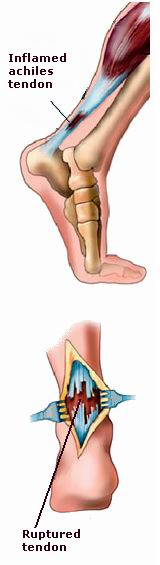
The Achilles tendon is the largest and strongest tendon in the human body, connecting the calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) to the heel bone (calcaneus). This tendon plays a vital role in walking, running, and jumping by helping the foot push off the ground during movement. However, the Achilles tendon is also susceptible to injury, particularly tendon rupture or tearing. When the tendon is torn or ruptured, it can cause significant pain, weakness, and loss of function in the affected leg.
Achilles tendon repair is a surgical procedure aimed at fixing a torn or ruptured Achilles tendon. It is typically considered when the tendon is severely damaged or when conservative treatments, such as physical therapy and rest, have failed. The repair can restore tendon strength and allow patients to regain normal function in the ankle and foot.
Achilles tendon injuries are common among athletes, particularly in sports that involve running, jumping, or sudden changes in direction. However, anyone can experience an Achilles tendon rupture, including people who do not engage in athletic activities. Timely repair of the tendon is crucial to restore mobility, reduce pain, and prevent long-term complications such as chronic weakness or re-rupture.
The Achilles tendon is prone to injury, especially when subjected to excessive stress or strain. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with Achilles tendon rupture is essential in both prevention and treatment:
1. Sudden Force or Trauma
The most common cause of an Achilles tendon rupture is sudden, forceful movements that place excessive strain on the tendon, such as when running, jumping, or quickly changing direction. These injuries are common in sports like basketball, tennis, soccer, and football.
2. Overuse or Repetitive Stress
Repeated use or overuse of the Achilles tendon can lead to microtears in the tendon fibers, weakening the tendon over time and making it more vulnerable to rupture. Athletes who participate in high-intensity sports with frequent jumping or running are at a higher risk for developing chronic Achilles tendonitis, which can eventually lead to rupture.
3. Age
Aging is one of the significant risk factors for Achilles tendon rupture. As people age, the tendons lose their elasticity and ability to heal quickly. The Achilles tendon becomes more prone to degeneration, making it more susceptible to injury, particularly in individuals over the age of 30.
4. Poor Footwear
Wearing poorly fitting shoes or shoes that do not provide adequate arch support or cushioning can place additional stress on the Achilles tendon, increasing the risk of injury. High heels and shoes with inadequate ankle support can also contribute to tendon strain and discomfort.
5. Previous Achilles Tendon Injury
A history of Achilles tendon injury or surgery increases the likelihood of re-injury or rupture in the future. Even after a tendon heals, it may remain weaker and more prone to injury, especially if not properly rehabilitated.
6. Gender
Men are more likely to suffer Achilles tendon ruptures than women, particularly among active individuals. This is likely due to the higher participation rate of men in sports and high-impact activities that stress the tendon.
7. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions may increase the risk of Achilles tendon injury, including:
-
Obesity, which places additional strain on the tendon.
-
Diabetes, which can affect tendon health and healing.
-
Hypercholesterolemia, which has been linked to tendon degeneration.
8. Use of Certain Medications
Certain medications, particularly fluoroquinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin), have been associated with an increased risk of Achilles tendon rupture. These drugs may weaken the tendon fibers, making them more susceptible to injury.
When an Achilles tendon injury occurs, it is important to recognize the symptoms early to seek appropriate treatment. The most common signs and symptoms of an Achilles tendon injury or rupture include:
1. Sudden, Sharp Pain
One of the hallmark signs of an Achilles tendon rupture is a sudden, sharp pain in the back of the ankle or calf, often described as feeling like being kicked or struck in the tendon area. The pain may be intense and can immediately impair mobility.
2. Swelling and Bruising
Following an Achilles tendon rupture, the area around the tendon may become swollen and bruised. Swelling is typically visible at the back of the ankle and may extend down the foot. Bruising may appear shortly after the injury.
3. Difficulty Walking or Bearing Weight
An Achilles tendon rupture or severe injury can cause significant difficulty with walking or bearing weight on the affected leg. Individuals may find it hard to push off the ground with the foot, leading to an inability to walk normally.
4. Weakness in the Ankle and Foot
Weakness in the calf muscles and foot is common after an Achilles tendon rupture. This weakness can make it challenging to perform basic activities like standing on tiptoes or walking up stairs.
5. Tenderness in the Tendon Area
The area around the Achilles tendon may become tender to the touch, particularly at the site of the tear or rupture. This tenderness can be exacerbated by physical activity or movement.
6. Inability to Flex the Foot
A significant symptom of a ruptured Achilles tendon is the inability to perform the "tiptoe test" — standing on tiptoes and flexing the foot downward. The dorsiflexion of the foot (pointing the toes upward) may also be limited or painful.
A thorough diagnosis is essential to determine the extent of the Achilles tendon injury and to plan appropriate treatment. The following diagnostic methods are commonly used:
1. Physical Examination
The physician will begin with a physical examination, looking for signs of swelling, bruising, and tenderness in the Achilles tendon region. The doctor will assess the patient’s range of motion, strength, and ability to perform certain movements, such as standing on tiptoes.
2. Thompson Test (Simmonds Test)
The Thompson test is a simple and commonly used test to confirm an Achilles tendon rupture. During the test, the patient lies prone, and the examiner squeezes the calf muscles. If the Achilles tendon is intact, the foot will point downward (plantar flexion) in response. If the tendon is ruptured, there will be no movement of the foot.
3. Imaging Studies
-
Ultrasound: An ultrasound can provide real-time imaging of the Achilles tendon and help identify tears or ruptures.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI can offer detailed images of the Achilles tendon, allowing doctors to assess the extent of the damage, whether partial or complete, and evaluate any associated injuries.
-
X-ray: While an X-ray cannot show soft tissue damage, it may be used to rule out bone fractures or other bony injuries around the ankle.
The treatment approach for Achilles tendon injuries depends on the severity of the damage, the patient’s activity level, and their overall health. Treatment options can be divided into conservative (non-surgical) and surgical interventions.
1. Conservative Treatment (Non-Surgical)
-
Rest and Ice: Resting the affected leg and applying ice to reduce swelling and pain is important for initial management of Achilles tendon injuries.
-
Immobilization: A cast or boot may be used to immobilize the ankle and allow the tendon to heal naturally. The patient may also be asked to avoid weight-bearing on the affected leg.
-
Physical Therapy: Once the initial pain and swelling subside, physical therapy can help strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility. Specific exercises, such as eccentric loading exercises, may be used to promote tendon healing.
2. Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails or if the injury is severe (e.g., a complete rupture), surgical repair may be necessary. The surgery involves suturing the torn ends of the Achilles tendon together or using tendon grafts to repair the damage. The surgery can be performed through a traditional open approach or a minimally invasive (percutaneous) technique, depending on the specific injury and surgeon preference.
Post-surgical rehabilitation is essential for full recovery, which typically includes immobilization in a boot or cast followed by a progressive rehabilitation program to restore strength and flexibility.
Preventing Achilles tendon injuries requires understanding the risk factors and adopting strategies to reduce strain on the tendon. Here are key prevention and management strategies:
1. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Regular stretching of the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of tendon strain. Strengthening exercises that target the calf muscles can also help support the tendon.
2. Proper Footwear
Wearing shoes with good arch support and cushioning can help minimize stress on the Achilles tendon, especially for those who participate in sports or activities that involve running or jumping.
3. Gradual Increase in Activity
Avoid sudden, intense activity that can place excessive stress on the Achilles tendon. When starting a new exercise or sport, it is important to gradually increase intensity and avoid overloading the tendon.
4. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excessive body weight can place added pressure on the Achilles tendon. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and exercise can reduce the risk of tendon injuries.
5. Early Treatment of Achilles Tendonitis
If you experience symptoms of Achilles tendonitis, such as pain or swelling in the tendon area, seek treatment early. Early intervention can prevent further damage and reduce the need for surgical repair.
Although Achilles tendon repair surgery has a high success rate, it comes with potential risks and complications:
1. Infection
As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the incision site, particularly if proper wound care and hygiene are not followed.
2. Re-rupture
A re-rupture of the Achilles tendon can occur, particularly if rehabilitation is not properly followed, or if the tendon is not given enough time to heal.
3. Scar Tissue Formation
Scar tissue can form around the repair site, which can affect tendon flexibility and strength. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in preventing excessive scarring.
4. Nerve Damage
Nerve damage near the surgical site can occur, leading to numbness or weakness in the foot or ankle.
5. DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis)
Surgical procedures involving the lower extremities can increase the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition where blood clots form in the veins of the legs.
Recovery from an Achilles tendon injury and repair surgery can be a lengthy process, requiring patience and dedication to rehabilitation. Here’s how to live with the condition and support a successful recovery:
1. Post-Surgery Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation plays a key role in recovering from Achilles tendon repair surgery. A comprehensive rehabilitation program will include strengthening exercises, stretching, and mobility training to improve range of motion and rebuild muscle strength.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
During the recovery process, lifestyle modifications such as avoiding high-impact activities, maintaining a healthy diet, and adhering to a rehabilitation schedule will help speed up recovery and reduce the risk of reinjury.
3. Mental Health Support
Living with an Achilles tendon injury or recovering from surgery can be frustrating and emotionally challenging. Seeking support from a mental health professional or joining support groups can help individuals cope with the stress of recovery.
1. What is Achilles tendon repair?
Achilles tendon repair is a surgical procedure performed to treat a rupture or tear in the Achilles tendon, the large tendon located at the back of the lower leg that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. The tendon is crucial for walking, running, and jumping. When this tendon ruptures, it can cause significant pain and loss of function. Achilles tendon repair aims to reattach or reconstruct the tendon to restore its function and improve mobility.
2. Why is Achilles tendon repair necessary?
Achilles tendon repair is necessary when the tendon is completely ruptured or severely torn, which often occurs due to a sudden increase in physical activity, sports injuries, or trauma. A torn Achilles tendon causes severe pain, difficulty walking, and inability to perform activities that require pushing off the foot. If left untreated, it can result in permanent weakness, instability, and impaired function of the foot and ankle.
3. How is Achilles tendon repair performed?
Achilles tendon repair is usually performed through a surgical procedure that can be done using the following steps:
-
Anesthesia: The patient is given either local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia, depending on the extent of the surgery.
-
Incision: A small incision is made along the back of the ankle to access the damaged Achilles tendon.
-
Reattachment or reconstruction: The surgeon either sutures the torn ends of the tendon back together or, in more severe cases, reconstructs the tendon using a tendon graft or other surgical techniques.
-
Closure: The incision is closed with stitches, and a splint or cast is applied to keep the foot and ankle immobilized while the tendon heals.
4. Is Achilles tendon repair painful?
Achilles tendon repair is not painful during the surgery, as it is performed under anesthesia. After the procedure, patients may experience some pain, swelling, and discomfort around the surgical site. Pain can usually be managed with prescribed medications and elevating the leg. Physical therapy will also play an important role in recovery and managing discomfort as the tendon heals.
5. How long does it take to recover from Achilles tendon repair?
Recovery from Achilles tendon repair varies by individual, but generally:
-
Immediate post-surgery: The patient will wear a splint or cast to keep the foot and ankle immobilized for about 2 to 6 weeks.
-
Physical therapy: After the cast is removed, physical therapy is often required to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility. This can take several months.
-
Full recovery: It typically takes 4 to 6 months to fully recover and return to regular activities, depending on the severity of the injury and how well the patient follows post-surgical care instructions.
6. What are the risks and complications of Achilles tendon repair?
While Achilles tendon repair is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications, including:
-
Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the incision site.
-
Re-rupture: In some cases, the Achilles tendon may tear again, particularly if the tendon is subjected to too much stress too soon.
-
Blood clots: Surgery can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the legs, which can be dangerous if they travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
-
Scar tissue: Excessive scar tissue formation can lead to stiffness and reduced range of motion.
-
Tendon weakness: In some cases, the tendon may not regain full strength or functionality after surgery.
7. Will I need to wear a cast or splint after Achilles tendon repair?
Yes, after Achilles tendon repair, patients typically need to wear a cast or splint to immobilize the foot and ankle for several weeks. This helps prevent movement of the tendon and promotes healing. After the initial healing period, a walking boot may be used to allow for gradual weight-bearing as the tendon continues to heal. Your doctor will provide specific guidelines for how long the immobilization device should be worn.
8. When can I return to normal activities after Achilles tendon repair?
The timeline for returning to normal activities varies depending on the individual’s healing process and the nature of the injury. Generally:
-
Initial healing: After 6 to 8 weeks, patients may begin light weight-bearing activities under the guidance of their doctor and physical therapist.
-
Return to sports or high-impact activities: It typically takes 4 to 6 months to return to full activity, such as running, jumping, or playing sports. However, some patients may require up to a year for complete recovery, especially if the rupture was severe.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy play an important role in regaining strength and mobility during recovery.
9. Can Achilles tendon repair be done without surgery?
In some cases, if the Achilles tendon is only partially torn or if the tear is in a less critical location, non-surgical treatments may be considered. These treatments may include:
-
Rest and avoiding weight-bearing activities to allow the tendon to heal naturally.
-
Bracing or casting to immobilize the ankle and reduce strain on the tendon.
-
Physical therapy to strengthen the tendon and improve flexibility.
However, for complete ruptures or severe tears, surgery is typically the most effective option to ensure proper healing and restore full function.
10. How can I prevent Achilles tendon injuries in the future?
To prevent Achilles tendon injuries in the future, consider the following tips:
-
Warm up properly: Always warm up before engaging in physical activities, especially those that involve running, jumping, or sudden movements.
-
Strengthening exercises: Regular exercises that strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility can help prevent strain on the Achilles tendon.
-
Gradual increase in intensity: Avoid sudden increases in exercise intensity or duration. Gradually build up to more strenuous activities to reduce the risk of injury.
-
Proper footwear: Wear shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning, especially during high-impact sports or activities.
-
Rest and recovery: Allow adequate rest between intense physical activities to give the Achilles tendon time to recover.
The other Orthopedic Procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Achilles Tendon Repair are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.

