5. Is septal deviation correction painful?
The procedure is usually done under local or general anesthesia, so patients do not feel
pain during surgery. Postoperative discomfort is managed with pain medication.
6. What is the recovery time after septal deviation correction?
Recovery typically takes 1 to 2 weeks. Patients may experience swelling, congestion, and
mild discomfort during this period.
7. Are there any risks or complications?
Risks include bleeding, infection, septal perforation, changes in nasal shape, and
persistent symptoms. These risks are minimized by experienced surgeons.
8. Will septal deviation correction improve breathing immediately?
Breathing often improves soon after surgery, but complete resolution may take several weeks
as swelling subsides.
9. Can septal deviation correction be combined with other procedures?
Yes, it is often combined with rhinoplasty or sinus surgery for comprehensive nasal
improvement.
10. How much does septal deviation correction cost?
Costs vary by surgeon, location, and procedure complexity, usually ranging from a few
thousand to several thousand dollars. Insurance may cover medically necessary septoplasty.
The other Cosmetic Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Reshaping Septal deviation correction are:
../hospitals/india/land, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and ../hospitals/india/land for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


