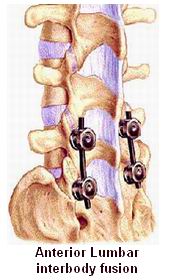
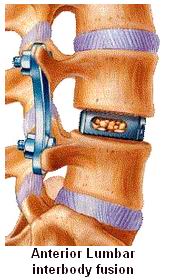
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF) is a specialized spinal surgery that addresses conditions affecting the lumbar spine, or lower back. This procedure involves removing a damaged or degenerated intervertebral disc between two lumbar vertebrae and replacing it with a bone graft or a cage filled with bone graft material. The purpose of this surgery is to stabilize the spine, alleviate pain, and restore the normal alignment of the vertebrae.
The anterior approach refers to the method of accessing the spine from the front of the body via the abdomen, rather than through the back. This approach allows the surgeon to directly access the disc space, avoiding the need to move or manipulate major muscles and nerves in the back. ALIF is generally recommended for conditions where traditional conservative treatments, such as physical therapy, medications, or injections, have been ineffective.
ALIF is commonly performed to treat degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis, and other forms of spinal instability. This procedure can provide significant relief for individuals experiencing debilitating back pain, nerve compression, and reduced mobility. ALIF is generally well-tolerated, offering faster recovery times compared to traditional posterior approaches (from the back).
Before considering the need for ALIF surgery, it’s important to understand the causes and risk factors associated with the conditions that may necessitate this procedure. The majority of patients requiring ALIF surgery suffer from conditions that lead to spinal instability, pain, and nerve compression.
1. Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
Degenerative disc disease is one of the most common reasons for undergoing ALIF. As people age, the discs between the vertebrae in the lumbar spine begin to break down. These discs can lose their ability to absorb shock and provide cushioning, which can lead to pain, stiffness, and potential nerve compression. When conservative treatments fail, ALIF offers an option for stabilization and relief.
2. Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the vertebra below it. This slippage often leads to nerve compression, causing significant pain, weakness, and discomfort. Spondylolisthesis can be caused by age-related wear and tear, spinal fractures, or congenital abnormalities. ALIF is used to restore proper alignment by fusing the affected vertebrae, thus preventing further slippage and nerve damage.
3. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal, which puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots. It can be caused by various factors, including aging, degenerative disc disease, or a herniated disc. This compression leads to pain, numbness, and weakness, particularly in the legs. In severe cases where conservative treatments are ineffective, ALIF can be used to stabilize the spine and relieve pressure on the nerves.
4. Trauma or Spinal Fractures
Trauma, such as from a car accident or fall, can result in fractures of the spine, leading to instability. If the vertebrae are misaligned or fractured, ALIF can be performed to realign the vertebrae and provide stability through fusion. This procedure helps avoid further complications like nerve damage or persistent pain.
5. Genetic and Lifestyle Factors
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing conditions requiring ALIF surgery due to genetic factors or lifestyle choices. Obesity, smoking, and sedentary lifestyles are common risk factors for developing spinal disorders that lead to ALIF. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding smoking can reduce the risk of spinal degeneration and improve the overall health of the spine.
The symptoms that lead individuals to consider ALIF are often related to severe back pain, leg discomfort, and difficulty moving. These symptoms are typically indicative of an underlying condition that affects the lumbar spine.
1. Chronic Lower Back Pain
One of the hallmark symptoms that patients experience is persistent lower back pain that does not improve with non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, pain medications, or injections. The pain may be exacerbated by activities like walking, bending, or standing for long periods.
2. Radiating Pain (Sciatica)
When the nerve roots in the lumbar spine are compressed due to a herniated disc or spinal misalignment, patients may experience radiating pain down their legs, a condition known as sciatica. The pain can be sharp or burning and may affect one or both legs.
3. Numbness and Tingling
Compression of the nerves in the lumbar spine can cause numbness or tingling sensations in the legs and feet. This is commonly referred to as paresthesia and can interfere with daily activities and mobility.
4. Weakness in the Legs
Nerve compression can also cause muscle weakness in the legs, making it difficult to walk or perform simple tasks. Some individuals may experience a feeling of instability or loss of balance, especially when walking or standing.
5. Decreased Range of Motion
Many patients with lumbar spinal issues experience limited range of motion in the lower back. They may find it difficult to bend forward, twist, or perform other movements without significant pain or stiffness.
6. Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control (Cauda Equina Syndrome)
In rare cases, severe nerve compression can lead to cauda equina syndrome, a condition that affects the nerves at the end of the spinal cord. Symptoms include loss of bladder control, incontinence, and sexual dysfunction, which require immediate medical attention.
A comprehensive diagnosis is crucial to determine whether ALIF is the appropriate treatment option. The diagnostic process involves a physical exam, imaging tests, and sometimes additional tests to evaluate the extent of spinal damage.
1. Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing conditions that may require ALIF surgery is a physical exam. During the exam, the healthcare provider will assess the patient’s posture, range of motion, and areas of pain. They will also look for signs of nerve involvement, such as muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling.
2. Imaging Tests
-
X-rays: X-rays provide a basic image of the spine’s structure and can show signs of degeneration, fractures, or alignment problems.
-
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues like discs, muscles, and nerves. This test is essential for evaluating disc herniation, nerve compression, and spinal stenosis.
-
CT Scan (Computed Tomography): A CT scan can be used to assess bone structure and abnormalities in the vertebrae. It is helpful for diagnosing fractures and assessing the degree of spinal misalignment.
-
Discography (if necessary): In some cases, a discography may be performed to assess the degree of damage to the intervertebral discs. This is especially useful when determining which disc needs to be removed during ALIF surgery.
The treatment approach for lumbar spine conditions can vary based on the severity of the issue, but when conservative methods fail, ALIF surgery can provide long-lasting relief and stability. Treatment options for ALIF typically fall into conservative and surgical categories:
1. Conservative Treatments
-
Physical Therapy: A customized physical therapy program can help improve spinal stability and relieve pain. It is typically used as a first-line treatment before considering surgery.
-
Medications: Pain medications such as NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) and muscle relaxants can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, epidural steroid injections may be used to reduce nerve inflammation.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding heavy lifting can help reduce pressure on the spine and alleviate symptoms.
2. Surgical Treatment: ALIF
When conservative treatments are ineffective, ALIF may be recommended. The procedure involves the following steps:
-
Accessing the Spine: The surgeon accesses the lumbar spine through the abdomen rather than the back.
-
Removing the Damaged Disc: The damaged intervertebral disc is removed, and the disc space is cleaned.
-
Inserting the Bone Graft or Cage: A bone graft or cage filled with bone material is inserted into the disc space. This promotes fusion between the vertebrae.
-
Stabilizing the Spine: The bones are held in place with screws or other stabilization devices while the body heals and fuses the vertebrae.
3. Post-Operative Rehabilitation
After surgery, patients are advised to undergo physical therapy to regain strength and flexibility. Recovery typically takes several weeks to months, depending on the individual’s overall health and adherence to rehabilitation.
While spinal conditions that lead to ALIF cannot always be prevented, several lifestyle changes and management strategies can reduce the risk of developing such conditions.
1. Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity, especially strengthening and stretching exercises, helps maintain flexibility and strength in the back muscles, which can reduce the risk of developing spine-related conditions.
2. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight helps alleviate pressure on the spine, reducing the risk of degenerative disc disease and other lumbar spine issues.
3. Proper Posture
Maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can help reduce strain on the spine. Ergonomic adjustments in work and daily activities can also promote spinal health.
4. Avoiding Smoking
Smoking reduces blood flow to the spine and impairs healing, which can worsen spine conditions. Avoiding smoking can significantly improve spinal health and recovery from spine surgery.
While ALIF surgery is generally considered safe and effective, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of:
1. Infection
Infection is a potential risk following surgery, particularly in the surgical site. Patients are given antibiotics during and after surgery to reduce the risk of infection.
2. Nerve Injury
Although rare, nerve injury can occur during ALIF surgery, leading to complications such as numbness, weakness, or pain in the legs or back.
3. Blood Clots
There is a small risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) following surgery. Blood-thinning medications and early mobilization after surgery help mitigate this risk.
4. Non-Union (Pseudoarthrosis)
In some cases, the vertebrae may not fuse properly after surgery, requiring additional treatment or surgery.
After ALIF surgery, it’s crucial for patients to follow their healthcare provider's advice for optimal recovery. This includes engaging in physical therapy, avoiding certain movements, and gradually returning to normal activities.
1. Post-Surgical Care
Proper post-operative care, including taking prescribed medications, avoiding heavy lifting, and attending follow-up appointments, is crucial for a successful recovery.
2. Lifestyle Adjustments
Patients should make lifestyle adjustments such as maintaining a healthy weight and staying active to promote spinal health and prevent complications.
3. Emotional Well-Being
Suffering from chronic back pain can have a significant emotional impact. Seeking support from family, friends, or support groups can help patients cope with the emotional challenges of recovering from surgery.
1. What is Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF)?
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF) is a type of spinal surgery performed to treat conditions such as degenerative disc disease, herniated discs, spinal instability, or scoliosis. In this procedure, the surgeon approaches the spine from the front (anterior) of the body, removes the damaged or degenerated disc, and then fuses the adjacent vertebrae together using bone grafts or implants. The goal is to stabilize the spine, reduce pain, and promote the growth of new bone between the vertebrae.
2. Why is ALIF performed?
ALIF is typically performed to address conditions that cause pain or instability in the lower back, such as:
-
Degenerative disc disease: When the discs between the vertebrae break down and cause pain.
-
Herniated discs: Discs that bulge or rupture, pressing on nearby nerves.
-
Spinal instability: When the spine becomes unstable due to fractures or degenerative changes.
-
Spondylolisthesis: A condition where one vertebra slips over another.
-
Spinal deformities: Such as scoliosis or lordosis, where the natural curvature of the spine is misaligned.
The procedure helps reduce pain, stabilize the spine, and restore normal spinal function.
3. How is ALIF different from other spinal fusion surgeries?
ALIF is unique because it is performed through an anterior approach, meaning the surgeon makes an incision in the front of the abdomen to access the spine. This approach is preferred because it allows the surgeon to reach the intervertebral disc space without disturbing the back muscles, nerves, or spinal cord. In contrast, other fusion techniques, such as posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF), involve accessing the spine from the back, which can lead to longer recovery times and more muscle disruption. ALIF often provides better outcomes in terms of alignment and healing, especially for certain types of spinal conditions.
4. What are the benefits of ALIF surgery?
The benefits of ALIF surgery include:
-
Reduced muscle and nerve disruption: Since the anterior approach avoids cutting through muscles or nerves in the back, there is typically less postoperative pain and a quicker recovery.
-
Better disc removal: The anterior approach allows for more complete disc removal and better disc space preparation.
-
Improved spinal alignment: The procedure allows for better realignment of the spine, which can relieve pressure on nerves and improve overall posture.
-
Lower risk of nerve damage: By accessing the spine from the front, ALIF generally carries a lower risk of damaging spinal nerves compared to posterior approaches.
5. How long does the recovery take after ALIF surgery?
Recovery time after ALIF surgery can vary, but most patients can expect the following:
-
Hospital stay: Typically, patients stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 days following the procedure for observation and pain management.
-
Initial recovery: After being discharged, patients can usually resume light daily activities after 2 to 4 weeks, though they should avoid bending, lifting, or twisting.
-
Full recovery: It can take anywhere from 3 to 6 months for the spine to fully heal and for patients to return to regular physical activity, depending on their individual healing process and the extent of the surgery.
Your surgeon will provide specific instructions to optimize healing and ensure a successful recovery.
6. What are the risks and complications of ALIF surgery?
While ALIF is generally a safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications, including:
-
Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site.
-
Blood clots: Blood clots, particularly in the legs, can develop during recovery.
-
Nerve injury: Though rare, there is a slight risk of nerve injury during the procedure.
-
Implant failure: The metal implants or bone grafts used in the fusion may fail, requiring revision surgery.
-
Nonunion: In some cases, the vertebrae may not fuse properly, requiring further treatments.
-
Damage to abdominal organs: Since the surgery is performed through the abdomen, there is a risk, though rare, of injury to abdominal organs, such as the intestines or blood vessels.
Your surgeon will discuss these risks in detail and take steps to minimize them during the procedure.
7. How long will I need to wear a brace after ALIF surgery?
Following ALIF surgery, most patients are advised to wear a brace for support during the early recovery phase, typically for 4 to 6 weeks. The brace helps provide stability to the spine while the bones begin to heal and fuse together. The exact duration will depend on your surgeon’s recommendation and how well you are healing.
8. Will I experience pain after ALIF surgery?
While ALIF is associated with less muscle and nerve disruption compared to other types of spinal fusion surgeries, some postoperative pain and discomfort are normal. You may experience:
-
Incision pain: Mild to moderate pain at the incision site, which should improve as healing progresses.
-
Back pain: Some discomfort in the back or legs may occur due to the healing process or inflammation.
Pain is typically managed with prescription medications, and most patients notice significant improvement within 2 to 4 weeks.
9. Can ALIF surgery be performed on everyone with back problems?
ALIF is not suitable for everyone, as it is typically recommended for individuals with specific spinal conditions, such as:
-
Degenerative disc disease
-
Spondylolisthesis
-
Herniated discs
-
Spinal instability
However, it may not be appropriate for patients with certain comorbidities or complex spinal deformities. It is important to undergo a thorough evaluation with your surgeon, who will assess your medical history, symptoms, and imaging results to determine if ALIF is the right treatment option for you.
10. How much does ALIF surgery cost?
The cost of ALIF surgery can vary depending on factors such as location, hospital fees, the surgeon’s expertise, and any additional treatments required (e.g., physical therapy). On average, the total cost for ALIF surgery, including hospital stay and follow-up care, can range from $20,000 to $50,000 or more. It’s important to discuss the cost with your surgeon and check with your insurance provider to understand your coverage options.
As with all major surgical procedures, complications can occur. Some of the most common complications following ALIF include:
- Thrombophlebitis
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Blood vessel damage
- Problems with the graft or hardware
Patients usually stay in the hospital after surgery for up to
one week. During this time, patients work daily with a physical therapist.
Rehabilitation after ALIF can be a slow process. Many surgeons prescribe outpatient
physical therapy beginning a minimum of six weeks after surgery.
The other Spine Surgery Procedures are:
Few Major Hospitals for Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion are:
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey and India are the most cost effective locations that offer up to almost 80% savings in comparison to the US.
SurgeryPlanet facilitates a plethora of services to the medical treatment traveler also which includes, a hassle free and discounted travel option, a welcome hand at the airport on arrival, travel in an air-conditioned car, round the clock service & support. Your medical evaluation is pre arranged with the least of waiting time. Once your assessment is complete and found medically fit, the procedure is immediately scheduled without a waiting period. Please read through our Services and Testimonials to understand and select your best options.
Major Treatments Abroad: Obesity / Bariatric Surgery | Spine Surgery | Stem Cell therapy | Fertility treatment | Knee replacement in India and Thailand | Heart Surgery | Organ transplant | Ayurveda Treatment | Heart valve replacement | Hip resurfacing | Hospitals in India and Thailand for Laparoscopic Sterilization| Best hospitals in Asia | JCI & ISO certified Hospitals | Cost effective medical procedures | Healthcare tourism | Complete privacy for affordable cost | Weight loss procedures | Infertility treatment | Board certified physicians | Low cost surgeries
SurgeryPlanet is an Healthcare Facilitator and not a Medical service provider. The information provided in this website is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition or use for any medical purposes. We provide information solely for medical travel facilitation and do not endorse any particular health care provider, hospital, facility, destination or any healthcare service or treatment listed. We are not an agent for, or affiliated to any health care provider, or service listed in our website and is not responsible for health care services provided by them. Choice of hospital or doctor for your healthcare services is your independent decision. Consult your domestic licensed health care provider before seeking the services of any health care provider you learn about from our website.


