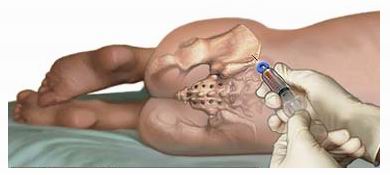
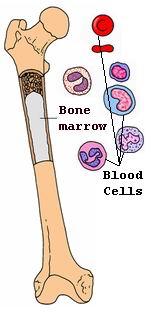
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT), also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), is a vital medical procedure used to treat a range of serious blood and immune system diseases. Bone marrow is the tissue found inside large bones such as the hip and thigh bones. It is responsible for producing the blood cells necessary for carrying oxygen, fighting infection, and clotting blood. When the bone marrow becomes diseased or damaged, it cannot effectively produce healthy blood cells, leading to various medical conditions. A bone marrow transplant is used to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow or stem cells.
Bone marrow transplantation is used for treating various disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, aplastic anemia, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, and other blood-related conditions. It is also used to treat certain genetic disorders and autoimmune diseases. The transplant procedure helps restore the body's ability to produce blood cells, improving the patient's immune system function and overall health.
There are two primary types of bone marrow transplants:
-
Autologous bone marrow transplant: The patient’s own bone marrow or stem cells are harvested, processed, and reinfused into the patient after undergoing high-dose chemotherapy or radiation.
-
Allogeneic bone marrow transplant: Bone marrow or stem cells are obtained from a donor, which can be a sibling, parent, or an unrelated person with a matching tissue type.
Bone marrow transplantation is a complex and highly specialized procedure, offering hope to patients who are facing life-threatening blood disorders. However, the treatment comes with significant risks, including graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), infection, and organ complications. Close monitoring and a multidisciplinary team approach are essential for a successful outcome.
The need for bone marrow transplantation arises from a variety of conditions that cause damage to the bone marrow or the blood cells it produces. Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors for bone marrow failure is crucial for determining whether a transplant is necessary. Some of the main causes and risk factors for conditions requiring bone marrow transplantation include:
1. Blood Cancers
The most common reason for undergoing a bone marrow transplant is blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
-
Leukemia: This is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow, where abnormal white blood cells are produced and crowd out the normal cells. This leads to the inability of the body to fight infection, control bleeding, or carry oxygen. A bone marrow transplant can help replace the damaged marrow with healthy cells, particularly after chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
-
Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which includes the bone marrow. In certain cases, particularly in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma, a bone marrow transplant is needed when other treatments have failed or the disease recurs.
2. Non-Cancerous Blood Disorders
Bone marrow transplantation is also used to treat various non-cancerous blood disorders, including:
-
Aplastic anemia: A condition where the bone marrow fails to produce enough blood cells, leading to severe anemia, infection, and excessive bleeding. Bone marrow transplantation may be needed to restore normal blood cell production.
-
Sickle cell anemia: A hereditary disease in which red blood cells become abnormally shaped (sickle-shaped), causing pain, organ damage, and frequent infections. A bone marrow transplant from a matched donor can potentially cure this condition.
-
Thalassemia: A genetic blood disorder where the body produces an abnormal form of hemoglobin, leading to severe anemia. Bone marrow transplantation is a potential cure for thalassemia major when other treatments are ineffective.
3. Inherited and Genetic Disorders
Certain genetic disorders affect the function of the bone marrow, leading to a need for transplantation. Some conditions that may require a bone marrow transplant include:
-
Fanconi anemia: A rare genetic disorder causing bone marrow failure, birth defects, and an increased risk of leukemia and other cancers. Transplantation can improve survival rates.
-
Diamond-Blackfan anemia: A congenital disorder that leads to anemia due to a lack of red blood cell production by the bone marrow.
-
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID): A genetic disorder affecting the immune system, making individuals extremely vulnerable to infections. Bone marrow transplants can help restore the immune system in these patients.
4. Autoimmune Disorders
In certain autoimmune conditions, the body’s immune system attacks the bone marrow or causes damage to the blood cells it produces. Some of the autoimmune disorders that may lead to a bone marrow transplant include:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): An autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation and damage to various organs, including the bone marrow.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: In severe cases, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to bone marrow failure and the need for transplantation.
5. Complications of Chemotherapy or Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy and radiation treatments, which are used to treat cancers, can damage the bone marrow. This damage may lead to bone marrow suppression, resulting in insufficient blood cell production. A bone marrow transplant may be required to restore bone marrow function and help the body produce healthy blood cells.
Before a bone marrow transplant, the patient may present with symptoms related to the condition being treated. The underlying conditions often lead to symptoms of bone marrow failure, and these symptoms can help doctors decide if transplantation is necessary. Some common symptoms include:
1. Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of bone marrow failure. When the bone marrow does not produce enough red blood cells, the body becomes unable to carry oxygen effectively, leading to chronic tiredness, weakness, and paleness.
2. Increased Susceptibility to Infections
The bone marrow produces white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. When bone marrow is compromised, immune system function is weakened, and individuals become more susceptible to bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
3. Easy Bruising or Bleeding
A lack of platelets, which help the blood to clot, can result in easy bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, nosebleeds, or heavy menstrual periods. Spontaneous bleeding, such as gum bleeding or blood in the urine, is also a common sign of bone marrow failure.
4. Shortness of Breath
When the bone marrow fails to produce sufficient red blood cells, the body’s ability to carry oxygen is reduced. This can cause shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion or when moving around.
5. Pale or Jaundiced Skin
Due to anemia (low red blood cells), individuals with bone marrow failure often appear pale. In cases of liver involvement, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) may occur due to increased red blood cell destruction.
6. Swollen Lymph Nodes or Spleen
Some conditions, such as lymphoma or leukemia, can cause the lymph nodes or spleen to become enlarged. This swelling can cause discomfort and may be noticeable as lumps or tenderness in the abdominal area or under the arms.
The diagnosis of conditions that require bone marrow transplantation typically involves a combination of physical exams, laboratory tests, and bone marrow examinations. Early diagnosis is crucial for determining the necessity of a transplant and identifying potential risks. Here’s how doctors diagnose the need for a bone marrow transplant:
1. Physical Examination
A thorough physical exam is performed to identify signs of bone marrow failure, such as paleness, bruising, and swollen lymph nodes. The doctor will also inquire about symptoms such as fatigue, frequent infections, or shortness of breath.
2. Blood Tests
-
Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood. Abnormal levels of these cells can indicate bone marrow dysfunction.
-
Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy: A small sample of bone marrow is extracted, typically from the hip bone, to examine the cells under a microscope. This test helps determine the type of blood disorder and guides treatment decisions.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic tests may be conducted to diagnose inherited conditions, such as Fanconi anemia or Diamond-Blackfan anemia, which affect bone marrow function.
3. Imaging Studies
Imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans may be used to examine the spleen, liver, and lymph nodes for signs of enlargement due to abnormal blood cell proliferation or bone marrow involvement.
The main treatment option for diseases affecting bone marrow is bone marrow transplantation. However, treatment plans vary depending on the underlying condition and the type of transplant being used. Below are the primary treatment options:
1. Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant
In autologous BMT, the patient’s own stem cells are harvested, treated, and reintroduced into their body after high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This type of transplant is most commonly used for multiple myeloma, lymphoma, or certain types of leukemia.
2. Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant
In allogeneic BMT, stem cells are obtained from a donor, who may be a sibling, parent, or unrelated donor with a matching tissue type. This procedure is used for diseases such as leukemia, aplastic anemia, and sickle cell disease.
3. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant
In some cases, stem cells from umbilical cord blood are used. This may be an option for patients who do not have a suitable living donor. Umbilical cord blood contains stem cells that can help replenish the patient’s bone marrow.
4. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is being explored as an emerging treatment for inherited blood disorders like sickle cell disease or thalassemia. The goal of gene therapy is to correct the genetic mutations in the patient's own cells, potentially reducing the need for a transplant.
While it is not always possible to prevent diseases requiring bone marrow transplants, several strategies can help manage risk factors:
1. Regular Medical Checkups
Regular blood tests and screening for individuals with genetic disorders or family histories of blood-related conditions are crucial for early detection. Early intervention can often prevent the need for a transplant.
2. Preventing Infections
Patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation have weakened immune systems, making them highly susceptible to infections. Vaccinations, antibiotics, and antifungal treatments are important to prevent infections.
Though bone marrow transplantation is a potentially life-saving procedure, it carries risks and complications, including:
1. Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD)
GVHD occurs when the donor’s immune cells attack the recipient’s body. This can cause symptoms such as skin rashes, liver damage, and gastrointestinal problems.
2. Infection
Post-transplant patients are highly susceptible to infections due to a compromised immune system. Close monitoring and antibiotic prophylaxis are essential.
3. Graft Failure
In some cases, the transplant may not “take,” resulting in graft failure. This can happen if the transplanted cells do not engraft or if the immune system rejects the new marrow.
After undergoing bone marrow transplantation, patients require ongoing medical care to monitor for complications and support recovery:
1. Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up visits to the healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring blood counts, immune function, and for detecting any potential complications, such as GVHD or infections.
2. Emotional and Psychological Support
The process of undergoing a bone marrow transplant can be physically and emotionally challenging. Counseling, support groups, and mental health support are essential to help patients cope with the psychological stress.
3. Physical Rehabilitation
Physical rehabilitation and exercise may be needed to restore strength and improve overall health after the transplant.
1. What is bone marrow transplantation?
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT), also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplant, is a medical procedure in which damaged or diseased bone marrow is replaced with healthy bone marrow or stem cells. This procedure is often used to treat various cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, as well as non-cancerous conditions like aplastic anemia and certain genetic disorders. The goal of BMT is to restore the body’s ability to produce healthy blood cells.
2. Why is bone marrow transplantation needed?
Bone marrow transplantation is needed when the bone marrow is unable to produce enough healthy blood cells due to conditions such as:
-
Leukemia: A cancer of the blood and bone marrow.
-
Lymphoma: Cancer that begins in lymphatic tissues.
-
Multiple myeloma: Cancer that affects plasma cells in bone marrow.
-
Aplastic anemia: A condition in which the bone marrow fails to produce sufficient red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
-
Inherited blood disorders: Such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia.
BMT helps to restore healthy blood cell production by replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
3. How does bone marrow transplantation work?
Bone marrow transplantation typically involves the following steps:
-
Preparation (conditioning): Before the transplant, patients undergo chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy to destroy unhealthy bone marrow cells and suppress the immune system to prevent rejection.
-
Stem cell infusion: Healthy stem cells are infused into the patient’s bloodstream. These stem cells can come from the patient’s own bone marrow (autologous transplant) or from a matched donor (allogeneic transplant).
-
Engraftment: The stem cells travel to the bone marrow, where they start producing healthy blood cells.
-
Recovery: Over time, the patient’s immune system and blood cell production recover. This process can take several weeks to months, and the patient is closely monitored for any complications.
4. What are the different types of bone marrow transplants?
There are two main types of bone marrow transplants:
-
Autologous transplant: The patient’s own bone marrow or stem cells are collected, stored, and then reintroduced after the patient undergoes chemotherapy or radiation.
-
Allogeneic transplant: The patient receives stem cells from a donor, which may be a relative (related allogeneic) or an unrelated matched donor (unrelated allogeneic). This type of transplant is more common for blood cancers.
5. What are the risks and complications of bone marrow transplantation?
Bone marrow transplantation carries some risks and potential complications, including:
-
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD): In an allogeneic transplant, the donor’s immune cells may attack the patient’s tissues, causing GVHD.
-
Infection: Since the immune system is suppressed after BMT, patients are more susceptible to infections.
-
Organ damage: Chemotherapy and radiation can sometimes cause damage to organs such as the liver, lungs, or heart.
-
Rejection of the transplant: In some cases, the patient’s body may reject the transplanted stem cells.
-
Relapse: There is a chance that the original disease (e.g., leukemia) may return after the transplant.
6. How long does bone marrow transplantation take?
The bone marrow transplant procedure typically takes several weeks to months, depending on the type of transplant and the patient’s condition:
-
Conditioning therapy: Chemotherapy or radiation therapy lasts about 1-2 weeks.
-
Stem cell infusion: The stem cell infusion itself takes only a few hours.
-
Recovery period: After the transplant, it may take several weeks for the stem cells to engraft and for the immune system to recover. Full recovery may take 6 months to a year or longer, depending on the patient’s progress and any complications.
7. What is the recovery process after bone marrow transplantation?
The recovery process after a bone marrow transplant involves:
-
Monitoring and hospital stay: Initially, patients are closely monitored in a hospital setting for infections, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and other complications.
-
Gradual recovery of the immune system: It takes time for the body to rebuild its immune system, and patients may need to take immunosuppressive medications to prevent GVHD.
-
Supportive care: This may include blood transfusions, antibiotics, and growth factors to stimulate blood cell production.
-
Follow-up visits: Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor recovery, detect relapse, and manage any complications.
8. How successful is bone marrow transplantation?
The success of bone marrow transplantation varies depending on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the type of disease being treated, the type of transplant, and how well the patient responds to the procedure. In general:
-
Autologous transplants (using the patient’s own cells) have a higher success rate since there is no risk of rejection.
-
Allogeneic transplants (using a donor’s cells) have a lower risk of relapse, but there are higher risks of complications like GVHD.
The success rate also improves when a well-matched donor is available. Overall, the survival rate after bone marrow transplantation is generally around 50-70%, but it can be higher or lower depending on the individual’s circumstances.
9. Who is a good candidate for bone marrow transplantation?
A good candidate for bone marrow transplantation is typically someone with:
-
Blood cancers: Such as leukemia, lymphoma, or multiple myeloma.
-
Non-cancerous blood disorders: Like aplastic anemia or sickle cell anemia.
-
Genetic disorders: Such as thalassemia.
-
The candidate should also be in good general health to withstand the intensive conditioning regimen of chemotherapy or radiation and have no severe organ dysfunction or other contraindications.
10. What are the costs of bone marrow transplantation?
The cost of bone marrow transplantation can be quite high, ranging from $100,000 to $500,000 or more, depending on the type of transplant (autologous vs. allogeneic), the location, and any complications that arise. The costs include hospital stays, medications, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, stem cell collection, and follow-up care. Health insurance may cover a portion of the cost, particularly if the transplant is medically necessary. It’s important for patients to discuss the financial aspects with their healthcare providers and insurance companies to understand the costs and coverage options.
The other Organ Transplant Procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Bone Marrow Transplantation are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.



