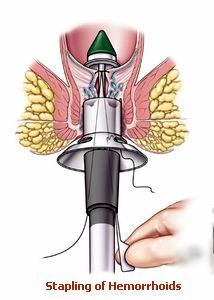
Stapler surgery for hemorrhoids is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves using a stapler-like device to remove or reposition hemorrhoidal tissue. This technique is specifically designed to treat hemorrhoids by cutting off the blood supply to the affected tissues, which leads to their shrinkage and eventual removal.
The main advantage of stapler surgery over traditional hemorrhoidectomy is its ability to treat hemorrhoids with less pain and a quicker recovery period. The procedure is also associated with fewer complications, especially in patients with grade 2 or grade 3 hemorrhoids, making it an attractive option for those suffering from severe hemorrhoidal symptoms.
How Stapler Surgery Works
-
Procedure Overview:
-
The surgeon uses a circular stapler device to remove a portion of the hemorrhoidal tissue while simultaneously repositioning it to a higher part of the rectum, where it is less likely to prolapse.
-
-
Minimal Incisions:
-
Unlike traditional hemorrhoidectomy, where large incisions are made around the anus, stapler surgery involves smaller incisions, which are less painful and lead to faster healing.
-
-
Blood Flow Reduction:
-
The stapler cuts the hemorrhoidal tissue, and the blood flow to the hemorrhoids is reduced, causing the tissue to shrink and the hemorrhoids to resolve over time.
-
-
Minimal Recovery Time:
-
Because the procedure is minimally invasive, patients often experience much less pain post-surgery and can return to their daily activities more quickly than with traditional surgical methods.
-
Hemorrhoids develop when the veins around the anus or rectum become swollen and inflamed due to increased pressure. This increased pressure can occur from a variety of causes and lifestyle factors.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
-
Chronic Constipation:
-
Straining during bowel movements, particularly due to constipation, is a leading cause of hemorrhoids. The pressure from straining can cause the veins in the anus or rectum to enlarge.
-
-
Pregnancy:
-
During pregnancy, the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the veins in the rectal area, leading to hemorrhoid development. Hormonal changes also contribute to the weakening of veins.
-
-
Obesity:
-
Excess body weight puts increased pressure on the pelvic and rectal veins, which can lead to hemorrhoids.
-
-
Sedentary Lifestyle:
-
Sitting for long periods, especially on the toilet, can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids by increasing pressure on the anal and rectal veins.
-
-
Heavy Lifting:
-
Frequent lifting of heavy objects increases intra-abdominal pressure, which can result in hemorrhoids.
-
-
Diarrhea:
-
Chronic diarrhea can irritate the anal region and lead to swollen veins, exacerbating hemorrhoids.
-
-
Aging:
-
As people age, the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus weaken, making it more difficult for the veins to return to normal size after being stretched.
-
Risk Factors for Developing Hemorrhoids
-
Family History:
-
If other family members have had hemorrhoids, you may be more likely to develop them as well.
-
-
Low-Fiber Diet:
-
A diet low in fiber can lead to constipation, making hemorrhoid development more likely due to straining during bowel movements.
-
-
Chronic Coughing:
-
Conditions that cause chronic coughing, such as smoking or respiratory disorders, can increase pressure on the rectal veins and contribute to hemorrhoid formation.
-
Hemorrhoids can cause a range of symptoms depending on their severity. Understanding these symptoms is important for identifying when a stapler surgery for hemorrhoids might be necessary.
Common Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
-
Rectal Bleeding:
-
One of the most common symptoms of hemorrhoids is blood in the stool or on toilet paper after wiping. The blood is typically bright red and may appear with bowel movements.
-
-
Pain or Discomfort:
-
Hemorrhoids can cause pain, especially when sitting or during bowel movements. The pain is often more severe with external hemorrhoids.
-
-
Itching and Irritation:
-
Itching or irritation around the anus is a common sign of hemorrhoids, especially if they are prolapsed (sticking out of the anus).
-
-
Swelling or Lumps:
-
Swelling or the feeling of a lump near the anus can indicate hemorrhoids. These lumps can be painful if they are thrombosed (clotted).
-
-
Prolapse:
-
Prolapsed hemorrhoids protrude from the anus and can sometimes be pushed back in. If left untreated, they may become more difficult to reduce.
-
-
Mucus Discharge:
-
Sometimes, hemorrhoids can cause a discharge of mucus from the rectum, leading to discomfort and an increased need to wipe.
-
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience persistent rectal bleeding, pain, or prolapsed hemorrhoids, it is important to consult with a doctor to determine the severity of your condition. If conservative treatments such as diet modification or over-the-counter medications do not work, stapler surgery for hemorrhoids may be considered.
The diagnosis of hemorrhoids typically involves a physical examination and may include a few additional tests depending on the severity of the condition and the patient’s symptoms.
Diagnostic Methods
-
Physical Examination:
-
During a physical exam, the doctor will inspect the anus and rectal area for signs of external hemorrhoids and may perform a digital rectal exam (DRE) to assess internal hemorrhoids.
-
-
Anoscopy:
-
An anoscope (a small tube with a light) is inserted into the rectum to allow the doctor to visualize internal hemorrhoids. This is a simple, quick test to examine the inside of the anal canal.
-
-
Colonoscopy:
-
If there is significant bleeding or suspicion of another underlying condition such as colorectal cancer, a colonoscopy may be recommended. This test involves inserting a flexible tube into the colon to examine the entire colon and rectum.
-
-
Sigmoidoscopy:
-
This procedure is similar to a colonoscopy but only examines the lower part of the colon and rectum. It can help identify hemorrhoids or other causes of rectal bleeding.
-
Hemorrhoids can often be managed through conservative measures such as dietary changes and over-the-counter treatments, but when these options fail or the hemorrhoids are severe, more invasive treatments may be necessary. Stapler surgery for hemorrhoids is one of the most effective options.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
-
Topical Creams and Ointments:
-
Over-the-counter creams or ointments, such as hydrocortisone, can reduce itching and swelling.
-
-
Fiber Supplements:
-
Increasing fiber intake through diet or supplements can help soften stools and reduce strain during bowel movements.
-
-
Sitz Baths:
-
Soaking in warm water can relieve discomfort and reduce swelling in the affected area.
-
-
Pain Relief Medications:
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and discomfort caused by hemorrhoids.
-
Surgical Treatment Options
-
Stapler Surgery (Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy):
-
Stapler surgery involves using a specialized stapling device to remove a portion of the hemorrhoidal tissue while repositioning the tissue higher up in the rectum. This reduces the likelihood of hemorrhoids prolapsing out of the anus.
-
-
Traditional Hemorrhoidectomy:
-
In cases of large or severe hemorrhoids, a traditional hemorrhoidectomy may be performed, where the hemorrhoids are excised using a scalpel or laser. This is typically more painful and requires a longer recovery.
-
-
Rubber Band Ligation:
-
This method involves placing a rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off blood flow, causing the hemorrhoid to shrink and eventually fall off.
-
-
Sclerotherapy:
-
A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid to shrink and scar it, causing it to shrivel.
-
Although it may not be possible to prevent hemorrhoids entirely, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of developing or aggravating hemorrhoids.
Preventive Measures
-
Increase Fiber Intake:
-
Eating a high-fiber diet (fruits, vegetables, and whole grains) helps prevent constipation and reduces the need to strain during bowel movements.
-
-
Drink Plenty of Fluids:
-
Staying hydrated helps soften stools and prevents constipation, which can contribute to hemorrhoids.
-
-
Exercise Regularly:
-
Regular physical activity can promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation, reducing the risk of hemorrhoids.
-
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting:
-
Sitting for long periods, especially on the toilet, can increase pressure on the rectal area. Try to avoid sitting for extended periods.
-
Post-Surgery Management
-
Pain Management:
-
After stapler surgery, pain is usually minimal, but over-the-counter pain relievers and sitz baths can help ease any discomfort.
-
-
Dietary Modifications:
-
Eating a fiber-rich diet post-surgery helps prevent constipation and reduce the risk of hemorrhoid recurrence.
-
-
Follow-up Appointments:
-
Regular follow-up visits to the surgeon are essential to monitor recovery and ensure there are no complications from the surgery.
-
Although stapler surgery for hemorrhoids is a minimally invasive procedure with relatively few complications, it is important to be aware of potential risks, including:
-
Recurrence of Hemorrhoids:
-
In some cases, hemorrhoids may return after surgery, especially if the underlying causes, such as poor diet or chronic constipation, are not addressed.
-
-
Infection:
-
Although rare, infection can occur in the surgical site, leading to pain and other complications.
-
-
Bleeding:
-
Minor bleeding after stapler surgery is common, but if bleeding is excessive or persistent, it may require medical intervention.
-
-
Prolapse or Mucosal Injury:
-
In some cases, the procedure can lead to mucosal injury or prolapse of the rectal tissue, although these complications are rare.
-
After stapler surgery, most patients experience a significant reduction in symptoms, and the majority can return to normal activities within a few weeks. However, ongoing management is necessary to maintain long-term relief from hemorrhoids.
Post-Operative Care
-
Rest and Recuperation: It’s important to rest for a few days following surgery and avoid strenuous activities or lifting heavy objects.
Long-Term Management
-
Maintain a High-Fiber Diet: Continued adherence to a high-fiber diet can help prevent constipation and reduce the risk of hemorrhoid recurrence.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in light physical activity can support bowel health and reduce pressure on the rectum.
-
Monitor for Recurrence: Keep an eye on any signs of hemorrhoids returning, such as bleeding, itching, or pain, and consult a healthcare provider if needed.
1. What is stapler surgery for hemorrhoids?
Stapler surgery for hemorrhoids is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat severe hemorrhoids, particularly prolapsed ones. The surgeon uses a circular stapler device to remove a portion of the hemorrhoidal tissue and then staples the tissue back into place, helping to reduce the hemorrhoids and alleviate symptoms.
2. What are hemorrhoids, and why do they require surgery?
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower part of the rectum or anus, causing pain, discomfort, bleeding, and itching. When these veins become enlarged or prolapsed, they can cause significant issues that may not respond to conservative treatments. In severe cases, surgery is required to remove or reposition the hemorrhoidal tissue.
3. How does stapler surgery compare to traditional hemorrhoidectomy?
Stapler surgery is less invasive than traditional hemorrhoidectomy, which involves removing hemorrhoidal tissue using a scalpel. Stapler surgery typically results in less pain, a quicker recovery time, and a lower risk of complications such as infection and bleeding.
4. Who is a good candidate for stapler surgery for hemorrhoids?
Stapler surgery is most effective for individuals with prolapsed hemorrhoids (grades 3 or 4) that do not respond to conservative treatments like dietary changes, medications, or rubber band ligation. It is also suitable for patients who want a minimally invasive option with a quicker recovery time.
5. What are the benefits of stapler surgery for hemorrhoids?
Some of the key benefits of stapler surgery include:
-
Less pain compared to traditional surgery
-
Faster recovery time (patients can often return to normal activities in a week or two)
-
Fewer complications, such as infection or bleeding
-
Minimal scarring
6. What are the risks or complications associated with stapler surgery?
While stapler surgery is considered safe, there are potential risks, including:
-
Pain and discomfort post-surgery
-
Bleeding or infection
-
Risk of anal stenosis (narrowing of the anal canal)
-
Recurrence of hemorrhoids
These risks can usually be minimized with proper post-surgical care and follow-up visits.
7. How long does the stapler surgery for hemorrhoids take?
The stapler surgery procedure typically takes between 30 to 45 minutes. The surgery is usually performed under general or regional anesthesia, and patients are generally able to go home the same day.
8. What is the recovery process like after stapler surgery for hemorrhoids?
Most patients experience minimal discomfort and can return to regular activities within 1 to 2 weeks. You may experience some mild pain, swelling, or bleeding initially, but these symptoms usually subside with time. It’s important to follow post-surgery care instructions, including dietary modifications (high fiber) and staying hydrated.
9. Can I eat normally after stapler surgery for hemorrhoids?
After surgery, it is essential to eat a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation and ensure smooth bowel movements. Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with plenty of water, will help to avoid straining, which could irritate the surgical area.
10. Will stapler surgery completely eliminate hemorrhoids?
Stapler surgery can effectively treat prolapsed hemorrhoids, but in some cases, hemorrhoids may return over time, especially if lifestyle factors like poor diet or chronic constipation persist. However, the procedure provides long-term relief for most patients, and recurrence is less common compared to traditional hemorrhoidectomy.
The other Gastro procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Stapler Surgery for Hemorrhoids are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Hospitals For Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids | Doctors For Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids | Surgery Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids | Cost Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids | Treatment Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids | Destinations Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids | Risks Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids In India | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids Recovery | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids Information | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids Thailand | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids In Malaysia | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids Abroad | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids Donors | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids Overseas | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids Low Cost | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids In Singapore | Stapler Surgery For Hemorrhoids In Argentina | Hemorrhoid | Anal Canal | Piles | Venous Plexuses | Internal Hemorrhoids | Prolapsed Hemorrhoid | External Hemorrhoid | Milligan Morgan Technique | Ferguson Technique
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


