Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to grow too quickly, resulting in thick, scaly patches on the skin. This condition can affect various parts of the body, including the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Psoriasis is not contagious but can be uncomfortable and distressing due to its visible symptoms.
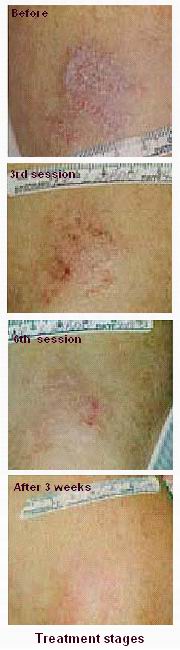
One of the most effective treatment options for moderate to severe psoriasis is laser therapy. Laser treatment for psoriasis uses targeted light energy to treat the affected skin and can help reduce inflammation, itching, and the appearance of psoriasis patches. It works by targeting the immune cells in the skin responsible for psoriasis, slowing down the rapid skin cell turnover and promoting healing.
Laser treatment for psoriasis can be especially beneficial for patients who have not responded well to topical treatments, oral medications, or phototherapy. It is a safe, precise, and non-invasive approach that can provide long-term relief and improve the quality of life for psoriasis patients.
Psoriasis is a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential to understand why laser treatment is an effective option for managing psoriasis.
1. Genetic Factors
A significant portion of psoriasis cases is believed to be hereditary. If you have a family member with psoriasis, particularly a parent or sibling, you are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Specific genes are linked to psoriasis, including the HLA-Cw6 gene, which plays a role in regulating immune responses.
2. Immune System Dysfunction
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. T-cells, a type of white blood cell, become overactive and cause inflammation in the skin. This results in the rapid production of new skin cells that build up on the surface, forming thick patches or plaques.
3. Environmental Triggers
Various environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis flare-ups. Common triggers include:
-
Infections: Certain infections, such as strep throat, can trigger or worsen psoriasis in genetically predisposed individuals.
-
Stress: Emotional stress can trigger psoriasis flare-ups or make existing symptoms worse.
-
Injury to the skin: Skin trauma or cuts, such as sunburns or scratches, can trigger new psoriasis lesions (the Koebner phenomenon).
-
Weather: Cold, dry weather can dry out the skin and trigger psoriasis, while humid climates may provide some relief.
4. Hormonal Changes
Changes in hormones, such as those that occur during pregnancy, puberty, or menopause, can influence the onset or severity of psoriasis. For instance, many women experience improvements in psoriasis during pregnancy but see flare-ups post-partum.
5. Medications
Certain medications, including beta-blockers, lithium, and antimalarial drugs, have been known to trigger or worsen psoriasis. It is important to discuss any existing medications with your dermatologist to avoid exacerbating the condition.
The symptoms and signs of psoriasis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, the hallmark of psoriasis is the formation of raised, scaly patches on the skin that may be red, inflamed, and covered with silvery-white scales. Some of the most common symptoms include:
1. Red, Scaly Patches
The most common sign of psoriasis is the appearance of raised red patches covered by silvery-white scales. These patches are often found on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp, although they can appear anywhere on the body.
2. Itching and Burning
Psoriasis lesions are often itchy and can cause a burning or stinging sensation. The discomfort from these sensations can interfere with daily activities and sleep.
3. Dry or Cracked Skin
Psoriasis can cause the skin to become dry, cracked, and painful, sometimes bleeding. These cracks are not only uncomfortable but can lead to secondary infections if not managed properly.
4. Thickened Nails
In some cases, psoriasis can affect the nails, leading to changes in nail color and thickness. Pitting, discoloration, or separation of the nail from the nail bed can occur.
5. Scalp Psoriasis
Psoriasis of the scalp can cause itching, flaking, and dryness, often leading to visible dandruff-like flakes. In severe cases, the condition may cause hair loss.
Psoriasis is typically diagnosed by a dermatologist based on the appearance of the skin lesions. In some cases, additional tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
1. Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing psoriasis is a thorough physical exam. Your dermatologist will assess the size, shape, and location of the lesions. The presence of classic psoriasis patches—red, scaly, and well-demarcated—is usually sufficient for diagnosis.
2. Skin Biopsy
In cases where the diagnosis is unclear, or if another condition is suspected, your dermatologist may recommend a skin biopsy. This involves taking a small sample of the affected skin tissue and analyzing it under a microscope. The biopsy helps confirm the presence of psoriasis and rule out other dermatological conditions.
3. Blood Tests
Though not always necessary, blood tests can sometimes help rule out other conditions or monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) tests may be conducted to check for systemic inflammation associated with psoriasis.
Laser treatment for psoriasis is typically recommended for individuals with moderate to severe psoriasis who do not respond well to topical treatments or who prefer a non-invasive alternative. The following are the primary types of laser therapy used to treat psoriasis:
**1. Excimer Laser
The Excimer laser is one of the most common types of laser therapy used to treat psoriasis. It delivers ultraviolet B (UVB) light directly to the affected skin areas. The high-intensity UVB light targets the overactive T-cells in the skin, helping to slow down the rapid skin cell turnover and reduce inflammation.
-
Pros: Effective for localized psoriasis, especially on the scalp, elbows, and knees.
-
Cons: Requires multiple sessions for long-lasting results.
2. Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) Therapy
Narrowband UVB therapy uses specific wavelengths of ultraviolet light to target psoriasis lesions. It is a highly effective form of light therapy that helps calm inflammation and slow down the rapid turnover of skin cells.
-
Pros: Non-invasive, relatively safe with fewer side effects.
-
Cons: Requires consistent treatment, and there is a small risk of skin aging or cancer with long-term use.
3. Psoralen Plus UV-A (PUVA)
PUVA therapy involves the use of a medication called psoralen, which makes the skin more sensitive to light, followed by exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA) light. This combined treatment helps slow the skin's rapid cell turnover.
-
Pros: Effective for thick or severe psoriasis.
-
Cons: Higher risk of skin damage and skin cancer due to the use of UV-A light, requires multiple treatments.
4. Targeted Laser Therapy
Targeted laser therapy uses focused light to treat specific patches of psoriasis without affecting surrounding skin. This type of treatment is especially useful for treating localized areas of psoriasis and helps reduce the risk of side effects.
-
Pros: Highly targeted and precise, fewer side effects.
-
Cons: May require several sessions for maximum effectiveness.
While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are several ways to manage and prevent flare-ups, especially after receiving laser treatment:
1. Avoid Triggers
Certain triggers can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, such as:
-
Stress
-
Infections (e.g., throat infections)
-
Skin injuries (cuts, burns, or scrapes)
-
Weather changes, especially dry, cold climates
Avoiding these triggers can help prevent flare-ups and keep psoriasis under control.
2. Skin Care Routine
Keeping the skin well-moisturized and avoiding harsh chemicals can prevent dryness and irritation. Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products can reduce skin inflammation.
3. Follow-Up Laser Treatments
For those who have received laser treatment, periodic maintenance sessions may be required to sustain the results and keep psoriasis under control.
4. Diet and Lifestyle
Some studies suggest that a healthy diet, rich in anti-inflammatory foods (like omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables), may help manage psoriasis symptoms. Avoiding alcohol and smoking can also have a positive effect on overall skin health.
While laser treatment for psoriasis is generally safe and effective, there are potential risks and complications:
1. Skin Sensitivity
After laser treatment, the skin may be sensitive and susceptible to sunburn. Sun protection is essential to prevent further damage or pigmentation changes.
2. Burning or Stinging Sensation
Some patients may experience a stinging or burning sensation during or after treatment, which typically subsides over time.
3. Skin Pigmentation Changes
In some cases, laser treatment can cause darkening or lightening of the skin (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation). This side effect is typically temporary but may be more noticeable in individuals with darker skin tones.
4. Temporary Worsening of Psoriasis
Occasionally, psoriasis may temporarily worsen after laser treatment before it starts to improve. This is typically a normal part of the healing process.
After laser treatment, managing psoriasis becomes a collaborative effort between the patient and healthcare provider. While laser treatment provides significant relief, lifestyle changes and ongoing care are essential for long-term results.
1. Follow-Up Care
Patients should continue to visit their dermatologist regularly to monitor the progress of their psoriasis. Follow-up sessions may be necessary to maintain clear skin.
2. Emotional Support
Psoriasis can affect a person’s self-esteem, especially when visible on areas like the face and hands. Joining a support group or seeking counseling may help individuals cope with the psychological effects of psoriasis.
3. Skin Maintenance
Even after laser treatment, it’s important to maintain a proper skincare routine. Using moisturizers regularly and avoiding products that irritate the skin will help keep it healthy and prevent flare-ups.
1. What is laser treatment for psoriasis?
Laser treatment for psoriasis is a non-invasive procedure that uses focused beams of light (laser) to target and treat the affected areas of skin where psoriasis plaques have formed. The laser targets the immune cells responsible for the skin’s inflammatory response and reduces the production of skin cells, which helps to alleviate symptoms of psoriasis such as redness, scaling, and thickening of the skin. This method is used when topical treatments are not effective or when patients prefer a more targeted approach.
2. How does laser treatment for psoriasis work?
Laser treatment for psoriasis works by delivering concentrated light energy directly to the affected areas of the skin. There are two main types of laser therapy used for psoriasis treatment:
-
UVB laser therapy: Uses ultraviolet light to target the skin and slow down the overproduction of skin cells.
-
Excimer laser therapy: This type of laser emits a targeted UVB light that focuses on small patches of psoriasis, delivering a higher dose of light to the specific areas, promoting healing without affecting surrounding healthy skin.
Both methods help reduce inflammation, improve skin texture, and slow down the rapid turnover of skin cells that occurs in psoriasis.
3. Is laser treatment for psoriasis effective?
Yes, laser treatment can be highly effective for many people with psoriasis, especially for localized or moderate cases. It is particularly beneficial for patients who have not responded well to topical treatments, or who have areas of psoriasis that are difficult to treat with creams or ointments. Many patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms, including a reduction in redness, scaling, and plaque formation. However, results can vary from person to person, and multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
4. How many sessions of laser treatment are needed for psoriasis?
The number of sessions required varies depending on the severity of the psoriasis and the type of laser used. Typically, 4 to 10 sessions may be needed, spaced a few days to a week apart. For more widespread psoriasis, the treatments may be more frequent. After the initial treatment course, patients may need maintenance sessions every few months to keep the symptoms under control. Your dermatologist will provide a personalized treatment plan based on the specific areas of psoriasis and your individual needs.
5. Is laser treatment for psoriasis painful?
Laser treatment for psoriasis is generally well-tolerated, but some patients may experience mild discomfort during the procedure. This may feel like a tingling or warming sensation on the skin. Some people compare it to the sensation of being in the sun for a short period of time. If necessary, topical numbing creams can be applied to help reduce any discomfort. After the procedure, patients may experience some redness or mild irritation, which usually subsides within a few hours to a few days.
6. Are there any side effects of laser treatment for psoriasis?
Laser treatment for psoriasis is generally safe, but like any treatment, there are some potential side effects, including:
-
Redness or irritation: The treated skin may appear red or inflamed immediately after treatment, but this typically resolves within a few hours.
-
Dryness or flaking: The skin may become dry or flaky as it heals.
-
Blistering: Rarely, blistering may occur, particularly if the treatment is too aggressive.
-
Hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation: Some patients may experience darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation) spots on the treated areas.
-
Sensitivity to sunlight: Treated skin may be more sensitive to the sun, so it’s important to avoid sun exposure and use sunscreen after the procedure.
Most side effects are temporary, and your dermatologist will provide specific aftercare instructions to help manage them.
7. How long does each laser treatment session for psoriasis take?
Each laser treatment session typically takes between 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the size and location of the treated areas. If you are undergoing treatment for larger areas of the body, the session may take slightly longer. The duration of the session will also depend on the type of laser being used and the number of areas being treated.
8. How soon will I see results from laser treatment for psoriasis?
Most patients begin to notice improvements in their psoriasis symptoms after about 2 to 3 sessions, with further improvements seen as treatment continues. Redness and scaling should begin to reduce, and the plaques may start to flatten out. Full results are often seen after 4 to 10 sessions, though this can vary depending on the individual’s response to treatment and the severity of the condition.
9. Can laser treatment for psoriasis be combined with other treatments?
Yes, laser treatment for psoriasis can be used in combination with other treatments, such as topical creams, phototherapy, or systemic medications, to enhance the results. Your dermatologist may recommend a combined treatment approach, especially for patients with more severe or widespread psoriasis. Laser treatment can help address localized plaques while other treatments work on broader areas or systemic inflammation. Be sure to discuss your treatment plan with your doctor to determine the best combination of therapies for your condition.
10. How much does laser treatment for psoriasis cost?
The cost of laser treatment for psoriasis varies depending on factors such as the clinic’s location, the size of the area being treated, and the number of sessions required. On average, each session can cost between $200 to $500. Since multiple sessions are typically needed, the total cost of treatment may range from $1,000 to $3,000. Many clinics offer discounts for multiple-session packages. It’s important to check with the clinic for an accurate estimate and whether your insurance covers laser treatments for psoriasis.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of laser treatment for psoriasis, covering the procedure, effectiveness, side effects, and costs. Feel free to adjust the content based on your medical website’s tone and audience!
The other Skin Procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Laser Treatment for Psoriasis are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


