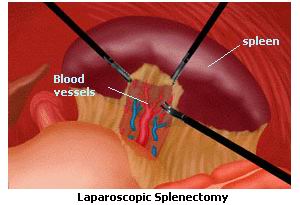
Laparoscopic splenectomy refers to the surgical removal of the spleen using laparoscopic (minimally invasive) techniques. The procedure is commonly performed for conditions like splenic rupture (due to trauma), splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), blood disorders, cancers, and infections affecting the spleen. Traditional splenectomy requires large incisions, which can result in significant pain, longer recovery, and a higher risk of complications. In contrast, laparoscopic splenectomy uses small incisions (often about 0.5 to 1.5 cm), allowing for quicker recovery, less postoperative pain, and fewer complications.
Why Laparoscopic Splenectomy?
-
Minimally Invasive: The laparoscopic approach uses small incisions, reducing the risk of complications like infections or bleeding.
-
Faster Recovery: Patients generally experience less pain, leading to a quicker return to daily activities.
-
Smaller Scars: The incisions used are smaller, resulting in less noticeable scars compared to open surgery.
-
Lower Risk of Infection: The smaller incisions decrease the risk of infection, a common complication in open surgeries.
-
Shorter Hospital Stay: Most patients can go home within a day or two after surgery, compared to longer stays following open surgery.
Laparoscopic splenectomy is increasingly becoming the preferred method due to these benefits, especially for patients with non-traumatic conditions like blood disorders or splenomegaly.
How Laparoscopic Splenectomy Works
-
Preparation and Anesthesia: The patient is administered general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free throughout the surgery.
-
Incisions: Several small incisions are made in the abdomen to allow for the insertion of the laparoscope and other surgical instruments.
-
Laparoscope Insertion: A laparoscope is inserted through one of the incisions. This tube has a camera that sends real-time images to a monitor, helping the surgeon visualize the spleen and surrounding structures.
-
Splenectomy Procedure: The surgeon uses specialized instruments to carefully detach the spleen from surrounding structures, including blood vessels and connective tissue.
-
Removal of the Spleen: Once the spleen is detached, it is placed in a small bag and removed from the abdomen through one of the incisions.
-
Closing the Incisions: The small incisions are then closed with sutures or surgical glue.
This minimally invasive technique offers significant advantages over traditional open splenectomy in terms of recovery time and overall patient comfort.
Causes for Laparoscopic Splenectomy
Laparoscopic splenectomy is typically performed for the following conditions:
-
Trauma and Injury:
-
Trauma or injury, often due to accidents or blunt force, can cause the spleen to rupture or become damaged. In such cases, prompt splenectomy is required to stop internal bleeding and prevent further complications.
-
-
Splenomegaly (Enlarged Spleen):
-
Splenomegaly can occur due to conditions such as liver disease (cirrhosis), lymphoproliferative disorders (like leukemia or lymphoma), or infections like malaria. An enlarged spleen can be painful and lead to complications like anemia or low platelet counts. Removal of the spleen may be necessary when these issues become severe.
-
-
Blood Disorders:
-
Certain blood disorders can lead to an overactive spleen, which prematurely removes red blood cells (hemolytic anemia), white blood cells (leukopenia), or platelets (thrombocytopenia). Splenectomy is often recommended to manage these disorders and restore normal blood cell counts.
-
-
Cancer:
-
Conditions such as lymphoma or leukemia may affect the spleen, causing it to become enlarged or dysfunctional. In some cases, splenectomy may be part of the treatment to remove cancerous tissue or alleviate symptoms.
-
-
Infections:
-
Severe infections affecting the spleen, such as sepsis or certain bacterial infections, may require splenectomy if the spleen is significantly damaged or if it poses a risk of spreading the infection.
-
-
Congenital or Inherited Conditions:
-
In rare cases, individuals are born with spleen dysfunction or diseases like hereditary spherocytosis or sickle cell anemia, which can lead to chronic splenic problems requiring surgical intervention.
-
Risk Factors for Splenectomy
Several factors increase the risk of developing conditions that require splenectomy:
-
Age: Older individuals are more likely to develop conditions like lymphoma, leukemia, or splenomegaly, requiring splenectomy.
-
Infections: Chronic infections or immune system conditions, like HIV, can increase the risk of spleen-related complications.
-
Genetic Disorders: Conditions like sickle cell disease or hereditary spherocytosis predispose individuals to splenomegaly and splenic dysfunction.
-
Alcohol Abuse: Chronic alcohol use can lead to liver disease, which may cause secondary splenomegaly and necessitate splenectomy.
Patients who require laparoscopic splenectomy often present with symptoms that indicate issues with the spleen. These symptoms are commonly seen in those with splenic enlargement (splenomegaly), splenic rupture, or blood-related disorders.
Symptoms of Spleen-Related Disorders
-
Pain in the Upper Left Abdomen:
-
The spleen is located in the upper left part of the abdomen. Pain or discomfort in this area, particularly after eating or during physical activity, may suggest an enlarged or damaged spleen.
-
-
Bloating and Fullness:
-
An enlarged spleen can press on other organs, causing a feeling of fullness or bloating in the abdomen.
-
-
Anemia:
-
Low red blood cell count, or anemia, can occur due to spleen dysfunction, particularly in conditions like autoimmune hemolytic anemia, leading to symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and paleness.
-
-
Frequent Infections:
-
The spleen is vital in fighting infections. When it becomes dysfunctional, the immune system may weaken, leading to frequent infections and an increased susceptibility to illnesses.
-
-
Unexplained Weight Loss:
-
Weight loss can occur in individuals with splenic disorders, especially if cancer or blood disorders like lymphoma are involved.
-
-
Easy Bruising and Bleeding:
-
A dysfunctional spleen can lead to low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia), causing easy bruising or prolonged bleeding from small cuts or injuries.
-
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience severe abdominal pain, bloating, frequent infections, unexplained weight loss, or easy bruising, seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms may indicate a condition that requires splenectomy.
Proper diagnosis is essential before performing laparoscopic splenectomy. Several tests are used to confirm the need for surgery and assess the condition of the spleen.
Diagnostic Tests for Spleen-Related Disorders
-
Physical Examination:
-
The doctor will palpate the abdomen to assess the size of the spleen, check for tenderness, and determine the location of any swelling.
-
-
Blood Tests:
-
Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test helps to assess the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, which may indicate a blood disorder requiring splenectomy.
-
Reticulocyte Count: Elevated levels may suggest that the spleen is prematurely destroying red blood cells.
-
Liver Function Tests: These tests can help determine whether liver disease is contributing to splenomegaly.
-
-
Imaging Tests:
-
Ultrasound: An abdominal ultrasound can provide detailed images of the spleen to detect enlargement or other abnormalities.
-
CT Scan: A CT scan can assess the spleen and surrounding structures for any masses, ruptures, or signs of cancer.
-
MRI: An MRI can offer a more detailed view of the spleen and other soft tissues, particularly in cases of lymphoma or other cancers.
-
-
Laparoscopy:
-
In some cases, a diagnostic laparoscopy may be performed to directly visualize the spleen and surrounding organs. This can be especially useful in cases of trauma or suspected cancer.
-
Surgical Treatment: Laparoscopic Splenectomy
For patients with splenic disorders that cannot be treated with medication alone, laparoscopic splenectomy is often the recommended treatment. The surgeon will remove the spleen using the laparoscopic technique described above.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
-
Medications:
-
Immunosuppressive drugs: In conditions like autoimmune hemolytic anemia, medications that suppress the immune system can help reduce the need for splenectomy.
-
Steroids: Corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation and improve blood cell counts in conditions like immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
-
-
Blood Transfusions:
-
In cases of anemia or other blood disorders, blood transfusions may be used temporarily to stabilize the patient until surgery can be performed.
-
Preventive Measures
-
Vaccinations:
-
Before and after splenectomy, patients should receive vaccinations for diseases like pneumococcus, meningococcus, and Hib to protect against infections.
-
-
Avoiding Trauma:
-
Since the spleen is highly vulnerable to trauma, individuals should take precautions to prevent injury, particularly in high-risk activities such as contact sports.
-
-
Avoiding NSAIDs:
-
Limiting the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can increase the risk of spleen-related complications, especially in those with existing blood or gastrointestinal issues.
-
-
Healthy Lifestyle:
-
Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can help prevent many of the conditions that lead to splenectomy, such as liver disease or certain cancers.
-
Post-Surgery Management
-
Post-Splenectomy Care:
-
After the spleen is removed, patients need to be vigilant about avoiding infections, especially during the first few months. Infections such as pneumonia or meningitis can be more severe without a spleen.
-
-
Follow-Up Care:
-
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor recovery and detect any potential complications early. Patients may also need to check blood counts regularly.
-
While laparoscopic splenectomy is generally a safe procedure, it is not without risks. Some potential complications include:
-
Infection:
-
Infection is a risk after any surgery. Patients who undergo splenectomy are at a higher risk of infections due to the spleen's role in immune defense.
-
-
Excessive Bleeding:
-
Though rare, excessive bleeding can occur during or after surgery, particularly if blood vessels are damaged during the removal of the spleen.
-
-
Blood Clots:
-
Postoperative blood clotting is a risk, especially in the early stages of recovery. Preventive measures like early ambulation and blood thinners may be recommended.
-
-
Increased Risk of Sepsis:
-
The absence of a spleen increases susceptibility to severe infections like sepsis. Vaccinations and antibiotics may be prescribed to help prevent infections.
-
After undergoing laparoscopic splenectomy, patients will need to make certain lifestyle changes to support their immune system and overall health:
-
Vaccination:
-
It’s critical to receive vaccinations for diseases like pneumonia, meningitis, and influenza, as the spleen is responsible for filtering out many harmful pathogens.
-
-
Regular Check-ups:
-
Ongoing medical check-ups are essential to monitor for any signs of infections or other complications following surgery.
-
-
Healthy Lifestyle:
-
A well-balanced diet, adequate hydration, and regular exercise will help maintain overall health and improve recovery.
-
-
Infection Prevention:
-
Avoid exposure to sick individuals and practice good hygiene. Patients who have had a splenectomy are also advised to take antibiotics at the first sign of infection.
-
1. What is laparoscopic splenectomy?
Laparoscopic splenectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the spleen is removed using small incisions, a laparoscope (a small tube with a camera), and specialized instruments. The surgery is typically performed to treat various conditions affecting the spleen, such as splenic tumors, trauma, blood disorders, or infections.
2. Why is laparoscopic splenectomy performed?
Laparoscopic splenectomy is performed to treat a variety of conditions, including:
-
Trauma: Removal of a ruptured or damaged spleen.
-
Splenic disorders: Such as splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), benign tumors, or cysts.
-
Blood disorders: Like thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), hemolytic anemia, or sickle cell disease, where the spleen plays a role in destroying blood cells.
-
Infections: Certain infections can cause the spleen to function abnormally, requiring removal.
3. How is laparoscopic splenectomy performed?
The procedure is done under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen. A laparoscope (a tube with a camera) is inserted through one of the incisions, and the surgeon uses specialized instruments to remove the spleen while guiding the surgery on a video monitor. The surgery may involve dividing ligaments or blood vessels connected to the spleen.
4. Is laparoscopic splenectomy painful?
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, so you won’t feel any pain during the procedure. Afterward, there may be mild to moderate discomfort, particularly around the incision sites, which is typically well-managed with pain medications. The pain usually subsides within a few days.
5. How long does laparoscopic splenectomy take?
Laparoscopic splenectomy typically takes between 1.5 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the surgery and the patient's individual health conditions.
6. What is the recovery time after laparoscopic splenectomy?
Recovery time varies, but most patients are able to leave the hospital within 1 to 3 days after surgery. Full recovery generally takes 2 to 4 weeks, with most people resuming normal activities within 1 to 2 weeks. The patient will need to follow specific post-operative instructions, including dietary modifications and avoiding heavy lifting during the recovery phase.
7. What are the risks or complications of laparoscopic splenectomy?
As with any surgery, risks include infection, bleeding, injury to surrounding organs (such as the stomach, colon, or pancreas), blood clots, and complications from anesthesia. There is also a small risk of developing a condition known as overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI), which makes the body more vulnerable to infections. Vaccination and preventive measures are typically recommended after spleen removal to reduce this risk.
8. How should I prepare for laparoscopic splenectomy?
Preparation includes fasting for several hours before the procedure, a thorough medical evaluation, imaging tests (like CT scans or ultrasound) to assess the spleen and surrounding structures, and possibly stopping certain medications like blood thinners. It’s important to follow your surgeon's specific instructions before the surgery.
9. What should I expect after laparoscopic splenectomy?
After surgery, you will be monitored for signs of complications such as infection or bleeding. You may experience mild pain, swelling, or fatigue, which typically improves with rest and pain medications. You will be advised to gradually resume normal eating and drinking. Follow-up visits are necessary to ensure proper healing and monitor your overall health.
10. Will I need any vaccinations after laparoscopic splenectomy?
Yes, after splenectomy, patients are at an increased risk for infections. Your doctor will recommend vaccinations to help protect against certain bacteria, including pneumococcus, meningococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae. These vaccines should ideally be administered before surgery if possible.
The other Gastro procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Laparoscopic Splenectomy are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Laparoscopic Splenectomy | Doctors For Laparoscopic Splenectomy | Surgery Laparoscopic Splenectomy | Cost Laparoscopic Splenectomy | Treatment Laparoscopic Splenectomy | Destinations Laparoscopic Splenectomy | Risks Laparoscopic Splenectomy | Laparoscopic Splenectomy In India | Laparoscopic Splenectomy Recovery | Laparoscopic Splenectomy Information | Laparoscopic Splenectomy Thailand | Laparoscopic Splenectomy In Malaysia | Laparoscopic Splenectomy Abroad | Laparoscopic Splenectomy Donors | Laparoscopic Splenectomy Overseas | Laparoscopic Splenectomy Low Cost | Laparoscopic Splenectomy In Singapore | Laparoscopic Splenectomy In Argentina | Splenectomy | Lymphatic System | Spleen | Hypersplenism | Splenomegaly | Cirrhosis Of The Liver | ITP | Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura | Abscess In The Spleen | Hereditary Elliptocytosis | Benign Tumors Of The Spleen | Splenic Cysts
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


