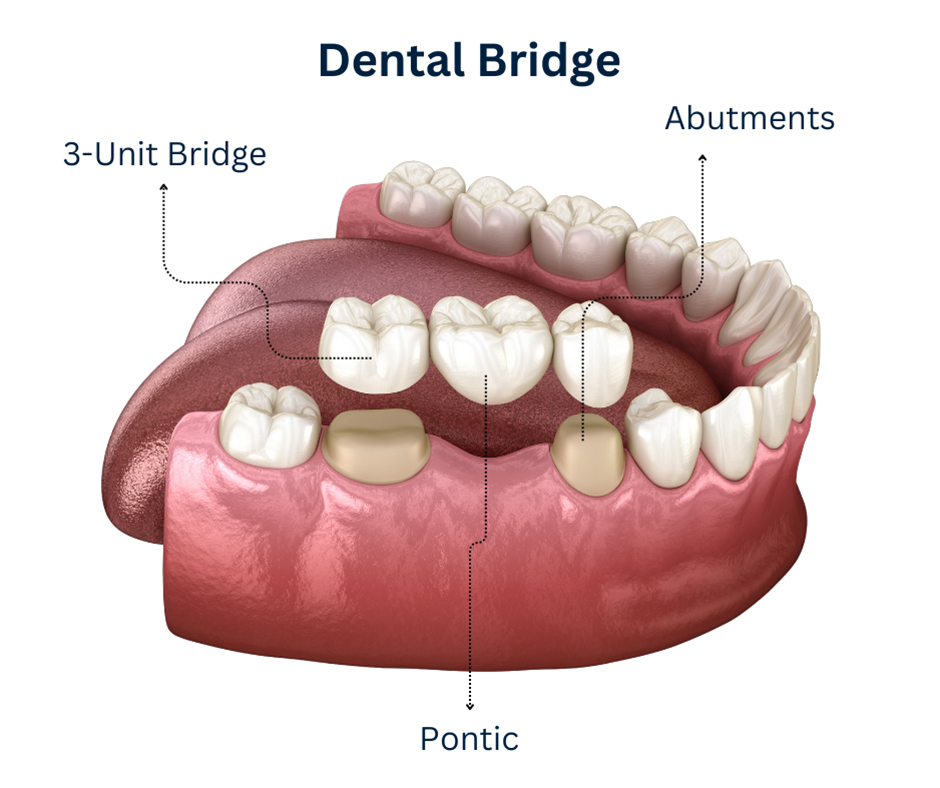
Dental bridges are a common and effective solution for replacing one or more missing teeth. They “bridge” the gap left by lost teeth using adjacent healthy teeth or dental implants as anchors. Missing teeth can significantly impact oral function, aesthetics, and overall dental health, and dental bridges serve both cosmetic and functional roles by restoring the natural appearance of the smile and enabling proper chewing and speaking.
In addition to aesthetic improvement, dental bridges help maintain facial structure, prevent neighboring teeth from shifting into the empty space, and redistribute bite forces evenly across the jaw. Advances in dental materials and technology have made dental bridges durable, comfortable, and highly customizable, making them an accessible option for many patients.
This comprehensive guide explores everything about dental bridges — causes and risk factors necessitating them, symptoms and signs of missing teeth, diagnostic processes, treatment options, prevention and maintenance, complications, and living with dental bridges.
Causes Leading to the Need for Dental Bridges
-
Tooth Loss from Decay or Trauma: The most common reason for missing teeth is dental caries (cavities) leading to extraction, or traumatic injury from accidents or sports.
-
Periodontal Disease: Advanced gum disease can weaken the supporting structures of teeth causing tooth loss.
-
Congenital Missing Teeth: Some individuals are born with missing teeth (hypodontia), creating functional and aesthetic gaps.
-
Failed Root Canals: Teeth that cannot be salvaged after endodontic treatment may require extraction.
-
Extraction Due to Orthodontics or Crowding: Sometimes teeth are removed as part of orthodontic treatment planning.
Risk Factors Contributing to Tooth Loss
-
Poor oral hygiene habits and infrequent dental visits.
-
Tobacco use, which increases risk of periodontal disease and oral infections.
-
Diabetes and other systemic illnesses affecting oral health.
-
Diet high in sugars and acids promoting decay.
-
Genetic predispositions to gum disease or tooth decay.
-
Age-related changes increasing susceptibility.
-
Visible Gap or Missing Tooth: The most obvious sign is the absence of one or more teeth.
-
Difficulty Chewing or Biting: Missing teeth reduce the ability to chew food effectively, causing discomfort or changes in eating habits.
-
Speech Impediments: Missing front teeth especially can affect pronunciation and clarity of speech.
-
Shifting or Tilting of Adjacent Teeth: Teeth adjacent to the gap may drift or tilt, causing bite misalignment and esthetic concerns.
-
Facial Sagging: Loss of teeth can lead to reduced support for cheeks and lips, contributing to a sunken facial appearance.
-
Sensitivity or Pain: Adjacent teeth may become sensitive due to exposure or increased pressure.
Clinical Examination
-
Dentist evaluates the oral cavity for missing teeth, condition of surrounding teeth, gums, and bite.
-
Check for decay or damage in abutment teeth (teeth adjacent to the gap).
-
Assessment of occlusion (how teeth come together) and jaw alignment.
-
Evaluation of gum health and bone support.
Radiographic Imaging
-
Dental X-rays: To assess the health and structure of the teeth and jawbone, particularly abutment teeth.
-
Cone Beam CT Scans (CBCT): 3D imaging for complex cases or planning implant-supported bridges.
Impressions and Digital Scans
-
Creating accurate molds or digital models of the teeth and bite for precise bridge fabrication.
Types of Dental Bridges
-
Traditional Bridges: Use crowns on adjacent teeth with a false tooth (pontic) between them. The most common type, suitable when abutment teeth are healthy and strong.
-
Cantilever Bridges: Attached to a single abutment tooth; used when only one side of the gap has a healthy tooth.
-
Maryland (Resin-Bonded) Bridges: Use metal or porcelain wings bonded to adjacent teeth with minimal preparation. Less invasive but less durable.
-
Implant-Supported Bridges: Use dental implants as anchors instead of natural teeth, ideal for larger gaps and preserving adjacent teeth.
The Procedure
-
Initial Consultation: Discuss options, take X-rays, and plan treatment.
-
Tooth Preparation: Adjacent teeth are shaped to accommodate crowns in traditional bridges.
-
Impression/Scan: Capture detailed tooth structure.
-
Temporary Bridge Placement: Protects prepared teeth during lab fabrication.
-
Bridge Fabrication: Custom-made to match natural teeth.
-
Bridge Cementation: Permanently fixed after adjustments and fit confirmation.
-
Follow-up: Regular dental check-ups to monitor bridge health.
Preventing Need for Bridges
-
Maintain rigorous oral hygiene: brushing twice daily, flossing, and mouthwash use.
-
Regular dental visits for professional cleaning and exams.
-
Healthy diet limiting sugary and acidic foods.
-
Smoking cessation.
-
Early treatment of dental decay and gum disease.
Caring for Your Dental Bridge
-
Brush gently around the bridge using a soft-bristled brush.
-
Use floss threaders or interdental brushes to clean under pontics.
-
Avoid hard, sticky, or chewy foods that can damage the bridge.
-
Visit your dentist regularly to check bridge stability and oral health.
Common Issues
-
Tooth sensitivity, especially after preparation.
-
Debonding or loosening of the bridge.
-
Decay beneath bridge crowns due to plaque accumulation.
-
Gum inflammation or recession around abutment teeth.
-
Wear or fracture of bridge materials over time.
Rare but Serious Complications
-
Damage to abutment teeth necessitating root canal therapy.
-
Allergic reactions to materials (very rare).
-
Bone loss under pontic areas without implant support.
-
Need for replacement bridge due to wear or failure.
Immediate Post-placement Care
-
Mild sensitivity and discomfort resolving within days.
-
Avoid sticky or very hard foods initially.
-
Maintain excellent oral hygiene to prevent complications.
Long-term Maintenance
-
Daily brushing and specialized flossing to clean around bridge.
-
Regular dental visits for professional cleaning and assessment.
-
Healthy lifestyle to maintain overall oral and systemic health.
Psychological and Functional Benefits
-
Restoration of smile aesthetics boosts confidence.
-
Improved ability to chew and speak naturally.
-
Prevention of further dental complications through maintaining proper bite and spacing.
1. What is a dental bridge?
A dental bridge is a fixed dental restoration used to replace one or more missing teeth by anchoring an artificial tooth (pontic) to adjacent natural teeth or implants.
2. Why would I need a dental bridge?
Dental bridges restore your smile, improve chewing and speaking, maintain the shape of your face, and prevent remaining teeth from shifting out of position.
3. What types of dental bridges are available?
Common types include traditional bridges (anchored to natural teeth), cantilever bridges (anchored on one side), Maryland bridges (using metal or porcelain wings), and implant-supported bridges.
4. How is a dental bridge placed?
The dentist prepares the adjacent teeth by reshaping them, takes impressions, and then fits the bridge in place, usually over two visits.
5. How long do dental bridges last?
With proper care, dental bridges typically last 5 to 15 years or longer before replacement might be necessary.
6. Are dental bridges painful?
The procedure is generally painless with local anesthesia. Some sensitivity or discomfort may occur during adjustment or after placement but usually resolves quickly.
7. How do I care for my dental bridge?
Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice daily, flossing under the pontic, and regular dental check-ups to prevent decay and gum disease around supporting teeth.
8. Can I eat normally with a dental bridge?
Yes, after adjustment, you can eat most foods comfortably. Avoid very hard or sticky foods to prevent damage to the bridge.
9. What are the risks or complications of dental bridges?
Potential risks include decay of supporting teeth, gum disease, bridge failure, or discomfort. Proper oral care and regular dental visits help minimize these issues.
10. How much do dental bridges cost?
Costs vary based on type, material, and location but typically range between $1,000 and $3,000 per tooth replaced. Insurance coverage depends on your plan.
The other Dental Procedures are:
Few Popular Hospitals for Dental Crowns or Caps are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



