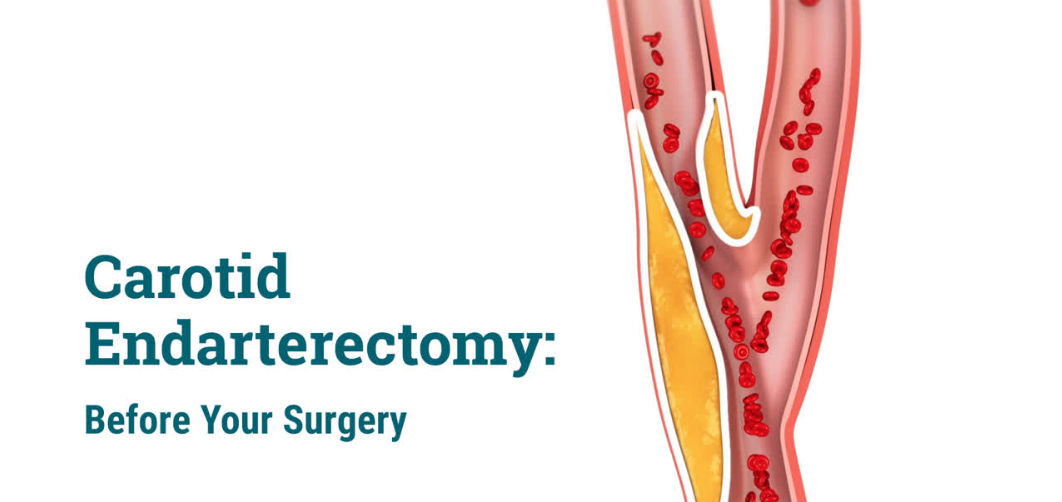
Carotid artery surgery or carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is a surgical procedure performed to treat carotid artery disease, a condition in which the carotid arteries (the major arteries that supply blood to the brain) become narrowed or blocked due to the build-up of plaque (a combination of fatty deposits, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances). When plaque accumulates in the carotid arteries, it restricts blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of a stroke.
The goal of carotid artery surgery is to remove the plaque from the affected artery and restore normal blood flow, thereby reducing the risk of stroke. This surgery is typically performed on patients who have a high-grade stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery, often diagnosed after a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), commonly referred to as a mini-stroke.
Carotid endarterectomy has been a standard treatment for carotid artery disease for decades and remains one of the most effective surgical interventions for preventing stroke caused by carotid artery blockage. While the procedure is generally safe, it does carry some risks, and careful consideration of the patient’s overall health and risk factors is essential.
Carotid artery surgery or endarterectomy is typically indicated when atherosclerosis (plaque buildup) in the carotid arteries is causing narrowing (stenosis), leading to impaired blood flow. Several causes and risk factors contribute to the development of carotid artery disease:
1. Atherosclerosis:
-
Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of carotid artery disease. It occurs when fatty deposits and cholesterol build up on the inner walls of the arteries, leading to plaque formation and narrowing of the arteries. This restricts blood flow to the brain and increases the risk of stroke.
2. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension):
-
High blood pressure is one of the leading risk factors for carotid artery disease. Elevated pressure in the arteries can damage the artery walls, making them more prone to plaque accumulation.
3. High Cholesterol Levels:
-
High levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially low-density lipoprotein (LDL), also known as "bad cholesterol," can contribute to the formation of plaque in the carotid arteries.
4. Smoking:
-
Smoking accelerates the buildup of plaque in the arteries and damages blood vessels, significantly increasing the risk of developing carotid artery disease.
5. Diabetes:
-
Diabetes increases the risk of atherosclerosis and contributes to the narrowing of blood vessels, including the carotid arteries. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and make them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
6. Family History and Genetics:
-
A family history of atherosclerosis, stroke, or heart disease increases the likelihood of developing carotid artery disease. Certain genetic factors can predispose individuals to higher cholesterol levels and plaque formation.
7. Age and Gender:
-
Age is a significant risk factor. The risk of carotid artery disease increases as a person ages, particularly for individuals over the age of 60. Additionally, men are more likely to develop carotid artery disease at a younger age compared to women. However, women’s risk increases significantly after menopause.
8. Lack of Physical Activity and Poor Diet:
-
A sedentary lifestyle, combined with an unhealthy diet high in saturated fats and processed foods, increases the risk of developing high cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes, all of which contribute to carotid artery disease.
The symptoms of carotid artery disease may not be immediately obvious, as the condition develops slowly over time. However, when the blood flow to the brain is compromised, it can lead to several signs and symptoms that require urgent attention.
1. Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA):
-
A stroke occurs when the blood flow to part of the brain is interrupted, leading to brain damage. A TIA (or mini-stroke) is a temporary blockage of blood flow, which can cause stroke-like symptoms that resolve within 24 hours. Both conditions are strong indicators that a carotid artery endarterectomy may be necessary.
-
Symptoms of a stroke or TIA include:
-
Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, typically on one side of the body.
-
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech (aphasia).
-
Loss of vision in one eye or double vision.
-
Sudden confusion or trouble with coordination and balance.
-
2. Reduced Blood Flow:
-
Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting may occur due to reduced blood flow to the brain.
-
Patients may also experience difficulty walking or maintaining balance because of inadequate blood supply to the brain.
3. Carotid Bruit:
-
A carotid bruit is an abnormal sound heard during a physical examination with a stethoscope placed over the carotid artery. It occurs due to turbulent blood flow caused by a narrowed artery and is a common sign of carotid artery disease.
The diagnosis of carotid artery disease that may require surgery typically involves several diagnostic tests to evaluate the extent of narrowing and the risk of stroke.
1. Physical Examination:
-
A healthcare provider will perform a neurological exam to assess symptoms such as weakness, sensory loss, or changes in coordination.
-
Auscultation of the carotid arteries with a stethoscope may reveal a carotid bruit, indicating turbulent blood flow due to plaque buildup.
2. Ultrasound (Carotid Doppler Study):
-
A carotid ultrasound is the most common test used to evaluate the flow of blood through the carotid arteries. This non-invasive test uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the carotid arteries and measure the degree of narrowing or blockage.
3. CT Angiography or MR Angiography:
-
CT angiography (CTA) or MR angiography (MRA) provide detailed images of the blood vessels in the neck and brain, allowing doctors to assess the severity of the blockages and determine whether surgery is needed.
4. Cerebral Angiography:
-
Cerebral angiography is a more invasive procedure in which a contrast dye is injected into the blood vessels, allowing detailed X-ray images of the carotid arteries and any blockages. It is typically used if other imaging techniques are inconclusive.
Carotid artery surgery or endarterectomy is primarily performed to remove plaque from the carotid arteries and restore blood flow to the brain. Several treatment options may be considered based on the severity of the disease and the patient’s overall health.
1. Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA):
-
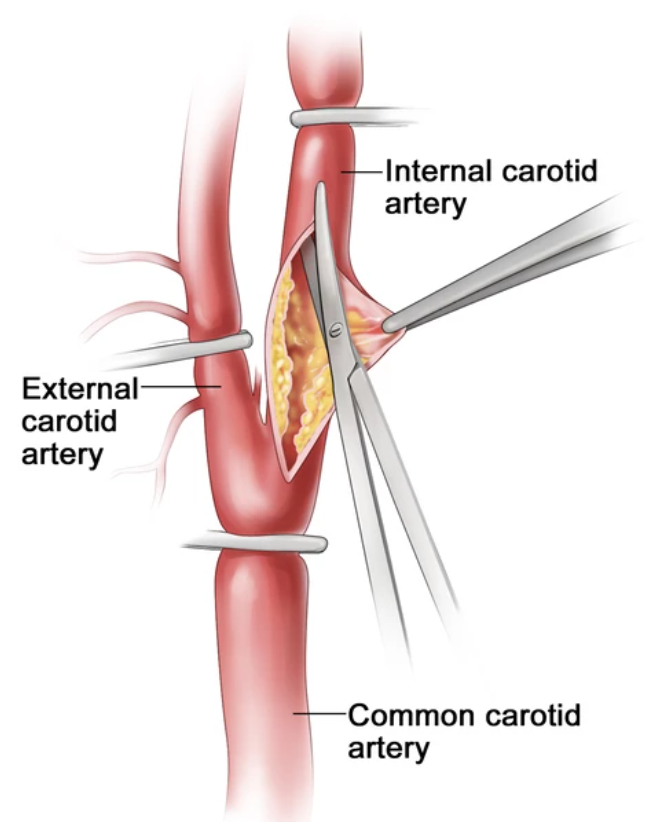
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is the most common surgery for carotid artery disease. In this procedure, the surgeon removes plaque from the carotid artery through a small incision in the neck, restoring blood flow to the brain.
-
The procedure involves making a small incision in the neck, exposing the carotid artery, and removing the plaque. The artery is then stitched back together.
-
CEA is most commonly performed on patients with 60-99% stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery, as this offers the greatest benefit in preventing stroke.
2. Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS):
-
For some patients, carotid artery stenting (CAS) may be an alternative to surgery. In this procedure, a stent is placed in the narrowed section of the carotid artery to keep it open. This may be recommended for patients who are not good candidates for surgery due to health issues.
3. Medications and Lifestyle Modifications:
-
For patients with early-stage carotid artery disease or those not yet requiring surgery, medications such as statins (to lower cholesterol), antiplatelet drugs (to prevent blood clots), and antihypertensive drugs (to control blood pressure) may be prescribed.
While carotid artery surgery is effective in preventing strokes caused by carotid artery disease, managing and preventing the condition before surgery is equally important.
1. Healthy Diet and Exercise:
-
Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce cholesterol levels and prevent plaque buildup in the arteries.
-
Regular exercise helps manage weight, lower cholesterol, and improve cardiovascular health.
2. Medication Adherence:
-
Taking prescribed medications such as statins or antiplatelet drugs helps reduce cholesterol levels and the risk of blood clots.
3. Blood Pressure and Diabetes Control:
-
Managing high blood pressure and diabetes is crucial for preventing carotid artery disease from progressing and for improving overall cardiovascular health.
4. Avoiding Smoking:
-
Smoking cessation is one of the most important steps to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and carotid artery disease.
Like any surgical procedure, carotid endarterectomy carries some risk of complications, including:
1. Stroke:
-
Although carotid endarterectomy is designed to reduce the risk of stroke, there is a small risk of stroke during or immediately after surgery due to the manipulation of the carotid artery or the release of plaque fragments into the bloodstream.
2. Infection:
-
As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the incision site, though this is typically rare.
3. Nerve Injury:
-
Nerve damage, particularly to the facial nerve or vagus nerve, can occur during the surgery, potentially causing temporary or permanent weakness or numbness in the face or throat.
4. Hematoma or Bleeding:
-
Hematoma or excessive bleeding can occur after the surgery, requiring additional treatment to manage blood loss.
After undergoing carotid artery surgery, patients need to follow a comprehensive management plan to ensure optimal recovery and prevent future issues:
1. Post-Surgery Care:
-
After surgery, patients may need to stay in the hospital for observation for 24-48 hours. Wound care and pain management are essential in the early recovery phase.
2. Lifestyle Changes:
-
Adopting heart-healthy lifestyle changes, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, is crucial in preventing the recurrence of carotid artery disease.
3. Ongoing Monitoring:
-
Regular follow-up appointments and imaging tests will be necessary to monitor the success of the surgery and check for any recurrence of blockages or complications.
4. Psychological and Emotional Support:
-
Some patients may experience anxiety or stress following surgery. Psychological counseling or joining support groups can help individuals adjust to changes in their health and regain confidence.
1. What is Carotid Artery Surgery / Endarterectomy?
Carotid artery surgery, also known as carotid endarterectomy, is a surgical procedure performed to remove plaque buildup from the carotid arteries, which are located in the neck and supply blood to the brain. The plaque, typically made up of cholesterol, fat, and other substances, can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of a stroke. The surgery aims to restore normal blood flow to the brain and reduce stroke risk.
2. Why is Carotid Artery Surgery needed?
Carotid artery surgery is needed when a patient has significant narrowing (stenosis) of the carotid artery due to plaque buildup, which can increase the risk of:
-
Stroke: A reduced blood flow to the brain can lead to a stroke.
-
Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs): Often referred to as "mini-strokes," these temporary blockages can lead to stroke-like symptoms.
-
Severe carotid artery disease: In cases where medication or lifestyle changes are not enough to manage the condition, surgery may be necessary.
3. How is Carotid Endarterectomy performed?
The procedure involves the following steps:
-
Anesthesia: The patient is given general anesthesia (to be asleep) or local anesthesia (numb the area but stay awake).
-
Incision: A small incision is made in the neck to expose the carotid artery.
-
Plaque removal: The surgeon carefully removes the plaque from the artery to restore normal blood flow.
-
Closure: Once the plaque is removed, the artery is closed, and the incision is sutured.
-
Recovery: The patient is monitored for several hours or days in the hospital before being allowed to return home.
4. What are the risks of Carotid Artery Surgery?
As with any surgery, carotid artery surgery carries certain risks, including:
-
Stroke: Though rare, a stroke can occur during or after surgery due to blood clots or damage to the artery.
-
Heart attack: If the plaque removal procedure causes stress on the heart, a heart attack could occur.
-
Nerve injury: The surgery may affect nearby nerves, causing temporary or permanent numbness, weakness, or difficulty swallowing.
-
Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the incision site.
-
Bleeding: Some bleeding may occur during or after the surgery.
5. How long does the Carotid Endarterectomy procedure take?
Carotid endarterectomy typically takes 1 to 2 hours. The duration may vary depending on the complexity of the blockage and the patient’s overall health. It is generally considered a straightforward procedure, but more complex cases may require additional time.
6. What is the recovery time after Carotid Artery Surgery?
Recovery from carotid artery surgery typically involves:
-
Hospital stay: Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days for monitoring.
-
Resuming activities: Patients can usually return to light activities within 1 to 2 weeks and resume normal activities after 4 to 6 weeks.
-
Follow-up care: Regular check-ups are required to monitor the healing process and ensure the artery remains open.
7. What are the benefits of Carotid Artery Surgery?
Carotid endarterectomy can provide several benefits:
-
Reduced risk of stroke: By removing the plaque and restoring blood flow, the risk of stroke and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) is significantly lowered.
-
Improved blood flow to the brain: The procedure enhances oxygen and nutrient delivery to the brain, reducing the risk of cognitive problems.
-
Prevention of further complications: It can prevent the worsening of carotid artery disease and other related health issues.
8. Who is a good candidate for Carotid Endarterectomy?
Good candidates for carotid artery surgery include:
-
Individuals with significant carotid artery stenosis (narrowing) who are at high risk for stroke.
-
Patients with a history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).
-
People who have failed conservative treatments such as medication, lifestyle changes, or stenting.
The decision for surgery depends on the degree of blockage, the patient’s health, and other risk factors. Your doctor will assess whether surgery is the best option.
9. Are there alternatives to Carotid Artery Surgery?
Yes, alternatives to carotid endarterectomy include:
-
Carotid artery stenting: A procedure where a small tube (stent) is inserted into the carotid artery to keep it open. This is less invasive than surgery but may not be suitable for all patients.
-
Medications: For individuals with less severe stenosis, medication to lower cholesterol, blood pressure, or prevent blood clots may be sufficient.
-
Lifestyle changes: Diet, exercise, and smoking cessation are essential for managing carotid artery disease and reducing the risk of complications.
10. How successful is Carotid Endarterectomy?
Carotid endarterectomy has a high success rate with most patients experiencing significant improvements. Studies show that the procedure reduces the risk of stroke by as much as 70-80% in patients with significant carotid artery stenosis. Success depends on the patient’s health, the extent of the blockage, and the quality of care provided. The risk of stroke or complications during surgery is low, especially in experienced hands.
The other Neurology Treatment procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Carotid Artery Surgery are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.